- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Daily Current Affairs Summary 18th APRIL 2025
Daily Current Affairs Summary 18th APRIL 2025
CDSCO Bans 35 Fixed-Dose Combination (FDC) Drugs
- The Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO), India's top regulatory body for pharmaceuticals, has recently issued a directive banning 35 unapproved FDC drugs across all states and Union Territories.
- This move comes after it was found that several FDC formulations were in violation of the New Drugs and Clinical Trials (NDCT) Rules, 2019, framed under the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940.
What are Fixed-Dose Combination (FDC) Drugs?
- FDCs are pharmaceutical products that combine two or more active ingredients in a fixed ratio for treating specific medical conditions.
- The active ingredient is the core biological component in a drug that is responsible for producing the intended therapeutic effect.
Classification of FDCs
- FDCs are grouped into four broad categories based on their composition and therapeutic use.
- These combinations are carefully assessed for safety, efficacy, and rationality before approval.
When is an FDC Considered a 'New Drug'?
Under the NDCT Rules, 2019, an FDC is classified as a new drug if:
- It combines two or more drugs, each already approved for individual use, into a fixed ratio formulation.
- It involves a change in the ratio of components in an already approved FDC, coupled with new therapeutic claims or indications.
Why Are FDCs Commonly Used?
- Better Therapeutic Effectiveness: Rationally chosen drug combinations often lead to enhanced clinical outcomes due to synergistic action.
- Improved Patient Compliance: Combining multiple drugs into one formulation reduces the pill burden and simplifies treatment regimens.
- Cost Efficiency: FDCs can be cheaper than buying individual medicines, thus making therapy more affordable for patients.
India’s Trade Deficit with China Touches $99.2 Billion
- India’s trade deficit with China soared to $99.2 billion in the fiscal year 2024–25, raising concerns over growing dependency and strategic vulnerabilities.
- This sharp increase is primarily due to a significant surge in imports of electronic goods, such as EV batteries and solar cells, along with other consumer durables.
- Meanwhile, India’s exports to China declined to just $14.3 billion during the same period, further widening the gap.
Key Concerns Arising from Rising Trade Deficit with China
- Pressure on Domestic Manufacturing: Low-cost imports from China put Indian manufacturers, especially in sectors like steel, chemicals, and electronics, at a serious disadvantage.
- Strategic Supply Chain Dependence: Persistent reliance on Chinese goods exposes India to external shocks and vulnerabilities, especially in critical sectors.
- National Security Implications: China could potentially leverage India’s dependency during border tensions or diplomatic negotiations, posing a strategic risk.
- Risk of Trade Diversion: Owing to high US tariffs, Chinese goods could be redirected towards India, increasing the risk of dumping at unfair prices.
- Bypassing US Trade Barriers: India could unintentionally become a transit point for Chinese goods into US markets, damaging India’s strategic ties with the US.
- Economic Impact: A continuously rising deficit leads to a sustained outflow of foreign exchange, impacting India’s external account stability.
Key Steps Taken by India to Address Trade Deficit with China
- Boosting Domestic Production: Through initiatives like the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme and Make in India, India aims to strengthen local industries and reduce import dependence.
- Building Local Supply Chains: Creation of Bulk Drug Parks and support for indigenous production in pharma and electronics to reduce reliance on Chinese inputs.
- Export Promotion Measures: Incentives like the RoSCTL (Rebate of State and Central Levies and Taxes) and the Interest Equalisation Scheme (IES) aim to make Indian exports more competitive globally.
- Trade Remedies and Regulatory Actions: Use of tools like Anti-Dumping Duties, Safeguard Measures, and the Market Access Initiative (MAI) scheme to protect domestic industries and ensure fair trade practices.
India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC): A Modern Silk Route
- Union Commerce and Industry Minister recently described IMEC as more than a trade route — calling it a modern-day Silk Route that connects civilizations through commerce and infrastructure.
