- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Daily Current Affairs Summary 7th MAY 2025
Daily Current Affairs Summary 7th MAY 2025

World Audio Visual and Entertainment Summit (WAVES) 2025
- The inaugural WAVES Summit 2025 took place in Mumbai, where the Prime Minister emphasized India’s creative economy as a key driver for future GDP growth, innovation, and inclusive development.
- WAVES aims to unlock a $50 billion market by 2029, positioning India as a significant player in the global entertainment industry.
- During the summit, the government announced the establishment of the Indian Institute of Creative Technology (IICT), aimed at fostering innovation in the creative sector.
- The Ministry of Information and Broadcasting, in collaboration with FICCI and CII, will set up IICT as a National Centre of Excellence.
Understanding the Creative Economy
- Definition: The creative economy (also known as the orange economy) refers to the sector where creative assets contribute to economic growth and development.
- Key Components: It encompasses industries such as Media & Entertainment, Advertising, Animation, Visual Effects, Gaming, Comics, and Extended Reality (AVGC-XR).
- The United Nations declared 2021 as the International Year of Creative Economy for Sustainable Development, highlighting its global significance.
India's Creative Economy Landscape
- Contribution to GDP: The creative economy contributes $30 billion to India’s GDP, employing 8% of the workforce.
- Exports: Creative exports from India exceed $11 billion annually.
- Challenges: The sector faces challenges such as misinformation, copyright issues, intellectual property concerns, market monopolization, limited digital access in rural areas, and lack of formal financing.
Initiatives to Promote India’s Creative Economy
- Creative Economy Fund: The government has announced a $1 billion fund to support the growth of the creative economy in India.
- All India Initiative on Creative Economy (AIICE): Launched by the Indian Chamber of Commerce to harness the vast potential of India’s creative industries.
- National Creators Award: This award recognizes the work of digital content creators in India, promoting online creativity and innovation.
Social Media Influencer Dies by Suicide After Losing Followers
Misha Agrawal, a popular Instagram influencer, tragically took her own life due to emotional distress caused by a decline in her follower count.
Importance of Influencers' Mental Health
- The global influencer industry is valued at $13.6 billion, according to a UK House of Commons report.
- Influencers play a significant role in shaping trends, opinions, and behavior, especially among the youth, often becoming role models.
- Despite the growing awareness of social media's impact on young users, the mental health struggles of influencers remain largely overlooked.
Why Social Media Influencers Face Mental Health Challenges
- Disconnection Between Real and Virtual Life: Influencers may appear to lead glamorous lives with gifts, sponsored trips, and fame. However, the reality involves constant posting, engagement, and performance, resulting in burnout, privacy loss, and anxiety.
- Pressure for Validation and Online Scrutiny: Influencers face immense pressure to gather likes, comments, and followers. Their self-worth often becomes tied to online popularity, and negative feedback such as trolling and abuse can cause severe emotional distress.
- Toxic Comparisons: Influencers are constantly exposed to edited, curated content, which can trigger harmful comparisons about lifestyle, success, and relationships. This has been linked to higher levels of depression and anxiety, both for influencers and their audiences.
- Stigma Surrounding Their Profession: Many influencers report being dismissed or judged due to the perceived unserious nature of their career, which exacerbates their mental health struggles.
Novel CAR-T Therapy Shows Promise in Cancer Treatment
- New Therapy: Brazilian scientists have developed the HSP-CAR30 therapy, targeting the CD30 protein. The therapy has successfully completed its initial trial.
- CD30 Protein: Found on certain T cells and B cells, CD30 plays a crucial role in cancer diagnosis and treatment planning.
- T-cells are specialized white blood cells with a primary function of cytotoxicity, meaning they kill other cells.
Key Developments in HSP-CAR30 Therapy
- Efficacy: The therapy has shown a 100% overall response rate, with 50% of patients achieving complete remission.
- Safety and Immunity: The therapy has no dose-limiting toxicities, and CAR30+ cells remained detectable in 60% of evaluable patients even a year after infusion.
