- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Daily Current Affairs Summary 9th MAY 2025
Daily Current Affairs Summary 9th MAY 2025
09-05-2025
477 snow leopards in Ladakh: Study
- A recent assessment by Ladakh’s Department of Wildlife Protection has recorded 477 snow leopards in the region.
- Ladakh hosts 68% of India’s total snow leopard population, making it one of the densest habitats globally.
Key Highlights of the Study:
- High snow leopard concentrations are found in Hemis National Park, Kargil, and Leh, forming one of the world's largest connected populations.
- Favorable factors include resource-rich grasslands, moderate climate, and abundant prey availability.
- About 61% of Ladakh’s snow leopards were found living in areas shared with human communities, showing successful coexistence.
- Cultural respect for wildlife, benefits from eco-tourism, and active conflict management practices contribute to their protection.
|
Snow Leopard Conservation Initiatives
|
About Snow Leopards (Panthera uncia):
- Native to 12 countries across South and Central Asia, they are a flagship species of high-altitude mountain ecosystems.
- In India, snow leopards are found in Jammu & Kashmir, Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, and Arunachal Pradesh.
- Conservation Status:
- Listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List.
- Protected under CITES Appendix I, CMS Appendix I, and Schedule I of the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972.
- Prefer habitats with steep rocky terrains and elevations between 3,000–5,000 metres.
- Known for their smoky-grey fur with dark rosettes, they are solitary and mostly active during dawn and dusk.
CCRAS has revived two rare Ayurvedic Manuscript
- The Central Council for Research in Ayurvedic Sciences (CCRAS) has revived two rare Ayurvedic manuscripts: Dravyaratnākara Nighaṇṭu and Dravyanamākara Nighaṇṭu.
- In Ayurvedic terminology, "Nighantu" refers to texts listing groups of drugs, their synonyms, properties, and the specific parts used.
About Dravyaratnākara Nighaṇṭu
- This manuscript was composed by Mudgala Paṇḍita in 1480 AD.
- It is divided into 18 chapters, offering detailed insights into drug synonyms, medicinal actions, and therapeutic properties.
- The text references earlier classical works like Dhanvantari Nighaṇṭu and Raja Nighaṇṭu, while also adding new medicinal substances.
- It includes information on drugs of plant, mineral, and animal origin, expanding the traditional Ayurvedic knowledge base.
About Dravyanamākara Nighaṇṭu
- This work is attributed to Bhisma Vaidya.
- It deals specifically with the homonyms of plant and drug names, a complex area critical to Ayurvedic identification.
- The manuscript is considered an independent appendix to the Dhanvantari Nighaṇṭu, serving to clarify overlapping names and meanings.
Revised SHAKTI Policy for Coal Allocation to Power Sector
- The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA), chaired by PM Narendra Modi, approved the Revised SHAKTI Policy for coal allocation to the power sector on 07 May 2025.
- The policy is part of ongoing coal sector reforms by the government.
- SHAKTI stands for Scheme for Harnessing and Allocating Koyala Transparently in India.
- Originally introduced in 2017 to shift from nomination-based coal allocation to a transparent auction/tariff-based bidding system.
Key Features of the Revised SHAKTI Policy
- The revised policy consolidates previous 8 categories into two main allocation windows to simplify operations and improve efficiency.
|
Two Windows for Fresh Coal Linkages |
|
|
Window-I (Coal at Notified Price)
|
Window-II (Coal at Premium Price)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Encourages competition, better capacity utilization, seamless pit-head thermal capacity addition, and affordable power generation.
- Promotes domestic coal availability, reduces import dependence, and supports stressed power assets.
- Aligns with Atmanirbhar Bharat by boosting domestic coal usage.
Benefits of the Revised SHAKTI Policy
- Greater Flexibility: Offers flexible coal allocation mechanisms.
- Wider Eligibility: More power producers, including imported coal-based plants, are now eligible.
- Better Accessibility: Easier coal access leads to increased power generation and lower electricity tariffs.
- Positive Economic Impact: Supports employment generation and economic activity via reliable power supply.
- Revenue for State Governments: More mining activity will increase state revenues, aiding regional development.
- Import Substitution: Domestic coal can replace imported coal in Imported Coal Based (ICB) plants.
- Support to Pithead Plants: Preference for establishing new thermal power projects near coal mines.
Key Additional Provisions
- Use of Un-requisitioned Surplus (URS) Capacity: Linkage coal can now be used to generate power from URS capacity, deepening power markets.
- No Mandatory PPAs under Window-II: Private players can now participate without having Power Purchase Agreements.
|
Other Key Coal Sector Reforms
|
National Scheme for Industrial Training Institute (ITI) Upgradation
- The "National Scheme for ITI Upgradation and Setting up of five National Centres of Excellence for Skilling" was approved under Budget 2024-25.