- He emphasized that IMEC will significantly improve trade efficiency and reduce costs across continents.
Key Economic Benefits of IMEC
- Up to 30% reduction in logistics costs, making trade more affordable and competitive.
- Around 40% reduction in transportation time, ensuring faster movement of goods.
- Seamless connectivity between Asia, the Middle East, and Europe through integrated infrastructure.
Implementation Strategy Proposed by the Minister
- Stakeholder Engagement: Collaboration among industry players, think tanks, and academia is essential for effective planning and execution.
- Innovative Financing Models: Use of instruments like long-term IMEC Bonds to attract private and institutional investment for large-scale projects.
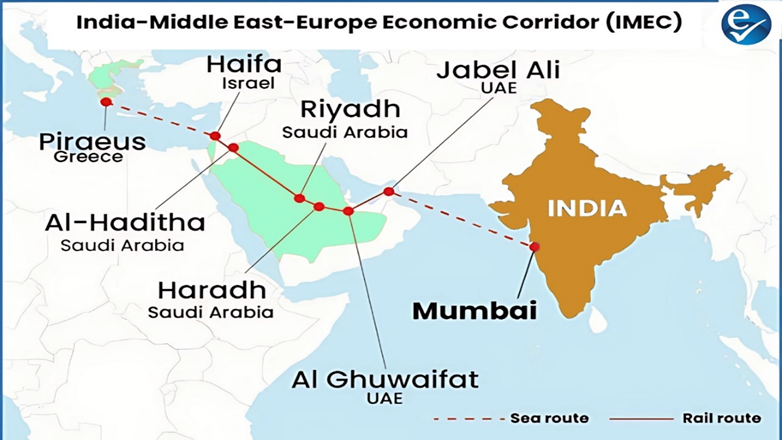
India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC)
About IMEC
- Type: A multi-modal connectivity project aimed at establishing integrated trade and infrastructure corridors.
- Formalization: Signed through a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) during the G20 Summit 2023 held in New Delhi.
- Participants: India, European Union, France, Germany, Italy, Saudi Arabia, UAE, and the United States.
- Core Objective: To develop a network of ports, railways, roads, pipelines, and sea routes to enhance regional and intercontinental trade.
Strategic Significance of IMEC
- Geostrategic Relevance:
- Reduces reliance on traditional maritime routes such as the Suez Canal.
- Increases resilience against global disruptions and bottlenecks in sea trade.
- Geoeconomic Impact:
- Enables deeper economic integration between India, the Middle East, and Europe.
- Facilitates smoother movement of energy, goods, and digital connectivity.
- Alternative to China’s BRI:
- Presents a democratic, transparent, and rules-based counter-model to the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
- Promotes a more inclusive global infrastructure development framework.
Historical Parallel: Silk Route
- The Silk Route was a major trade network operational from the 2nd century B.C. to the 15th century A.D..
- It connected Asia to Europe, enabling the exchange of goods, cultures, and ideas across continents.
- IMEC echoes this legacy by building a modern, strategic trade corridor in a digitally connected global economy.
Tamil Nadu Forms Committee to Revisit Centre-State Relations
The Tamil Nadu government has established a high-level committee to examine the dynamics of Centre-State relations and suggest ways to strengthen the constitutional rights of Indian states.
- The committee is headed by Justice Kurian Joseph, former judge of the Supreme Court of India.
- Its primary task is to propose measures that reinforce federal balance and empower states within the framework of the Indian Constitution.
Historical Reference: Rajamannar Committee (1969)
- Constituted by the DMK government in Tamil Nadu, this was the first state-appointed committee to examine Centre-State relations.
- Objective: To review the Constitution and recommend greater autonomy for states in legislative, executive, and judicial domains.
Key Findings of Rajamannar Committee:
- Criticized Article 365, calling it a tool for excessive central interference.
- Strongly recommended repealing Article 356 to prevent misuse of President’s Rule.
