- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
India-Japan 2+2 Foreign and Defence Ministerial Meeting
India-Japan 2+2 Foreign and Defence Ministerial Meeting
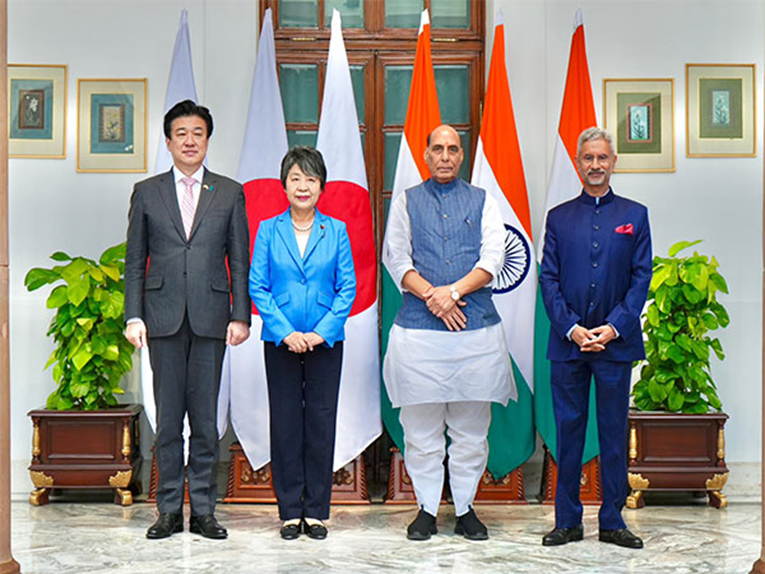

India and Japan recently conducted their third 2+2 Foreign and Defence Ministerial Meeting in New Delhi. The meeting, held against the backdrop of increasing geopolitical tensions and China's assertiveness in the Indo-Pacific, focused on strengthening bilateral cooperation and addressing key strategic issues.
Key Highlights:
- Commitment to a Free and Open Indo-Pacific:
- Both nations reiterated their dedication to maintaining a free, open, and rules-based Indo-Pacific.
- This commitment is driven by concerns over China's growing military presence in the region.
- Support was expressed for ASEAN’s unity and centrality, aligning with the ASEAN Outlook on the Indo-Pacific (AOIP), which emphasizes ASEAN’s role in regional stability and adherence to the United Nations Charter.
- Strengthening Defence and Security Cooperation:
- Defence cooperation was emphasized as a crucial pillar of the Special Strategic and Global Partnership between India and Japan.
- Japan’s National Security Strategy, updated in 2022, has further reinforced bilateral defence relations.
- Progress in multilateral exercises such as Veer Guardian (2023), Dharma Guardian (military), JIMEX (naval), SHINYUU Maitri (air force), and Malabar (with Australia and the US) was highlighted.
- Advancements in unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs) and robotics were noted.
- The 2008 Joint Declaration will be revised and updated to reflect contemporary security challenges and align with the evolving global security landscape.
- Tackling Terrorism and Extremism:
- Both countries condemned terrorism and violent extremism, with a focus on cross-border terrorism.
- The meeting emphasized bringing perpetrators of the 26/11 Mumbai attacks to justice and eliminating terrorist safe havens, financing channels, and halting the movement of terrorists.
- Specific mention was made of groups such as Al Qaeda, ISIS/Daesh, Lashkar-e-Tayyiba (LeT), and Jaish-e-Mohammad (JeM).
- Technological Collaboration:
- Discussions included the transfer of Japan’s Unified Complex Radio Antenna (UNICORN), which integrates multiple antennas to minimize radar signatures and enhance situational awareness.
- Japan’s UNICORN system can detect missiles and drones over a wide area.
- Both nations agreed to explore opportunities for Japanese naval ship maintenance in India and further defence technology cooperation.
- Women, Peace, and Security (WPS):
- Both countries emphasized the importance of women’s roles in peacekeeping operations.
- Support was given to the Women, Peace, and Security (WPS) agenda, formalized by UN Security Council Resolution (UNSCR) 1325, which highlights the critical roles of women in conflict prevention, resolution, peacebuilding, and post-conflict recovery.
What is 2+2 Meetings:2+2 meetings are high-level diplomatic dialogues involving the foreign and defence ministers of two countries. They provide a platform for in-depth discussions on strategic, security, and defence issues, aiming to enhance bilateral relations and address mutual concerns. India’s 2+2 Partners:
|
Significance of ASEAN for India and Japan:
- For India: ASEAN is vital for its Act East policy, enhancing trade, connectivity, and regional influence. India participates in infrastructure projects and economic agreements to strengthen ties and ensure maritime security in crucial sea lanes.
- For Japan: ASEAN is a major trade partner and investment destination. Japan leverages its economic presence through development aid and infrastructure projects and is a signatory to the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), enhancing economic ties with ASEAN.
What is ASEAN?
ASEAN, or the Association of Southeast Asian Nations, is an intergovernmental organization that unites 10 Southeast Asian countries for political and economic purposes: Indonesia, Vietnam, Laos, Brunei, Thailand, Myanmar, The Philippines, Cambodia, Singapore, and Malaysia.
Evolution of India-Japan RelationsEarly Exchanges
Post-World War II Relations
Strategic Partnerships
Key Areas of Cooperation
Historical Note
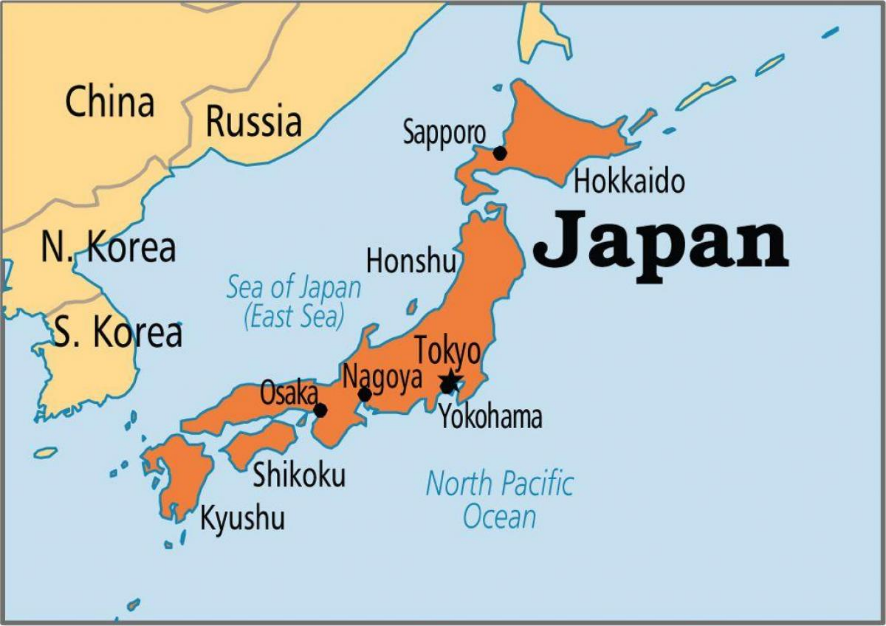
Key Facts About Japan
|
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi
UPSC Prelims Result 2024 Out: Expected Cut Off & Other Details, UPSC Prelims 2024 Answer with Explanation, Daily Prelims Quiz, Daily Current Affairs, MONTHLY CURRENT AFFAIRS TOTAL (CAT) MAGAZINE, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Karol Bagh, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Delhi, Daily Mains Question Answer Practice, ENSURE IAS UPSC Toppers, UPSC Toppers Marksheet, Previous Year Interview Questions, UPSC Syllabus