What is Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell (CAR-T) Therapy?
- Definition: CAR-T therapy involves collecting a patient's T cells from their blood and genetically modifying them in a lab to fight cancer.
- Mechanism: A special receptor, known as Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR), is added to T cells, enabling them to recognize and attack cancer cells more effectively.
- Success in Blood Cancers: CAR-T therapy has shown significant success in treating blood cancers, including Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL), Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma, and Multiple Myeloma.
Advantages of CAR-T Therapy
- Long-Term Remission: CAR-T therapy can keep cancer in remission for extended periods, reducing the need for frequent treatments and improving quality of life.
- Personalized Treatment: The therapy uses the patient's own modified T-cells, enhancing its effectiveness and minimizing side effects.
- Short Treatment Duration: The entire CAR-T therapy process takes approximately 45 days.
Challenges of CAR-T Therapy
- Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS): CRS is a systemic inflammatory response caused by cytokines released from infused CAR T cells. It can lead to reversible organ dysfunction.
- Neurotoxicity: Ranging from headaches and confusion to seizures, cerebral edema, and coma.
- Antigen Escape: Tumors may develop resistance by losing the antigen targeted by CAR-T cells.
Gundaram Inscriptions Discovered in Telangana Shed New Light on Satavahana Period
Eleven inscriptions found in Gundaram Reserve Forest offer valuable insights into the cultural and political landscape of the early Deccan (1st century BCE – 6th century CE), particularly the Satavahana period.
Key Findings from the Gundaram Inscriptions
- Hāritiputra Inscription:
- Written in early Brahmi script.
- Suggests a political alliance between the Satavahana and Chutu dynasties.
- The Chutus were contemporaries of the Satavahanas.
- Trident & Damaru Inscription:
- Features a trident and damaru symbol.
- Marks the earliest known religious iconography in South India.
- Indicates the early association of political authority with religious symbolism.
About the Satavahana Dynasty (2nd Century BCE to 2nd Century CE)
- Dynasty Overview: The Satavahanas, also known as the Andhras, succeeded the Mauryas in the Deccan region, covering present-day Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, and Maharashtra.
- Prominent Rulers:
- Simuka: Founder of the Satavahana dynasty, who overthrew the Kanva dynasty.
- Gautamiputra Satakarni:
- The dynasty reached its peak under him.
- Known for his military victories against the Shakas (Western Satraps) and for consolidating Satavahana power.
- The Nasik and Nanaghad inscriptions provide crucial details about his reign.
- Hala: Famous for his literary work Gathasaptasati (written in Prakrit).
- Unique Naming Practice: Many Satavahana kings included their mother’s name in their own, unlike other dynasties.
- Coins: The Satavahanas were among the first Indian dynasties to issue coins featuring portraits of their rulers.
Niti Aayog Report Highlights Challenges for Enhancing MSME Competitiveness in India
Union Budget 2025-26 Focus: The Union Budget recognises MSMEs as one of the key drivers of India's development, alongside agriculture, investment, and exports.
Challenges in Enhancing the Competitiveness of MSMEs
- Formalisation: Around 90% of the informal sector comprises MSMEs (ILO, 2023).
- Access to Finance: MSMEs face an ₹80 lakh crore credit gap due to limited access to formal loans and high-risk perception (CRISIL).
- Skill Gaps: A 3.9% decline in knowledge-based hiring (from approximately 13%) presents a challenge for growth and innovation in MSMEs (WIPO, 2023).
- Data Gaps:
- Limited reliable data on MSMEs, especially regarding jobs, exports, etc., hampers effective policymaking.
- Even the UDYAM database lacks detailed insights, further restricting informed decision-making.
- Other Issues: MSMEs face challenges such as low product variety, outdated technology, and a lack of medium-sized firms, leading to the "missing middle" in manufacturing.