- Advocated for strengthening the Inter-State Council under Article 263 to facilitate cooperative federalism.
- Expressed concern over the limited role of the Finance Commission in ensuring fiscal federalism.
Other Key Committees on Centre-State Relations
Sarkaria Commission (1983)
Set up by the Union Government to analyze Centre-State relations and recommend ways to improve cooperation.
Notable Recommendations:
- Opposed abolishing All-India Services, citing their role in maintaining national unity.
- Stated that President’s Rule (Article 356) should only be used as a last resort.
- Urged that active politicians should not be appointed as Governors, to preserve neutrality.
- Emphasized genuine implementation of the three-language formula in all states to promote linguistic harmony.
Punchhi Commission (2007)
Formed to revisit Centre-State dynamics in light of changing socio-political realities.
Major Recommendations:
- Suggested the creation of a formal impeachment process for Governors, similar to the President’s under Article 61.
- Recommended that the Centre consult States while making laws on subjects in the Concurrent List.
- Called for restrained use of Article 356, discouraging its blanket application.
Kailash Mansarovar Yatra: A Sacred Pilgrimage Set to Resume
India and China are in discussions to resume the Kailash Mansarovar Yatra, which has remained suspended since 2019 due to various geopolitical and health-related reasons.
About Kailash Mansarovar
- Kailash Mansarovar is a revered pilgrimage site located in the Western Himalayan ranges, within the Tibetan Autonomous Region.
- The pilgrimage includes Mount Kailash, the highest peak of the Kailash Range, and Lake Mansarovar, which holds the distinction of being the world’s highest freshwater lake.
- It holds deep religious significance for followers of Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism, who consider the site sacred.
- In Hindu belief, Mount Kailash is regarded as the abode of Lord Shiva, while Jainism associates it with the liberation of the first Tirthankara, Rishabhdev.
- Buddhists regard the mountain as the center of the universe, known as Mount Meru in their cosmology.
Access Routes for the Yatra
- The Yatra was traditionally conducted through two primary routes:
- Lipulekh Pass in Uttarakhand
- Nathu La Pass in Sikkim
- These routes offer land-based access to pilgrims, combining trekking, road travel, and at times air connectivity, depending on the package and route chosen.
The proposed resumption of the Yatra marks a significant development for both diplomatic cooperation and spiritual tourism, reconnecting devotees with a journey deeply rooted in faith, culture, and tradition.
Wet-bulb temperature
Harvard Study Reassesses Human Survival Threshold
A recent study by Harvard researchers challenges the long-standing belief that the human survivability limit for wet-bulb temperature is 35°C, proposing a lower threshold of around 31°C for safe human endurance.
What is Wet-Bulb Temperature?
- Wet-bulb temperature refers to the lowest temperature that air can reach through evaporation of water at constant pressure.
- It is measured by wrapping a wet cloth around the bulb of a thermometer and allowing the water to evaporate.
- The cooling effect from evaporation lowers the thermometer reading, providing the wet-bulb temperature value.
- This metric reflects both heat and humidity, making it more realistic for assessing human heat stress than air temperature alone.
- A high wet-bulb temperature means evaporation (and thus sweating) becomes less effective, reducing the body's ability to cool itself.
- It is a critical factor in areas like climate science, agriculture, health, and disaster preparedness.
- Conditions above the survivability threshold—even for short periods—can lead to fatal heat stress, particularly in vulnerable populations.
Global Trade Outlook and Statistics-2025
Released by the World Trade Organization (WTO)
Key Projections and Findings
- The WTO’s Global Trade Outlook 2025 highlights a 0.2% contraction in the volume of global merchandise trade.
- The sharpest decline is expected in North America, where exports are projected to fall by 12.6%.
- The report raises concerns over heightened downside risks that could worsen trade conditions further.
- These risks include the implementation of “reciprocal” tariffs and the wider spillover effects of policy uncertainty.