- It will be implemented as a Centrally Sponsored Scheme.
- Transform existing ITIs into government-owned, industry-managed aspirational skill institutes, with support from State Governments and industry.
- Total Outlay: ₹60,000 crore over five years (Central Share: ₹30,000 crore, State Share: ₹20,000 crore, Industry Share: ₹10,000 crore).
- 50% of the Central Share (₹15,000 crore) will be co-financed equally by the Asian Development Bank and the World Bank.
- Focus Areas:
- Upgrade 1,000 Government ITIs through a hub and spoke model with revamped industry-aligned trades (courses).
- Expand capacity in five National Skill Training Institutes (NSTIs).
- Set up five National Centres of Excellence for Skilling within these NSTIs.
- Use an industry-led Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) model for outcome-driven implementation.
- About ITIs:
- ITIs have been the backbone of Vocational Education and Training (VET) in India since the 1950s.
- They operate under State Governments and are accredited by the Directorate General of Training (DGT), under the Ministry of Skill Development & Entrepreneurship.
- Currently, there are about 15,034 ITIs, of which 78% are privately owned.
- Challenges in ITI Ecosystem
- Quality Gap compared to Global Standards
- Low Placement rates
- Low Social Acceptance
- Underutilization
- Relevant Schemes: STRIVE, Model ITI, and Enhancing Skill Development Infrastructure in North Eastern States (ESDI).
India’s Operation Sindoor
- India launched Operation Sindoor in response to the terror attack in Pahalgam, marking the largest cross-border strike since Balakot.
- India invoked its right to respond, pre-empt, and deter further cross-border attacks.
- Operation Sindoor is a major military offensive targeting terrorist infrastructure in Pakistan and Pakistan-occupied Kashmir (PoK).
- The strikes were measured, calibrated, and non-escalatory, using niche technology weapons for precision strikes.
- Pakistan stated it reserves the right to respond under Article 51 of the UN Charter.
India’s Precision Strike Weapons:
- SCALP (Storm Shadow) Missile: An air-launched, long-range (450 km) cruise missile designed for deep-strike missions on high-value targets.
- HAMMER (Highly Agile Modular Munition Extended Range): A precision-guided stand-off munition with a range of 50–70 km.
- Loitering Munitions (Kamikaze Drones): Drones that hover over target zones and autonomously or remotely identify and destroy threats.
- METEOR: A next-gen Beyond Visual Range Air-to-Air Missile (BVRAAM) effective in dense electronic-warfare environments.
- BRAHMOS: A supersonic cruise missile operating on the ‘Fire and Forget Principle’ with varied flight paths to the target.
|
Article 51 of the UN Charter:
|
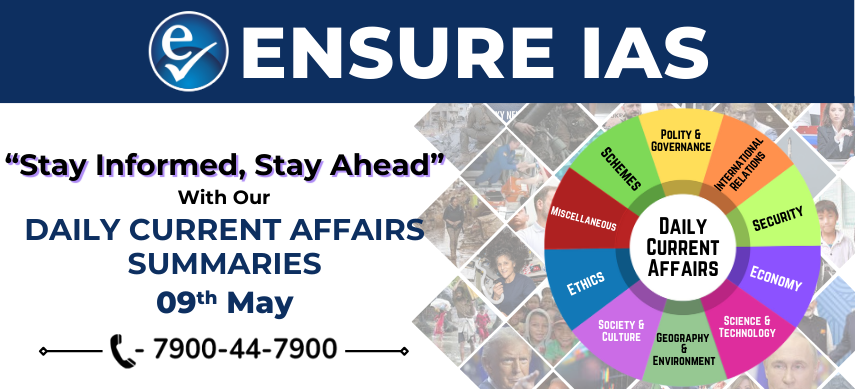
New Security Guidelines for Satellite-Based Internet Services under GMPCS License
- The Department of Telecommunications (DoT) has issued new security guidelines for Satellite Internet Services under the Unified License (UL) framework.
- These directives apply to the Global Mobile Personal Communications by Satellite (GMPCS) license, which supports mobile satellite communication in regions lacking terrestrial connectivity.
- GMPCS services are especially critical in remote mining zones, oil and gas fields, defence sectors, and disaster-hit areas.
Terresrial Network
Key Security Guidelines:
- Security Clearance: Each gateway/hub in India must receive prior security clearance from relevant authorities.
- Network Localization: Core functions of the Network Control and Monitoring Centre (NCMC)—like lawful interception and data routing—must be based within India.
- Service Restrictions: Operators must have systems to block or restrict services to users or areas in times of conflict or national emergency.
- Special Monitoring Zones (SMZs): Areas within 50 km of international borders and up to 200 nautical miles in Exclusive Economic Zones (EEZ) are to be specially monitored.