Ways to Improve Competitiveness of MSMEs
- Finance Accessibility: Improve access to finance by reforming the Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGTMSE), supporting NBFCs, and easing state-level subsidy norms.
- Skilling: Align training programs with industrial needs, focusing on financial literacy and business skills for MSME owners.
- Data: Upgrade the UDYAM portal with detailed, cluster-wise, and state-level data to aid in better policymaking.
- Technology & Innovation: Develop targeted policies for small firms and strengthen Institutes for Collaboration (IFC) to foster innovation.
Odisha Government's Sahajog Initiative to Aid Urban Poor
- Launch of Sahajog Initiative: The Odisha Government has introduced the Sahajog initiative to help the urban poor by identifying eligible beneficiaries and connecting them with appropriate schemes. This includes providing mass awareness and doorstep service delivery.
- Urban Poverty in India: Urban poverty is linked to inadequate access to employment, food, healthcare, and education, along with a lack of community representation. It is also worsened by a lack of social networks.
- Poverty Statistics: The extreme poverty rate in urban India stands at 17.2%, compared to only 2.8% in rural areas, as per the Poverty & Equity Brief by the World Bank.
Challenges of Urban Poverty:
- Living Conditions: Many urban poor reside in slums that lack basic facilities such as toilets, clean water, and proper ventilation. Access to essential services like healthcare, education, and transport remains scarce and expensive.
- Barriers to Welfare: Migrants often lack proper identification or proof of residency, which hinders their access to welfare schemes. Additionally, there is no urban counterpart to rural welfare programs like MGNREGA, creating a significant income gap.
- Visibility of Inequality: Urban poverty is more visible, leading to feelings of deprivation. An example is Dharavi in Mumbai, where luxury skyscrapers sit beside impoverished slums, highlighting stark inequalities.
- Weak Social Support: Cities generally lack strong community ties, unlike rural areas. This social void exacerbates loneliness and contributes to mental health challenges.
- Exclusionary Urbanization: Urban planning often overlooks informal settlements like slums, further marginalizing their residents.
Government Initiatives to Address Urban Poverty:
-
- Housing: Under the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana-Urban (PMAY-U), the government aims to provide housing for all urban poor.
- Sanitation: Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation 2.0 (AMRUT 2.0) aims to improve sanitation infrastructure in urban areas.
- Employment and Skill Development: The Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana National Urban Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NULM) and PM Street Vendor's AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi) promote employment and entrepreneurship opportunities.
- Food Security: The One Nation One Ration Card scheme allows for ration card portability across the country, improving food security for migrants.
- Healthcare: Under Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana, health benefits are made portable, and self-certification is available for beneficiaries of the PM Ujjwala Yojana.
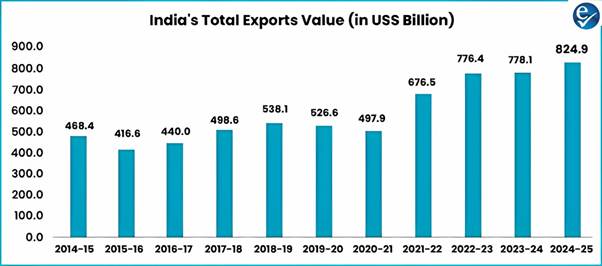
India's Record Exports in FY 2024-25 Amid Global Economic Slowdown
- Total Exports: India achieved its highest-ever exports in the financial year 2024-25, totaling $824.9 billion, which is a 6.01% increase from $778.1 billion in 2023-24.
- Global Slowdown Impact: This growth occurred despite the global economic slowdown triggered by various factors, including:
- Trade disruptions due to the Red Sea crisis
- The Ukraine war
- Drought in the Panama Canal
- Increase in Non-Tariff Measures
- Rising energy prices
Key Data and Trends
- Merchandise Exports: Merchandise exports saw a marginal increase, reaching $437.4 billion in 2024-25, up from $437.1 billion in 2023-24.
