- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Daily Current Affairs Summary 8th MAY 2025
Daily Current Affairs Summary 8th MAY 2025

Centre Notifies Cashless Treatment of Road Accident Victims Scheme, 2025
- Lunched by: Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH)
- The scheme was launched under powers granted by the Motor Vehicles Act, 1988.
- Eligibility: Any person injured in a road accident involving a motor vehicle on any road.
- Coverage: Victims can get cashless treatment up to ₹1.5 lakhs at designated hospitals for up to 7 days from the date of the accident.
- Nodal Agency: Implementation is managed by the State Road Safety Council.
- Designated Hospitals: States must onboard all capable hospitals, including those empanelled under Ayushman Bharat PM-JAY, for trauma and poly-trauma care.
- Payments to Hospitals: Hospitals can raise claims which are verified by the State Health Agency, with payments made from the Motor Vehicle Accident Fund within 10 days.
- Scheme Monitoring: Monitored by a committee chaired by the Secretary of MoRTH.
Why Road Safety Measures Are Crucial in India
- In 2022, India recorded ~4.6 lakh road accidents leading to ~1.68 lakh deaths.
- India has the highest number of road accidents globally.
- The scheme supports India's commitment to the UN Decade of Action for Road Safety, aiming to halve traffic deaths by 2030.
Other Steps Taken by India to Improve Road Safety
- Motor Vehicles (Amendment) Act, 2019 enforces strict penalties and uses technology for better traffic law enforcement.
- Road Safety Audits are mandatory at design, construction, and maintenance stages of all National Highway projects.
- The electronic Detailed Accident Report (e-DAR) Project aims to create a centralised road accident data repository.
- A special Award Scheme for Good Samaritans recognises those who help road accident victims within the Golden Hour (first 60 minutes after injury).
Bitcoin Trading in India and Hawala: A Rising Parallel? – Supreme Court Remarks
- The Supreme Court, during a bail hearing, observed that Bitcoin (cryptocurrency) trading in India resembles a sophisticated version of the hawala system.
- The Court highlighted the lack of a clear regulatory regime governing virtual currencies in India.
What is Cryptocurrency?
- Cryptocurrency is a form of digital currency based on blockchain technology and built using a unique software code.
- Examples include Bitcoin, Ethereum, etc.
- Blockchain is an open-source, decentralized public ledger that records transactions permanently across a computer network.
- Key features of cryptocurrency:
- It is non-fiat, meaning it operates independently of government or central bank control.
- It has no intrinsic value, relying purely on market demand.
What is Hawala?
- Hawala is an informal money transfer system used to move funds from one location to another using hawaladars (agents).
- The system is trust-based and operates without actual cash movement, as debts are settled between hawaladars.
- Transactions are off-the-record, with no formal documentation or bank involvement.
Why Are Cryptocurrency and Hawala Being Compared?
- In blockchain networks, nodes (computers maintaining the network) function like hawaladars, operating through mutual trust and consensus.
- Both systems facilitate fund transfer outside the traditional banking system, making them vulnerable to illicit use.
- Both are considered unregulated and often unreported, making detection of misuse difficult.
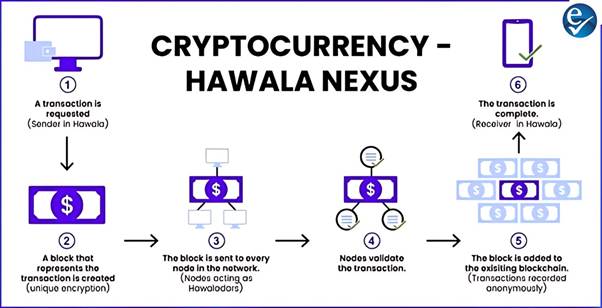
Why Is Their Nexus Increasing?
- Unregulated and Outside Banking Channels: Both systems operate outside conventional financial frameworks, attracting those seeking anonymity.
- Lower Costs: Unlike banks, both systems avoid heavy commissions and currency conversion charges.
- Lack of Transparency:
- Cryptocurrency records transactions anonymously on public ledgers,
- Hawala transactions are done in cash without paper trails.
- Encryption and Passcodes:
- Cryptocurrency uses unique encryption keys for access,
- Hawala relies on shared passcodes between the sender and receiver for verification.
ISRO Moves Gaganyaan Mission to First Quarter of 2027
- ISRO has rescheduled the Gaganyaan mission to the first quarter of 2027.
- The successful completion of Test Vehicle Abort Mission-1 (TV-D1) and the first uncrewed Test Vehicle Abort Mission set the stage for the upcoming tests.
- The second Test Vehicle Mission (TV-D2) will precede the uncrewed orbital flights of Gaganyaan.
- Vyommitra, a gynoid (female robot), will undertake the first uncrewed mission of Gaganyaan.
About Gaganyaan Mission
The objective is to demonstrate India’s human spaceflight capability by launching a crew of three astronauts into a 400 km Low Earth Orbit for a 3-day mission, followed by a safe return to Earth via sea landing.
