- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Daily Current Affairs Summary 16th APRIL 2025
Daily Current Affairs Summary 16th APRIL 2025

Policy Paper: “Indian Agriculture to 2047”
Released by: ICAR-National Institute of Agricultural Economics and Policy Research (ICAR-NIAP)
Focus: Transformation and future roadmap of India’s agri-food system

Structural Transformation in India’s Agri-food System
- India transitioned from a food-deficit to a food-surplus nation, driven by the Green Revolution, input subsidies, and MSPs.
- Agriculture’s contribution to national income fell from 43% to 18% over the decades.
- In contrast, the workforce shares in agriculture declined more gradually from 74% to 46%.
- Landholding patterns witnessed fragmentation, with marginal holdings (≤1 hectare) rising from 51% to 68%.
- The average size of operational landholdings decreased significantly from 2.28 hectares to 1.08 hectares.
- There has been a notable shift towards diversification within agriculture.
- Animal husbandry now contributes 31% to agricultural GVA, while fisheries account for 7% as of 2022–23.
Key Challenges in Agri-food System Transformation
- Agricultural land is shrinking due to rapid population growth, urban sprawl, and industrial development.
- Fertilizer usage is unbalanced, impacted by skewed subsidy structures and regional inefficiencies.
- Low nutrient use efficiency and excessive reliance on certain fertilizers aggravate the issue.
- Groundwater resources are overexploited, and overall water use efficiency remains suboptimal.
- Climate change has led to a 25% reduction in agricultural productivity growth, driven by extreme weather events.
- Additional bottlenecks include underdeveloped markets, weak credit systems, and inefficient value chains.
- Policy bias toward cereal crops has further limited diversification and resilience in the agri-food system.
Recommendations for a Sustainable Agri-food Future
- Strengthen water management through rainwater harvesting, groundwater recharge, and expanded micro-irrigation.
- Gradually phase out electricity subsidies to encourage efficient resource use.
- Promote nano fertilizers to improve nutrient delivery and reduce environmental impact.
- Encourage sustainable agricultural practices such as crop rotation and intercropping.
- Increase public and private investment in agricultural research and development (R&D).
- Upgrade market infrastructure and integrate efficient value chains for better price realization.
- Reform agricultural pricing policies to support diversification and reduce cereal dependency.
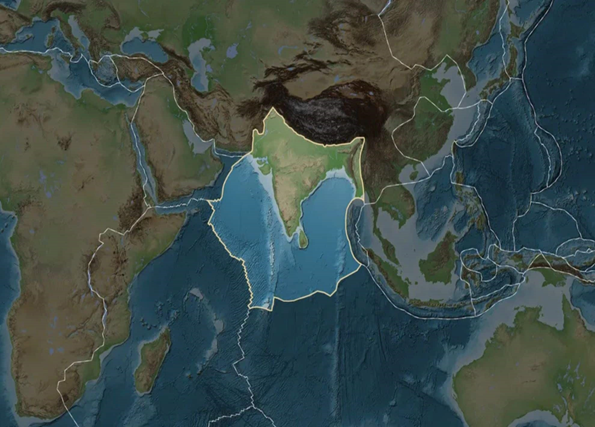
New research suggest that Indian Continental Plate is splitting apart
Recent tectonic studies propose a third mechanism affecting the Indian Plate's interaction with the Eurasian Plate.
Indian Continental Plate is splitting apart
Indian Continental Plate is splitting apart
Geological Context
- The Indian Continental Plate is one of Earth's major tectonic plates.
- It is bordered by four significant plates: the Eurasian, Arabian, African, and Australian Plates.
- Around 60 million years ago, the Indian Plate began its northward drift.
- This ongoing convergence with the Eurasian Plate gave rise to the Himalayas and the Tibetan Plateau.
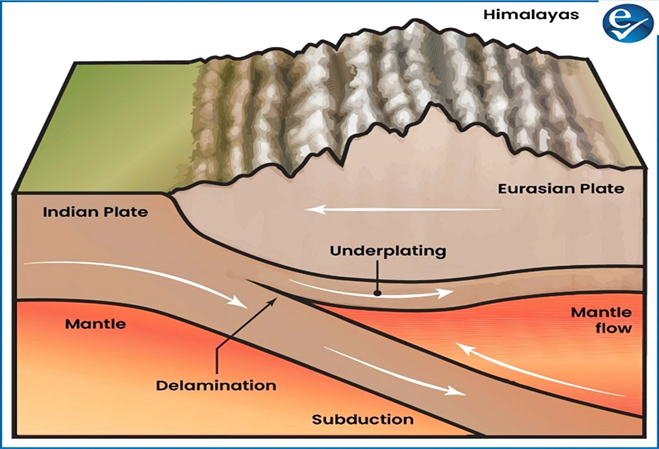
Traditional Theories Explaining the Uplift
- Underplating Theory: The denser Indian lower crust slides beneath the lighter Eurasian crust during convergence.
- Subduction Theory: Denser plates typically sink below lighter ones during collisions, a process called subduction.
- However, continental plates are thick and buoyant, unlike oceanic plates, and resist subduction into the mantle.
Emerging Theory: Delamination and Plate Splitting
- Recent findings suggest a new mechanism — delamination — may be occurring.
- Delamination involves the dense lower layer of the Indian Plate peeling off and sinking into the mantle.
- This process could be causing the Indian Plate to split internally as it continues to collide with the Eurasian Plate.
Q-Shield by QNu Labs: World’s first unified Quantum cryptography platform
QNu Labs has launched Q-Shield, the world’s first platform of its kind for unified cryptography management.