- Services Exports: Services exports reached a historic high of $387.5 billion in 2024-25, reflecting a 13.6% increase from $341.1 billion in 2023-24.
Factors Driving Export Growth
- Policy Push: The government boosted exports with initiatives like the New Foreign Trade Policy, sector-specific schemes, Trade Facilitation, Districts as Export Hubs, and MSME support.
- Diversification of Export Markets: Rising demand from Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America helped India offset slowdowns in other global markets.
- Trade Agreements: New bilateral and multilateral trade deals, including the India-UAE Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA), opened up new markets and reduced barriers, especially for services and electronics.
- Supply Chain Realignment: India emerged as a reliable alternative in the China-plus-one strategy, attracting global companies to shift part of their supply chains to India.
Punjab Government's Resolution on Additional Water to Haryana
The Bhakra Beas Management Board (BBMB) has ordered the release of an additional 4,500 cusecs of water to Haryana, a decision opposed by Punjab.
About Bhakra Beas Management Board (BBMB)
- BBMB was established under Section 79 of the Punjab Reorganisation Act, 1966.
- Functions of BBMB:
- Administers, operates, and maintains the Bhakra-Nangal Project, Beas Project Unit-I (Beas Satluj Link Project), and Beas Project Unit-II (Pong Dam).
- Regulates the supply of water and power from the Bhakra Nangal and Beas Projects to Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan, Himachal Pradesh, Delhi, and Chandigarh.
Mechanism for Water Regulation
- Constitutional Framework:
- Entry 17 of the State List: Empowers states to handle matters related to water supply, irrigation, canals, and drainage.
- Entry 56 of the Union List: Deals with the regulation and development of inter-state rivers and river valleys.
- Article 262: Grants Parliament the power to make laws to resolve disputes over inter-state river waters.
- Parliament Enactments:
- River Boards Act, 1956: Allows the Central Government to establish River Boards to advise states on regulating and developing inter-state rivers or valleys.
- Inter-State Water Disputes Act, 1956: Empowers the Central Government to set up a Water Disputes Tribunal if a dispute cannot be resolved through negotiations.
MHA Organizes Civil Defence Exercise
- The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has decided to conduct a Civil Defence Exercise across 244 Civil Defence Districts in the country.
- Civil Defence Districts: These are districts considered vulnerable to enemy attacks due to their strategic and tactical importance.
Civil Defence Exercise
- The Civil Defence Exercise is designed to assess how civilians and government systems respond during emergencies, such as war, missile attacks, aerial strikes, or disasters.
- The exercise evaluates the operational effectiveness and coordination of various Civil Defence measures, including:
- Testing the effectiveness of air raid warning systems.
- Ensuring the operational readiness of Hotline or Radio Communication Links with the Indian Air Force.
- Assessing the functionality of control rooms.
- Training civilians and students to protect themselves in case of hostile attacks.
- Reviewing provisions for early camouflaging of vital installations and rehearsing evacuation plans.
- The last similar drill was conducted before the 1971 India-Pakistan war.
Civil Defence Provisions in India
- The Civil Defence Act, 1968 was passed after the India-China War (1962) and the India-Pakistan War (1965).
- The Act provides measures to protect people, property, and places from hostile attacks (air, land, sea, or other sources).
- It authorized the formation of Civil Defence Corps and the creation of rules and regulations for Civil Defence.
Supreme Court Publishes Declaration of Judges' Assets
- The Supreme Court (SC) has made it mandatory for judges to publish their asset declarations on the Supreme Court website.
- On 1st April 2025, the Full Court of the SC decided that judges must declare their assets:
- Upon assuming office
- Whenever a substantial acquisition is made, to the Chief Justice of India (CJI).
- Judges are not legally required to publicly declare their assets, unlike public servants and elected representatives.
- However, in 1997, the SC adopted a resolution for judges to declare all assets, including those of spouses and dependents, to the CJI.
- In 2009, the SC decided to publish the asset declarations of judges on its website on a voluntary basis.