- For the first time, the report includes forecasts for services trade, expanding beyond its traditional merchandise trade focus.
- In contrast to merchandise trade, the volume of global services trade is expected to grow by 4.0% in 2025.
National Critical Mineral Mission
The Ministry of Mines has today issued the guidelines for setting up of Centres of Excellence (CoE) under the National Critical Mineral Mission (NCMM).
About National Critical Mineral Mission
- Launch: In January 2025.
- Ministry: Ministry of Mines
- Objective:
- To secure India’s critical mineral supply chain by ensuring mineral availability from domestic and foreign sources.
- Strengthening the value chains by enhancing technological, regulatory, and financial ecosystems to foster innovation, skill development, and global competitiveness in mineral exploration, mining, beneficiation, processing, and recycling.
World Meteorological Organisation (WMO)
Commemorated through Meghayan-25 Symposium by the Indian Navy
To mark the formation of the World Meteorological Organisation and observe WMO Day 2025, the Indian Navy hosted the Meghayan-25 Symposium, celebrating advancements in meteorological sciences and global cooperation.
About the WMO
- The World Meteorological Organisation (WMO) was officially established on 23rd March 1950.
- It functions as a specialized agency under the United Nations.
- WMO comprises 193 Member States and Territories, with India as an active member.
- Its core mission is to facilitate global cooperation in the fields of meteorology, climatology, operational hydrology, and related geophysical sciences.
- The organization helps improve the quality of life and resilience of societies through early warning systems, climate services, and environmental monitoring.
- WMO plays a key role in climate awareness by releasing the “State of the Global Climate” report, which highlights pressing environmental trends.
- The headquarters of WMO is located in Geneva, Switzerland, serving as the nerve center for its global initiatives.
Clinidium lalitae: A Newly Discovered Beetle Species
Scientists from the Zoological Survey of India (ZSI) have recently discovered a new species of beetle named Clinidium lalitae.
Key Details About the Species
- The species was identified in the Talle Valley Wildlife Sanctuary, located in Arunachal Pradesh.
- It belongs to the subfamily Rhysodinae, which comprises a rare group of ground beetles.
- Clinidium lalitae is notable for its distinct morphological features, which set it apart from other related species.
- These beetles are typically found on forest floors, where they thrive in undisturbed natural habitats.
- As part of forest ecosystems, they contribute significantly to nutrient cycling and soil health.
Urdu language
Supreme Court upholds Urdu signage in Maharashtra.
SC also observed that language belongs to a community, to a region, to people; and not to a religion.
Must Read: Urdu is not an alien language: SC
About Urdu language
- It is an Indo-Aryan language.
- Linguists consider Standard Urdu and Standard Hindi to be different formal registers both derived from the Khari Boli dialect, which is also known as Hindustani.
- It originated and developed in the Indian sub-continent.
- It is included in the Eighth Schedule of the Constitution.
The National Anti-Doping Agency (NADA)
NADA India Hosts a National Conference on Building Together a Clean Sport Ecosystem.
About NADA
- Ministry: It is an autonomous body under the Ministry of Youth Affairs & Sports.
- Aim: Creating a dope-free environment and promoting fair play in sports in India.
- NADA India implements the anti-doping programme in India, in line with the World Anti-doping Code 2021.
- The key areas of functioning include Sample Collection (SC), Results Management (RM), Anti-Doping Education & Awareness, Research and Intelligence & Investigations (I&I).
Tuti Island
Tuti Island has been devastated by two years of war between the Sudanese army and the paramilitary Rapid Support Forces (RSF).
About Tuti Island
- It is located at the confluence of the Blue and White Niles in Khartoum, Sudan.
- It is a historic oasis and one of the city’s oldest settlements.
- It is a crescent-shaped island and formed by silt deposition.
|
Also Read |
|
UPSC Foundation Course |
|
| UPSC Monthly Magazine | CSAT Foundation Course |




