- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Daily Current Affairs Summary 17th APRIL 2025
Daily Current Affairs Summary 17th APRIL 2025
India Justice Report: Chronic Under-Resourcing Hindering Justice Delivery
The India Justice Report (IJR) reveals deep-rooted structural gaps in India's justice delivery system, across four critical pillars — Police, Judiciary, Prisons, and Legal Aid. These inefficiencies risk further marginalizing vulnerable sections and obstructing equitable access to justice.
1. Police: Burdened and Undermanned
- The national police force suffers from a 23% vacancy rate, severely affecting its capacity.
- Forensic units are even worse off, with over 50% vacancies nationwide.
- Women’s representation in senior police roles stands at only 8%, reflecting poor gender inclusion.
- No state or Union Territory has achieved the 33% reservation benchmark for women in police, recommended since 2009.
- These staffing gaps and lack of diversity weaken community engagement and trust in law enforcement.
2. Judiciary: Overloaded and Unequal
- India has just 15 judges per 10 lakh population, far below the 1987 Law Commission's ideal of 50 judges per 10 lakh.
- Gender imbalance remains high — women account for only 38% in lower courts and a mere 14% in High Courts.
- Representation of Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, and OBCs remains minimal across states.
- Karnataka is the only state fulfilling the mandated reservations for SC, ST, and OBCs in judicial appointments.
- These disparities hamper inclusivity and fairness in judicial outcomes.
3. Prisons: Overcrowded and Understaffed
- 30% of prison staff positions remain vacant, weakening prison management and rehabilitation efforts.
- Indian prisons operate at 131% occupancy, highlighting a serious overcrowding issue.
- Undertrials make up 76% of the prison population, pointing to delays in judicial processing and access to timely bail.
- The combination of staff shortages and overcrowding affects both prisoner welfare and reform initiatives.
4. Legal Aid: Declining Community Participation
- Para Legal Volunteers (PLVs), vital for legal outreach, have reduced by 38% nationally.
- This drop reflects weakening grassroots legal support, especially for marginalized and rural communities.
- The declining volunteer base undermines the vision of accessible and affordable justice for all.
Way Forward: Incentivizing Justice Reform
- To address these gaps, the report suggests performance-based incentives for states showing improvements.
- States can be rewarded for filling judicial vacancies, enhancing police training, or strengthening prison rehabilitation frameworks.
- A data-driven, outcome-based reform model is essential to ensure long-term sustainability and inclusivity in the justice system.
- Without urgent reforms, existing disparities may deepen, affecting the very foundation of rule of law and democratic governance.
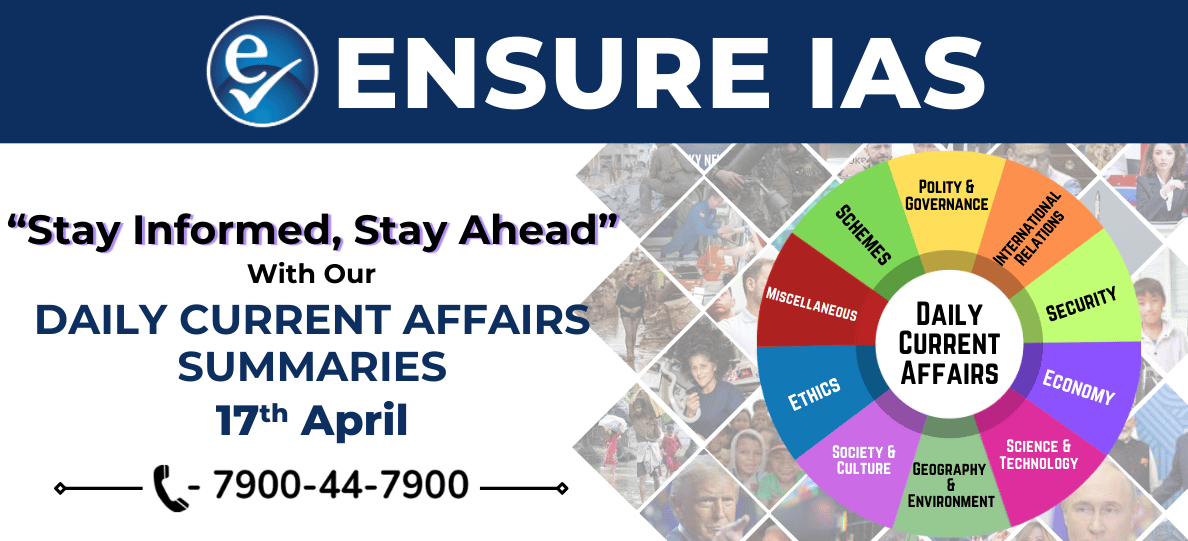
India's Quantum Leap: QpiAI Launches 25-Qubit Quantum Computer under NQM
- On World Quantum Day (April 14th), Bengaluru-based startup QpiAI, selected under the National Quantum Mission (NQM), unveiled one of India's most advanced quantum systems.