- The current decision reiterates the 1997 "Restatement of Values of Judicial Life," which sets standards for judicial conduct for Supreme Court and High Court judges.
1997 Restatement of Values of Judicial Life
- Judges must avoid actions that could undermine the public's trust in the judiciary.
- Judges should not hear or decide cases involving family members or close friends.
- Judges must refrain from publicly expressing political opinions that may be relevant to judicial matters.
- Judges must not accept gifts or hospitality from anyone, except family and friends.
- Judges should not engage in trade or business.
- Judges should not seek financial benefits related to their office unless they are clearly available.
Share of Gold in India’s Forex Reserves
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has increased its share of gold in the foreign exchange reserves to 11.70%, which is equivalent to 879.59 metric tonnes.
- India’s gross foreign exchange reserves consist of:
- Foreign currency assets held by the RBI
- Gold held by the RBI
- Special Drawing Rights (SDRs)
- Reserve Position in the International Monetary Fund (IMF)
- Some countries do not consider the Reserve Position in the IMF as part of their foreign exchange reserves, as it may not be available on immediate demand.
Why are Central Banks Hoarding Gold?
- Diversification Away from the US Dollar: Central banks are reducing their dependence on the US Dollar to minimize the risks of dollar devaluation.
- Hedging Against Inflation: Gold is seen as a safe asset to protect against rising global inflation and the decreasing purchasing power of currencies.
- Geopolitical Risks: With ongoing tensions between countries like the US, China, and Russia, gold offers better security compared to fiat currencies or government bonds.
- Note: Fiat currency refers to money issued by governments but not backed by a physical commodity like gold or silver.
Risks Associated with Storing Gold
- Reduced Liquidity and Flexibility: Converting large gold reserves into cash takes more time and is costlier compared to liquidating foreign currency assets.
- Zero Yield: Unlike bonds or currency deposits, gold does not generate any interest or dividends.
- Storage and Security Costs: Physical gold requires secure storage, which adds to costs for insurance, transportation, and vaults (e.g., Bank of England).
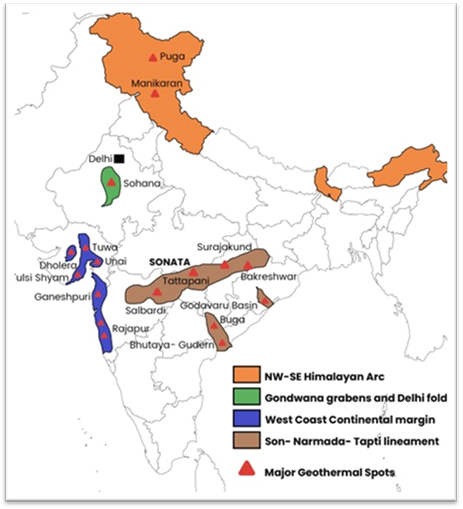
Northeast's First Geothermal Production Well Drilled
- The first geothermal production well in Northeast India has been successfully drilled at Dirang in Arunachal Pradesh by the Centre for Earth Sciences and Himalayan Studies (CESHS).
- The project is the outcome of international scientific collaboration between CESHS, Norwegian Geotechnical Institute (NGI), Icelandic geothermal firm Geotropy ehf, and the drilling team from Guwahati Boring Service (GBS).
About Geothermal Energy
- Geothermal energy refers to heat energy from the Earth, combining geo (earth) and thermal (heat).
- It is extracted for direct heating, cooling, or converted into electricity.
- The internal heat is generated from radioactive decay and continuous heat loss from the Earth’s formation.
Advantages of Geothermal Energy
- It is a clean, inexpensive renewable energy.
- Can operate year-round, providing a stable energy source.
Disadvantages of Geothermal Energy
- Potential land subsidence.
- High transportation costs for energy.
- Possible release of toxic chemicals from geothermal wells.
Steps to Promote Geothermal Energy
- The Geological Survey of India (GSI) published the ‘Geothermal Atlas of India, 2022’, identifying potential geothermal sites across India.
