- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Granting Habitat Rights and Implications
Granting Habitat Rights and Implications
14-10-2023

Why in News?
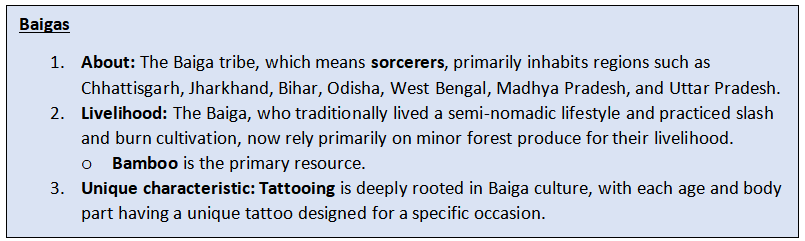
Recently, The Chhattisgarh Government has granted habitat rights to its Baiga PVTG, following the Kamar PVTG's recent acquisition in August 2023.
- The Baiga PVTG has become the second group in Chhatisgarh to be granted these rights.
- Chhattisgarh is home to seven PVTGs, including Kamar, Baiga, Pahadi Korba, Abujhmadiya, Birhor, Pando, and Bhujia.
What are Habitat Rights?
-
About:
- Habitat rights recognition grants communities’ rights over their habitation territory, socio-cultural practices, economic means, biodiversity knowledge, traditional resource use, and protection of their natural and cultural heritage.
- Habitat rights protect traditional livelihoods and ecological knowledge, enabling PVTG communities to develop their habitats through a combination of government schemes and initiatives.
- According to the Forest Rights Act (FRA), "habitat" includes customary habitats and those in reserved and protected forests of PVTGs and other forest-dwelling Scheduled Tribes.
-
Process of Habitat Declaration:
- The procedure is based on a comprehensive guideline issued by the Ministry of Tribal Affairs in 2014.
- The process involves consulting with traditional tribal leaders to assess the extent of culture, traditions, and occupation.
- The definition and declaration of habitats require coordination between state-level departments like Forest, Revenue, Tribal, and Panchayati Raj, and the UNDP team.
-
Legal Aspect:
- The Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006 (also known as FRA), grants habitat rights to PVTGs.
- The recognition of habitat rights grants PVTGs ownership over their customary territory, including habitation, economic means, livelihood means, and biodiversity knowledge.

Significance and Implications of Granting Habitat Rights
-
Preservation of Culture and Heritage:
- Granting tribal rights is crucial for preserving the cultural, social, and traditional heritage of tribal communities, enabling them to maintain their distinct languages, rituals, customs, and knowledge systems.
-
Empowerment and Social Justice:
- Tribal rights empower communities by providing legal recognition, ensuring their participation in decision-making, and rectifying historical injustices, contributing to a more just and equal society.
-
Livelihood Protection:
- Tribal communities rely on natural resources for livelihoods, and granting rights over lands and resources helps sustain traditional occupations like hunting, gathering, fishing, and farming.
-
Sustainable Development:
- Governments can foster sustainable development by granting rights to tribal communities, who prioritize conservation and environmental well-being, as indigenous practices often prioritize these aspects.
-
Biodiversity Conservation:
- Tribal communities possess unique knowledge about ecosystems, flora, fauna, and sustainable resource management, recognizing their rights helps preserve biodiversity and ensures sustainable resource management.
Conclusion
Granting tribal rights is crucial for creating a society that values and protects the rights, cultures, and traditions of all citizens, including tribal communities. This further helps in achieving constitutional ideals envisaged for tribals enshrined in Article 46 of Directive Principles of Sate Policy, Schedule 5th and 6th.