- The 25-qubit superconducting quantum computer, named QpiAI-Indus, marks a significant technological milestone for the country.
- It is India’s first full-stack quantum computing system, integrating quantum hardware, scalable control electronics, and hybrid-optimized software.
- This development showcases India's growing capabilities in building a holistic quantum ecosystem, from hardware to application layers.
Understanding Quantum Computing and Its Core Principles
- Quantum computers harness the power of quantum mechanics to solve problems that are intractable for classical computers.
- Unlike traditional computers that use binary bits (0 or 1), quantum computers operate using qubits, which can exist in multiple states simultaneously.
Key Principles:
- Superposition: A qubit can exist in a blend of 0 and 1 states, allowing parallel computation.
- Entanglement: Interlinked qubits influence each other’s state, enabling faster and coordinated processing even over large distances.
- Quantum Interference: Enhances the probability of correct outcomes by amplifying desired states and suppressing errors.
These principles enable exponential computational power, especially for optimization, simulation, and cryptography tasks.
National Quantum Mission (NQM)
Significance of Quantum Computing for India
- Global Positioning: Places India alongside leading nations like the United States, China, and France in the global quantum race.
- Quantum-Secure Communication: Facilitates the development of ultra-secure, high-speed quantum networks resistant to cyberattacks.
- Scientific Research: Accelerates drug discovery and chemical simulations through accurate molecular modeling.
- Advancement in AI/ML: Enhances machine learning and artificial intelligence by enabling faster and more efficient data processing.
- Smart Manufacturing: Supports precision design, improved prototyping, and reduces cost and time in industrial product development.
The launch of QpiAI-Indus under the National Quantum Mission is a defining step in India’s journey toward quantum self-reliance.
It reflects the nation's ability to build indigenous quantum infrastructure, paving the way for innovation across science, industry, security, and governance.
Supreme Court Issues Comprehensive Guidelines to Combat Child Trafficking
- In the landmark case of Pinki v. State of Uttar Pradesh, the Supreme Court issued strong directives to expedite justice in child trafficking cases.
- The Court instructed all High Courts to ensure that trials related to child trafficking are completed within six months and progress reports are submitted regularly.
- It flagged the low conviction rate in such cases, attributing it to factors like easy bail for traffickers, hostile witnesses, and trial delays.
Key Directives Issued by the Supreme Court
1. Mandatory Reporting and Classification
- All cases of missing children must be treated as potential abduction or trafficking unless proven otherwise.
- Police and Anti-Human Trafficking Units (AHTUs) must mandatorily report every trafficking-related case without delay.
2. Strengthening Child Protection Systems
- Each state must establish a State-level Anti-Human Trafficking Bureau in its capital city.
- Child Welfare Committees (CWCs) must be set up and function efficiently in every district.
- Hazardous industries must be inspected regularly, and strict actions taken against violators employing children.
- Child-friendly courts, like those in Telangana and West Bengal, must be established to protect and support child victims during trials.
3. Victim-Centric Measures
- Victim support systems must be enhanced to ensure psychological and legal aid to trafficked children.
- Community policing initiatives should be promoted to build trust and early identification of trafficking risks.
- Strong coordination with NGOs is essential for effective rescue, rehabilitation, and awareness-building campaigns.
Child Trafficking Status
|
Existing Legal and Institutional Measures to Curb Child Trafficking
|
The Supreme Court's directions reflect a growing urgency to combat child trafficking holistically through judicial reform, institutional strengthening, and community participation.
The integration of legal measures, digital platforms, and coordinated support systems is key to building a child-safe India.
China Imposes Export Restrictions on Rare Earth Elements Amid Trade Tensions
- In a retaliatory move against U.S. tariffs, China has tightened export controls on Rare Earth Elements (REEs), raising global concerns over the weaponization of trade.
- This decision holds strategic significance due to China’s dominant role in the global REE supply chain, especially for sectors like electronics and semiconductors.
Understanding Rare Earth Elements (REEs)
- REEs are a group of 17 soft, lustrous, silvery-white heavy metals listed in the periodic table.
- Examples include Cerium (Ce), Yttrium (Y), and Europium (Eu).