- The Renewable Energy Research and Technology Development Programme (RE-RTD) by MNRE aims to promote indigenous R&D for cost-effective renewable energy, including geothermal.
- Singareni Collieries Company Limited (SCCL) has commissioned a 20 kW pilot geothermal power plant in Manuguru area of Bhadradri Kothagudem district, Telangana.
Mission for Advancement of High-impact Areas on Electric Vehicles (MAHA-EV) Mission
- The Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF) has announced the selection of seven e-Nodes to receive support under its MAHA-EV mission.
- Each selected electric mobility node (e-nodes) will work on the project in consortia mode, involving academic institutions, R&D laboratories, and mandatory industry participation.
About MAHA-EV Mission
- The MAHA-EV mission is a program launched by ANRF, a statutory body with the goal of seeding, funding, and coordinating research and development across institutions in India.
- The mission aims to catalyze India's leadership in next-generation electric mobility solutions, focusing on the goals of sustainability, innovation, and self-reliance.
Piprahwa Relics
The Ministry of Culture takes steps to halt the auction of piprahwa relics by Sotheby’s Hong Kong.
About Piprahwa Relics
- History: Excavated in 1898 by William Claxton Peppé from the Piprahwa Stupa (ancient Kapilavastu, the birthplace of Lord Buddha).
- Relics include bone fragments, crystal and soapstone caskets, a sandstone coffer, and offerings like gold ornaments and gemstones.
- An inscription in Brahmi script identifies the relics as those of the Buddha, deposited by the Sakya clan.
Luna 12 – Tidal Energy Initiative by Faroe Islands
- The Faroe Islands Space Program is implementing an innovative project named Luna 12, which aims to generate electricity by utilizing the Moon's gravitational pull.
- Luna 12 is a tidal kite that operates underwater and captures ocean currents off the coast of the Faroe Islands, converting them into renewable energy.
- These tidal kites function like underwater turbines, using the power of tidal movements and ocean currents, which are primarily driven by the gravitational force of the Moon.
- Luna 12 belongs to the Dragon Class of tidal kites, developed by the Swedish company Minesto, known for its marine energy technology.
- The project highlights the importance of tidal energy, which is more predictable and consistent compared to other renewable sources like solar and wind energy, making it a reliable addition to the clean energy mix.
Operation Shiva and Shri Amarnath Yatra
- Indian Security Forces have launched Operation Shiva to ensure safety and security during the Amarnath Yatra.
- The operation comes in the wake of the recent Pahalgam terror attack and ongoing tensions between India and Pakistan, highlighting the need for heightened vigilance.
About Shri Amarnath ji
- The Amarnath Cave is located at an altitude of 13,000 ft in the Anantnag district of Jammu and Kashmir.
- It is a sacred pilgrimage site that houses the naturally formed ice lingam, representing the phallic symbol of Lord Shiva.
- Alongside the main lingam, two smaller ice formations represent Goddess Parvati and Lord Ganesha, symbolising the divine family.
- The pilgrimage is held annually during the Shravan month (July–August), when the ice lingam reaches its maximum size.
- The origin and significance of the yatra are detailed in the Sanskrit text “Bringesha Samhita”, which describes the legend and rituals associated with the site.
Nilgiri Tahr
- Traditional Nilgiri Tahr habitats in the Coimbatore Forest Division are showing signs of population revival, as per a recent synchronised census conducted in Tamil Nadu and Kerala.
- The Nilgiri Tahr is endemic to the Western Ghats and is the only mountain ungulate species found in southern India among the 12 ungulate species in the country.
- It primarily inhabits open montane grasslands and is distributed across the Western Ghats, stretching from the Nilgiris in the north to the Kanyakumari hills in the south.
- The species faces several threats including habitat loss, competition from livestock, hydropower projects, monoculture plantations, and occasional hunting.
