- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Astronomers Detect Eleven New Active Galactic Nuclei
Astronomers Detect Eleven New Active Galactic Nuclei

Relevance: GS III; Science and Tech; Space Technology;
Why in the News?
Astronomers from the Russian Academy of Sciences, using the Spektr-RG (SRG) space observatory, have detected 11 new Active Galactic Nuclei (AGNs) during their all-sky X-ray surveys.
- The team has also previously identified more than 50 AGNs and several cataclysmic variable stars.
What are Active Galactic Nuclei (AGNs)?
- There are active supermassive black holes at the center of galaxies that are emitting gas and dust as light all along the electromagnetic spectrum. These are known as Active Galactic Nuclei’s (AGNs).
- There are majorly three types of Active Galactic Nuclei (AGNs):
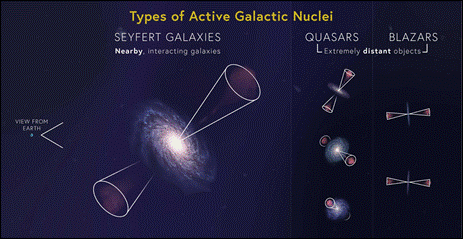
- Seyfert Galaxy is one among the most luminous and persistent energy sources in the universe and is critical to understanding galaxy formation and evolution. All new detected 11 AGNs were classified as Seyfert galaxies, a type of AGN that is common and well-studied:
-
- 7 galaxies were classified as Seyfert Type 1 (Sy 1), characterized by broad optical emission lines.
- 3 galaxies were classified as Seyfert Type 1.9 (Sy 1.9), showing partially broadened lines.
- 1 galaxy was classified as Seyfert Type 2 (Sy 2), which exhibits narrow emission lines only.
- The newly detected AGNs were identified during an optical and X-ray inspection of sources listed in the ARTSS1-5 catalog, using SRG’s ART-XC telescope.
- Characteristics of the 11 Newly Detected AGNs: All 11 AGNs are located at redshifts ranging from 0.028 to 0.258, indicating they are relatively nearby in cosmic terms. Their X-ray luminosities fall within the typical range of 2 to 300 × 10³⁹ erg/s, which is consistent with known AGN profiles.
|
About the Spektr-RG (SRG):
Aims and Objectives of the Mission:
|
Way Forward: SRG’s surveys are expected to revolutionize our understanding of the high-energy universe by providing the most detailed X-ray maps to date. The mission enables the discovery of new cosmic objects, studies of galaxy evolution, and insights into the physics of black holes and the intergalactic medium.
|
PYQ Significance: Mains: Q. Launched on 25 th December, 2021, James Webb Space Telescope has been much in the news since then. What are its unique features which make it superior to its predecessor Space Telescopes? What are the key goals of this mission? What potential benefits does it hold for the human race? (UPSC CSE 2022) |
|
Also Read |
|
| Public Administration Optional | |
| UPSC Monthly Magazine | Question Answer Practice For UPSC |