- Though REEs are abundantly found in the Earth's crust, their extraction is challenging due to low natural concentration and complex processing.
- They play a critical role in modern applications such as:
- Defense systems (e.g., radars, missiles, and drones)
- Electronics (e.g., smartphones, computers)
- Clean energy technologies (e.g., solar panels, wind turbines)
- Industrial catalysts and metal alloys
Global Distribution and China's Dominance
- Top REE reserve holders include:
- China (44 million tonnes)
- Vietnam, Brazil, Russia, and India (6.9 million tonnes)
- China is the leading global producer, contributing to over two-thirds of global REE production.
- It also controls more than 85% of the global REE supply chain owing to its advanced processing and refining technologies.
Implications of China's Export Restrictions
- Global supply chain disruptions are likely, especially for industries dependent on REEs, such as electric vehicles, electronics, and renewable energy.
- The defense industry could face major challenges, as REEs like dysprosium and yttrium are crucial for manufacturing fighter jets, precision missiles, and military drones.
- These restrictions highlight the strategic vulnerabilities in global REE sourcing and processing.
India’s Response to Reduce REE Dependence on China
1. Domestic Resource Utilization
- India is focusing on expanding its REE production through public sector enterprises like Indian Rare Earths Limited (IREL).
- IREL has announced plans to boost production by 400% by 2032 to tap into India’s 6.9 MT of REE reserves.
2. International Collaborations and Tech Partnerships
- India signed the TRUST Initiative with the United States in February 2025 to strengthen REE supply chain cooperation.
- This follows the broader Minerals Security Partnership (MSP) signed in 2023 for securing critical mineral supply chains globally.
3. Policy and Legal Reforms
- The Indian government has amended mining laws to encourage private sector participation in REE extraction and processing.
- These reforms aim to diversify sourcing, attract investments, and build technological capability in the REE value chain.
WHO Member States Finalize Draft Pandemic Agreement for Global Preparedness
- Member states of the World Health Organization (WHO) have successfully concluded negotiations on a draft Pandemic Agreement aimed at bolstering global health security.
- The draft was finalized by the Intergovernmental Negotiating Body (INB), established by the World Health Assembly in 2021 for this specific purpose.
Role of the Intergovernmental Negotiating Body (INB)
- INB was entrusted with the task of drafting a comprehensive international agreement to enhance pandemic prevention, preparedness, and response.
- After multiple rounds of negotiations, the draft is now scheduled for submission to the World Health Assembly in May 2025 for final consideration.
Overview of the WHO Pandemic Agreement
- Objective: To create a robust international mechanism to prevent, prepare for, and respond to future pandemics in a coordinated manner.
- The agreement outlines legally binding commitments and cooperative measures among nations for effective health emergency management.
Key Provisions of the Draft Treaty
- Pandemic Prevention & Surveillance: Countries must conduct regular risk assessments of emerging pathogens to identify and contain threats early.
- One Health Approach: Emphasizes the interconnected health of humans, animals, plants, and ecosystems to detect zoonotic diseases at source.
- Technology and Knowledge Transfer: Promotes transparent licensing systems and encourages technology-sharing for the benefit of developing nations.
- Access and Benefit Sharing: Proposes creation of a WHO Pathogen Access and Benefit-Sharing System to ensure equitable access to pathogen samples and medical tools globally.
Why a Global Pandemic Agreement is Needed
- The COVID-19 pandemic exposed the gaps in global health coordination and emergency response frameworks.
- A unified treaty ensures global collaboration across all sectors—governments, science, civil society—for stronger collective defense.
- The agreement prioritizes equity in access to essential medical tools like vaccines, personal protective equipment, diagnostics, and therapeutics.
- It aims to mobilize sustainable finance by enabling resource allocation for preparedness, health system strengthening, and emergency response.
|
Existing Framework: International Health Regulations (IHR), 2005
|
Surat Emission Trading Scheme (ETS): A Market-Based Solution to Air Pollution
- A recent study reveals that the Surat Emission Trading Scheme has successfully reduced particulate pollution by 20–30%.
- It also led to a significant reduction in compliance costs for industries, making it both environmentally and economically effective.
What is Surat ETS?
- Launched in 2019 in Surat, Gujarat, it is the world’s first emission trading market specifically for particulate matter (PM).
- The scheme is a pioneering initiative aimed at using market-based mechanisms to reduce industrial air pollution.
- Its primary goal is to curb emissions by promoting cost-effective pollution control strategies.
How Does Surat ETS Work? (Cap-and-Trade Model)
- The system follows the cap-and-trade principle, where a total emissions limit is set across all participating industries.