- To protect the species, Project Nilgiri Tahr was launched as a flagship conservation initiative by the Tamil Nadu government, aiming to preserve the state’s official animal.
- In terms of legal and global protection, the Nilgiri Tahr is listed as Endangered on the IUCN Red List and included under Schedule I of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972, ensuring the highest level of protection in India.
UNDP–India Collaboration under NAMASTE Scheme
- The Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment (MoSJE) has partnered with the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) to strengthen the wastepickers component of the NAMASTE scheme.
- Under this collaboration, UNDP is providing financial support to set up State Project Management Units (PMUs) to ensure effective implementation of the scheme.
- The NAMASTE (National Action for Mechanised Sanitation Ecosystem) scheme was jointly launched by MoSJE and the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA) in 2023.
- The scheme aims to ensure the safety, dignity, and welfare of sanitation workers, including manual scavengers and wastepickers.
Wastepicker Component of NAMASTE Scheme
- This component of the scheme was officially launched in 2024 with a focus on improving the working and living conditions of wastepickers.
- It aims to digitally profile and register 2.5 lakh wastepickers across the country for targeted benefits.
- Registered wastepickers are to be provided health insurance coverage under Ayushman Bharat–Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PMJAY).
- The scheme also offers skill upgradation training to improve their employability and income potential.
- Wastepickers will be encouraged to form collectives and cooperatives to manage Decentralized Waste Collection Centers (DWCCs), thereby enhancing their livelihoods and social security.
Airglow
- A rare image of Airglow was captured above the La Silla Observatory in Chile’s Atacama Desert, one of the darkest places on Earth.
- Airglow occurs when atoms and molecules in the upper atmosphere become excited due to ultraviolet rays from the Sun.
- These excited particles then emit light to release their excess energy, creating a faint natural glow in the sky.
- Airglow is present every night, but it is usually too faint for the naked eye to see and requires high-precision cameras in extremely dark locations for detection.
- The phenomenon is similar to auroras, but differs in cause—while auroras are triggered by high-energy particles from the solar wind, airglow is caused by regular solar radiation interacting with the Earth's atmosphere.
Sugar (Control) Order, 2025
- Issuance of the New Order: The Centre has introduced the Sugar (Control) Order, 2025, replacing the 1966 order to update and modernize the regulations governing the sugar sector.
- Real-time Data Sharing: The new order mandates the integration of sugar mills with the Food Department portal via an API, ensuring real-time data sharing for better transparency and monitoring.
- Expanded Product Coverage: The order now includes additional sugar products such as khandsari (traditional unrefined sugar) and raw sugar, aligning with global standards to maintain fair pricing for farmers.
- Inclusion of By-products: The new order covers by-products like molasses and ethanol, ensuring their regulation to help maintain adequate domestic sugar availability.
- Standardization of Definitions: To ensure consistency across the industry, the order adopts the definitions of sugar products as outlined by the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI).
Indo-Pacific Partnership for Maritime Domain Awareness (IPMDA)
- The United States has approved a military hardware and logistics support package for India to enhance its role in the Indo-Pacific Partnership for Maritime Domain Awareness (IPMDA).
- Objective of IPMDA: IPMDA is a technology-driven initiative aimed at improving maritime domain awareness in the Indo-Pacific region.
- It seeks to increase transparency in the region's vital waterways, ensuring better monitoring and safety.
- Initiation at the QUAD Summit: The IPMDA was announced during the 2022 QUAD Summit in Tokyo.
- The QUAD consists of India, Australia, Japan, and the United States, working collaboratively to address maritime security challenges.
- Technological Integration: The initiative utilizes advanced technology to provide partner countries in Southeast Asia, the Indian Ocean region, and the Pacific with near real-time information about maritime activities within their zones.
Victims of Terrorism Associations Network (VoTAN)
- The UN Office of Counter-Terrorism (UNOCT) launched the Victims of Terrorism Associations Network (VoTAN), a global platform designed to support victims and survivors of terrorism.