Components of the Gaganyaan Mission
- Launch Vehicle Mark-3 (LVM-3):
- Previously known as GSLV Mk-III, it is a three-stage rocket.
- First stage: Two solid-fuel boosters attached to the rocket core.
- Second stage: Powered by two liquid-fueled Vikas 2 engines.
- Third stage: Equipped with CE-20 indigenous cryogenic engine using liquid hydrogen and oxygen.
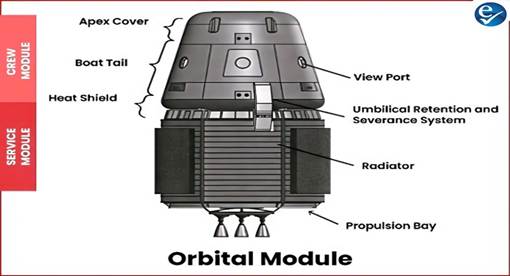
- Orbital Module (8.2 tonnes):
- Launched into Low Earth Orbit by the LVM-3 rocket.
- Consists of two main parts:
- Crew Module:
- Accommodates up to three astronauts for a week.
- Equipped with parachutes for controlled descent during re-entry.
- Includes an Environmental Control and Life Support System (ECLSS) for air quality, temperature, waste, and fire management.
- Features a crew escape system for astronaut safety in case of ascent malfunction.
- Service Module:
- Provides propulsion to raise the orbital module’s altitude post-separation.
- Powers the module’s return journey to Earth.
- Crew Module:
Human Development Report, 2025
The United Nations Development Programme Releases 2025 Human Development Report, titled "A Matter of Choice: People and Possibilities in the Age of AI," highlights AI’s critical role in shaping future human development.
Key Findings of the Report
- India’s HDI Rank: India improved by 3 spots, ranking 130th out of 193 countries in the 2025 report.
- HDI Status: India remains in the medium human development category with an HDI value of 0.685.
- HDI measures achievements in health (life expectancy), knowledge (education), and standard of living.
- Life Expectancy: India’s life expectancy reached 72 years in 2023, the highest since the index began.
- Schooling: The average mean years of schooling in India is 13 years, up from 8.2 years in 1990.
Challenges Despite Progress
- National Income: India’s Gross National Income (GNI) per capita rank is seven spots lower than its HDI rank.
- Inequality: Gender inequality remains significant; India ranks 102nd on the Gender Inequality Index (GII) due to challenges in reproductive health, political representation, and workforce participation.
Global Trends in Human Development
- Slowing Progress: Global human development has slowed to its weakest pace since 1990.
- Increasing Inequality: The inequality between low and very high HDI countries has increased for the fourth consecutive year.
2025 Human Development Report’s AI Related Observations
- India's AI Landscape:
- India has the highest self-reported AI skills penetration globally.
- India ranks 4th in the Global AI Index among 36 evaluated countries, the only lower-middle-income country in the top 10.
- 20% of AI researchers in India now stay in the country, a significant increase from almost zero in 2019.
- Global Expectations for AI:
- 61% of global respondents expect AI to augment jobs.
- 51% expect AI to automate jobs.
India and UK Conclude Free Trade Agreement (FTA)
What is Free Trade Agreement (FTA)?
- Meaning: A Free Trade Agreement (FTA) is an agreement between countries or regional blocks to reduce or eliminate trade barriers and enhance trade.
- India currently has FTAs with countries like Japan, South Korea, Sri Lanka, Singapore, ASEAN, and Malaysia.
- Scope: An FTA typically covers trade in goods and services but may also include intellectual property rights, investment, government procurement, and competition policy.
Recently, India and the United Kingdom (UK) successfully concluded a Free Trade Agreement (FTA) after around 3 years of negotiations.
Key Highlights of the India-UK FTA
- Tariff Elimination: The deal eliminates tariffs on about 99% of tariff lines, covering nearly 100% of trade value, benefitting India.
- Bilateral trade currently stands at USD 60 billion.
- Ease of Mobility: The FTA facilitates the mobility of professionals, including investors, intra-corporate transferees, their partners, and dependent children with the right to work.
- Double Contribution Convention: Indian workers temporarily in the UK and their employers will be exempt from paying social security contributions in the UK for three years.
- Opportunities for Skilled Youth: Indian youth can benefit from the UK’s digitally delivered services and advanced digital infrastructure.
- Export Opportunities: Sectors such as textiles, marine products, leather, footwear, engineering goods, auto parts, and organic chemicals will become more competitive in exports.
- Benefit Services: The deal will provide new opportunities and jobs in sectors like IT/ITeS and financial services.
- Other Benefits: The FTA aims to address non-tariff barriers and promote good regulatory practices.
Vesak Day: Honoring the Life and Teachings of Buddha
- India reaffirmed its commitment to Buddha’s teachings at UN Vesak Day 2025, held in Vietnam.