- Each industrial unit receives a fixed pollution permit defining how much it can emit.
- Industries that emit less than their cap can sell their unused permits to those that exceed their limit.
- This promotes efficient allocation of emission allowances, incentivizing pollution control without compromising productivity.
- Similar models have been successfully implemented for greenhouse gases in Europe and carbon emissions in China.
Trading Mechanism and Platform
- Permit trading takes place on a digital exchange platform managed by NeML (NCDEX e-Markets Ltd.).
- This transparent and regulated platform ensures real-time trading, verification, and compliance tracking.
- It allows industries to optimize their pollution control strategies based on economic incentives.
Southwest Monsoon 2025: Rainfall Likely to be Above Normal
According to the India Meteorological Department (IMD), the 2025 southwest monsoon season (June–September) is expected to record above-normal rainfall, likely to be 105% of the Long Period Average (LPA), with a margin of ±5%.
Understanding Long Period Average (LPA) of Rainfall
- LPA refers to the average rainfall received over a specific region during a defined period, usually calculated over a 30-year time frame.
- It is a standard climatological benchmark used by IMD to assess whether rainfall in a particular season is deficient, normal, or excess.
- The current LPA for the southwest monsoon season over India as a whole is based on the 30-year period from 1971 to 2020.
- This LPA value is 87 cm, representing the mean seasonal rainfall across the country during this reference period.
- Forecasts issued by IMD are generally expressed as a percentage of this LPA, making it a critical reference point in monsoon prediction.
Why LPA Matters?
- It helps in quantitatively categorizing rainfall patterns such as below normal, normal, or above normal.
- It serves as the foundation for agricultural planning, water resource management, and disaster preparedness.
- Accurate LPA-based predictions assist in mitigating monsoon-related risks like floods, droughts, and crop failures.
BSE Celebrates 150 Years in 2025
- The year 2025 marks the 150th anniversary of the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE).
- It was originally established in 1875 as 'The Native Share & Stock Brokers' Association' in Mumbai.
- BSE holds the distinction of being Asia’s first stock exchange and among the oldest globally.
Key Milestones and Achievements
- In 2017, BSE created history by becoming the first stock exchange in India to be publicly listed.
- It is recognized as the world’s fastest stock exchange, with a median trade speed of 6 microseconds.
Core Functions of BSE
- BSE offers a transparent and efficient platform for trading in multiple financial instruments.
- These include equities, derivatives, currencies, debt securities, and mutual funds.
- It plays a pivotal role in capital formation and supports the growth of Indian financial markets.
Regulatory Oversight
- The functioning of BSE is regulated by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
- SEBI is a statutory regulatory body, established under the SEBI Act, 1992, to protect investor interests and maintain market integrity.
Open Acreage Licensing Policy (OALP)
Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas has awarded 28 blocks under OALP Round-IX.
About OALP
- It was introduced under the Hydrocarbon Exploration and Licensing Policy (HELP)
- HELP was unveiled in 2016, replacing the New Exploration Licensing Policy (NELP).
- OALP mechanism Allows the investors to carve out blocks of their choice by assessing Exploration and Production (E&P) data.
- National Data Repository (NDR), an integrated data repository of E&P data of Indian sedimentary basins, facilitates the implementation of OALP
real-time LAMP (rt-LAMP)
Researchers have tested the real-time LAMP (Loop Mediated Isothermal Amplification) or rt-LAMP method for early and accurate diagnosis of tuberculosis (TB).
About rt–LAMP
- It is an open platform system for TB diagnosis.
- It is achieved by repurposing existing RT-PCR machine.
- RT-PCR is a laboratory method used to make many copies of a specific genetic sequence for analysis.
- It uses six primers (short DNA pieces), while RT-PCR uses only two.
- Therefore, rt-LAMP giving positive results in just 10–20 minutes.
Countercyclical Capital Buffer (CCyB)
RBI has decided not to activate the CCyB.
- This will ensure uninterrupted credit flow to key sectors and avoid a slowdown in GDP growth.
About CCyB
- Genesis: Introduced by RBI in 2015 under Basel III, but never used so far.
- Mandate: Banks must build extra capital during good times to support credit during downturns.
- Goal: Prevent excessive lending during booms and reduce systemic financial risks.
- Trigger for Usage: RBI’s framework envisages the credit-to-GDP gap as the main indicator.
- Other supplementary indicators may also be used.
|
Also Read |
|
UPSC Foundation Course |
|
| UPSC Monthly Magazine | CSAT Foundation Course |