- Background: The Group of Friends of Victims of Terrorism, chaired by Spain and Iraq, was established nearly six years ago with the mission of protecting victims' rights and addressing their needs.
- Genesis of VoTAN: VoTAN is a significant outcome of the 2022 UN Global Congress on Victims of Terrorism, which highlighted the need for a structured network to support affected individuals.
- Primary Goal: The network aims to create a safe and supportive environment where victims and survivors can connect, share experiences, build resilience, and engage as advocates, educators, and peacebuilders.
- Financial Support: The initiative has received financial support from Spain, which plays a key role in sustaining the network's activities.
Major Dhyan Chand Khel Ratna Award
- Satwiksairaj Rankireddy and Chirag Shetty were conferred with the Major Dhyan Chand Khel Ratna Award for their exceptional achievements in badminton.
- The pair achieved the World No. 1 ranking in the Badminton World Federation rankings in 2023 and clinched the gold medal at the Asian Games held in Hangzhou.
- The award was originally established in 1991–92 as the Rajiv Gandhi Khel Ratna and was renamed the Major Dhyan Chand Khel Ratna Award in 2021.
- It is considered India’s highest sporting honour, given for the most outstanding performance by a sportsperson over the previous four years.
- Only performances in internationally recognized sporting events are taken into consideration for this award.
- The award includes a cash prize of ₹25 lakh, along with a medal and a certificate of honour.
- Typically, only one award is presented each year, highlighting its prestige and exclusivity.
Operation Hawk
CBI launched Operation Hawk to crack down on global cybercrime networks involved in online child sexual exploitation.
- The operation follows Operation CARBON (2021) and Operation Megh Chakra (2022) to track suspects and dismantle such networks with international links.
Lakkundi Temples – Proposed for UNESCO Tentative List
- The Lakkundi temples in Karnataka are set to be finalised for inclusion in the UNESCO tentative list of World Heritage Sites.
- Lakkundi is located in the Gadag district of Karnataka and is referred to as ‘Lokki Gundi’ in ancient inscriptions.
- The temples were constructed during the reign of the Kalyana Chalukyas, also known as the Western Chalukyas.
- The village is home to over 50 ancient temples and 101 intricately designed stepped wells, locally known as Kalyani.
- Among these, the Kasi Vishwanatha Temple stands out as the most ornate and elaborately decorated structure.
- Lakkundi also holds religious significance as a prominent Jain center.
- It houses a notable Jain temple dedicated to Lord Mahavira, which is one of the largest and oldest Jain shrines in the region.
US-Ukraine Mineral and Energy Deal
- The United States has signed a strategic agreement with Ukraine to gain preferential access to its mineral and energy reserves.
- This includes participation in new oil and gas exploration projects across Ukraine.
Ukraine’s Mineral Reserves
- Ukraine is rich in valuable mineral resources, including rare earth elements (REEs) and other critical minerals.
- Rare Earth Elements (REEs) include 17 elements that are abundant in nature but difficult and expensive to extract.
- Critical minerals are rare and strategically important, though their classification varies by country.
- Ukraine possesses 22 out of the 50 strategic materials identified by the United States as critical to its national interest, including key elements like graphite and lithium.
- For comparison, India has identified 30 minerals as critical to its own economic and strategic needs.
National Security Advisory Board (NSAB)
- The Government of India has recently appointed a new chairman and seven new members to the National Security Advisory Board (NSAB).
- The NSAB was originally established in December 1998 as an advisory body comprising eminent individuals from outside the government.
- Its members are drawn from diverse fields including industry, media, academia, civil society, and strategic affairs.
- The board functions with the support of the National Security Council Secretariat (NSCS), which provides necessary administrative and analytical assistance.
- The primary role of NSAB is to conduct long-term analysis and offer strategic perspectives on national security issues to the National Security Council (NSC).
- It also provides policy recommendations and actionable measures on matters that are specifically referred to it by the NSC.
|
Also Read |
|
| FREE NIOS Books | |