- Indigenous Manufacturing Requirement: A minimum of 20% of the satellite ground infrastructure must be locally manufactured within five years.
- NavIC Support: Licensees are encouraged to incorporate NavIC-based positioning systems into their services.
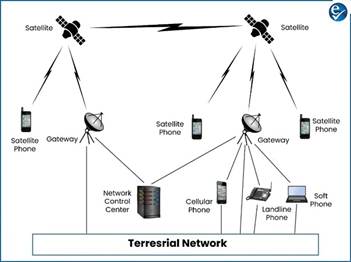
Gully Erosion
- Gully erosion has been observed in 19 Indian states and the Delhi region.
- Six states—Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Jharkhand, Gujarat, and Chhattisgarh—covering 38% of India's area, account for 92% of the country's gully-affected land.
- Gully erosion happens when fast-flowing water carves out deep channels in the soil.
- It leads to the loss of fertile land, vegetation, and crops.
- It disrupts water flow in catchment areas and contributes to land degradation.
- Severe gully erosion can even lead to desert-like conditions in affected regions.
Gut Microbiota
- A recent study warns that climate-related food shortages may disrupt the balance of gut microbes.
- Poor crop yields can lead to less diverse diets, which reduces gut microbiota diversity.
- Elevated CO₂ levels in the atmosphere lower key nutrients in staple crops like rice and wheat.
- The human gut contains around 100 trillion microorganisms.
- An imbalance in gut microbes (dysbiosis) is linked to conditions like diabetes, inflammatory bowel disease, eczema, and brain disorders.
- Gut health is influenced by multiple factors at once—such as food scarcity, heat, pollution, and infections—making the effects complex and unpredictable.
Atmospheric memory
- New research shows that atmospheric memory plays a key role in triggering and ending monsoons.
- The air holds past weather data in the form of water vapor, which influences monsoon timing.
- Earlier, it was believed that monsoons were mainly driven by immediate sunlight changes.
- The atmosphere behaves based on its history—rain continues if it's already raining, and dryness persists if it's been dry.
- This tendency of the atmosphere to stick to its current state is known as bistability.
- Even with the same solar input, the atmosphere can behave differently depending on previous conditions.
Draft framework For India’s Climate Finance Taxonomy
- The Finance Ministry's Department of Economic Affairs has sought public input on India's draft Climate Finance Taxonomy.
- This taxonomy aims to classify economic activities aligned with India’s climate goals and low-carbon development.
- Its main goals include promoting climate mitigation, adaptation, and smoother industry transition toward sustainable practices.
- It also seeks to attract more climate finance while preventing misleading green claims (greenwashing).
- The framework is guided by eight core principles, such as alignment with national climate commitments and development goals.
- It emphasizes support for transition efforts and encourages the use of home-grown, eco-friendly technologies.
Copper
- The Filo del Sol and Josemaría sites in Argentina rank among the top ten largest copper-producing mines globally.
- Copper is a soft, flexible, and stretchable metal known for its excellent ability to conduct heat and electricity.
- In 2024, Chile leads the world in copper production, followed by the Democratic Republic of Congo, Peru, and China.
- In India, Rajasthan holds the highest copper reserves at 52%, followed by Madhya Pradesh with 23%, and Jharkhand with 15%.
- Notable copper mining areas in India include the Singhbhum Copper Belt in Bihar, Khetri Copper Belt in Rajasthan, and Balaghat District in Madhya Pradesh.
Pulitzer Prize
- In 2024, The New York Times secured four Pulitzer Prizes, while The New Yorker earned three, showcasing excellence in journalism.
- The Pulitzer Prize is a prestigious set of annual awards given by Columbia University, located in New York City.
- These awards were founded by Joseph Pulitzer, a Hungarian-American journalist and newspaper publisher, who donated funds to Columbia upon his death in 1911.
- The Pulitzers honor exceptional contributions in the fields of journalism, literature, and music.
- The first Pulitzer Prizes were officially awarded in the year 1917.
Indo-Pacific Logistics Network
- The Quad nations—Australia, India, Japan, and the USA—recently conducted an Indo-Pacific Logistics Network (IPLN) simulation exercise in Honolulu, Hawaii.
- The IPLN is designed to help Quad members share logistics capabilities across the Indo-Pacific for faster and more efficient civilian disaster response.
- This initiative allows coordinated action during natural disasters by improving the use of joint logistics among the four countries.
- Alongside the Indo-Pacific Partnership for Maritime Domain Awareness, the IPLN reinforces the Quad's commitment to a free, open, and secure Indo-Pacific region.
- It also showcases the importance of practical cooperation in addressing shared regional challenges through strategic collaboration.
|
Also Read |
|
UPSC Foundation Course |
|
| UPSC Monthly Magazine | CSAT Foundation Course |