- Vesak Day, also known as Buddha Purnima, is observed on the full moon day in May.
- It is the most sacred day for millions of Buddhists across the world.
- Vesak marks three major events in the life of Gautama Buddha, all of which happened on the same day:
- His birth in 563 B.C.,
- His enlightenment (Nirvana), and
- His passing away (Mahaparinirvana) at the age of 80 in 483 B.C.
- In 1999, the UN General Assembly officially recognized Vesak as an international day to honor Buddhism.
Peizocatalysis
- Researchers have developed a cost-effective, metal-free porous organic catalyst for efficient hydrogen (H₂) production.
- This catalyst works using peizocatalysis, a process that converts mechanical energy into chemical energy.
- It uses piezoelectric materials to generate charge carriers required for water splitting, leading to hydrogen production.
What is the Piezoelectric Effect?
- The piezoelectric effect is the ability of certain materials to generate an electric charge when mechanical stress is applied.
- The term "piezoelectric" comes from the Greek word “piezo”, meaning “push”.
- This effect is reversible—materials that produce electricity when stressed can also deform when exposed to an electric field.
- Common piezoelectric materials include Berlinite, cane sugar, quartz, Rochelle salt, topaz, and bone.
Global Network of Age-friendly Cities and Communities (GNAFCC)
- Kozhikode city has been honoured with membership in the WHO’s Global Network of Age-friendly Cities and Communities (GNAFCC).
- GNAFCC was established in 2010.
- The network has 1300 members from 51 countries.
- Its aim is to connect cities, communities, and organizations globally to create great places for people to grow older in.
- It seeks to inspire change by showcasing what can be done and how.
- It connects cities and communities worldwide to enable the exchange of information, knowledge, and experiences.
- GNAFCC also supports cities and communities in finding appropriate, innovative, and evidence-based solutions.
Thrissur Pooram Festival
- The Thrissur Pooram festival has begun at the Vadakkumnathan Temple in Kerala.
- Vadakkumnathan is a Shiva temple that received the UNESCO Asia Pacific Heritage Award for Cultural Heritage Conservation in 2015.
- Thrissur Pooram is celebrated in the Malayalam month of Medom (April–May).
- It is considered the ‘Mother of all Poorams’ in Kerala.
- The festival features a grand assembly of Gods and Goddesses visiting the Vadakkumnathan Temple premises.
- The celebrations include richly caparisoned elephants and traditional musical performances like Chenda Melam and Pancha Vadyam.
National Archives of India (NAI)
- The National Archives of India (NAI) has digitised over 10 crore pages of historic documents.
- NAI was established in 1891 at Calcutta (now Kolkata) as the Imperial Records Department.
- It functions as an attached office under the Ministry of Culture.
- The present location of NAI is in New Delhi, with one Regional Office in Bhopal and three Records Centres in Bhubaneswar, Jaipur, and Puducherry.
- It serves as the custodian of records of enduring value, including public records, private papers, oriental records, cartographic records, microfilms, etc.
- NAI is headed by the Director General of Archives, who implements the Public Records Act, 1993 and Public Records Rules, 1997.
Saola (Asian Unicorn)
- A team of international scientists recently mapped the genome of the Saola, often referred to as the "Asian unicorn."
- Saola is found in the mist-covered evergreen forests of the Annamite Mountains along the Vietnam–Laos border.
- It has two parallel, sharp-ended horns around 20 inches long, present in both males and females.
- Though a cousin of cattle, the Saola resembles an antelope in appearance.
- It has distinctive white markings on its face and large glands on its muzzle, likely used to mark territory or attract mates.
- The Saola is listed as Critically Endangered on the IUCN Red List.
Multi-Influence Ground Mine (MIGM)
- The Indian Navy and DRDO have successfully tested the indigenously developed Multi-Influence Ground Mine (MIGM).
- MIGM is an advanced underwater naval mine aimed at strengthening India’s defense against modern stealth ships and submarines.
- It has been designed and developed by the Naval Science and Technological Laboratory (NSTL) under DRDO.
- MIGM uses multiple sensors to detect acoustic, magnetic, and pressure signals from marine vessels.
- It is equipped with built-in electronics and processors that analyze sensor data to trigger suitable actions.
- The mine is deployable from platforms such as ships and submarines.
Alcatraz Island
Recently, the USA President instructed the rebuilding and reopening of the infamous Alcatraz prison, on Alcatraz Island to house ruthless and violent offenders.
About Alcatraz Island
- Location: San Francisco Bay, California, USA.
- Features: Small barren island (also called as “the rock”) once used as a fort, a military prison, and later, a high-security federal prison.
- Sanctuary for seabirds including cormorants, western gulls, and faunal species like deer mice and slender salamanders, etc.
- Currently, a popular tourist destination, recognised as a National Historic Landmark.
|
Also Read |
|
UPSC Foundation Course |
|
| UPSC Monthly Magazine | CSAT Foundation Course |