India's QNu Labs Launches QShield: A CyberSecurity platform
Key Features of Q-Shield
- Concept: Q-Shield allows seamless cryptographic operations across diverse environments—cloud, on-premises, or hybrid systems.
- It ensures flexibility and adaptability for modern IT infrastructure with varied deployment models.
Significance and Impact
- Q-Shield offers an end-to-end security framework for protecting data both in transit and at rest.
- It is designed to secure sensitive information from evolving cyber threats.
- The platform helps enterprises safeguard their critical infrastructure from unauthorized access and disruptions.
- Critical Infrastructure refers to essential sectors whose compromise could have severe consequences for national security and economic stability.
- Examples include the Communications Sector, Energy Sector, and other vital public and private systems.
Meningitis: WHO Releases First-Ever Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment, and Care

WHO launches first-ever guidelines on meningitis diagnosis
- The World Health Organization (WHO) has launched its first official guidelines on meningitis management.
- These guidelines align with the broader Defeating Meningitis by 2030 Global Roadmap, initiated in 2020.
Understanding Meningitis
- Meningitis is the inflammation of the protective membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord.
- It remains a significant global public health threat, particularly in low- and middle-income countries.
- The condition can be of infectious or non-infectious origin, depending on the cause.
- Infectious meningitis is caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites.
Transmission Pathways
- The mode of transmission varies depending on the specific pathogen.
- Most bacterial meningitis pathogens, such as meningococcus, pneumococcus, and Haemophilus influenzae, are commonly found in the human nose and throat.
- These bacteria can spread through respiratory droplets or close contact with an infected person.
Prevention and Control
- Vaccination is the most effective preventive measure against common bacterial forms of meningitis.
- Timely use of antibiotics also plays a crucial role in preventing complications and reducing mortality.
- Public health efforts focus on early diagnosis, vaccination coverage, and infection control practices.
BatEchoMon: India’s First Automated Bat Monitoring System
BatEchoMon (short for Bat Echolocation Monitoring) was developed by the Indian Institute for Human Settlements (IIHS), Bengaluru.

Key Features of BatEchoMon
- It is an autonomous system designed to detect and analyze bat echolocation calls in real-time.
- The system functions as a Bat Detector, capable of recording ultrasonic calls of insectivorous bats.
- These ultrasonic signals are converted into audible sounds for human interpretation.
- The system is powered by a Raspberry Pi microprocessor, making it compact and energy-efficient.
- It uses convolutional neural network (CNN) algorithms to accurately detect and identify bat species based on their echolocation patterns.
ESA’s Biomass Mission: Mapping the World’s Forest Carbon
The European Space Agency (ESA) is preparing to launch its dedicated Biomass mission focused on forest carbon monitoring.
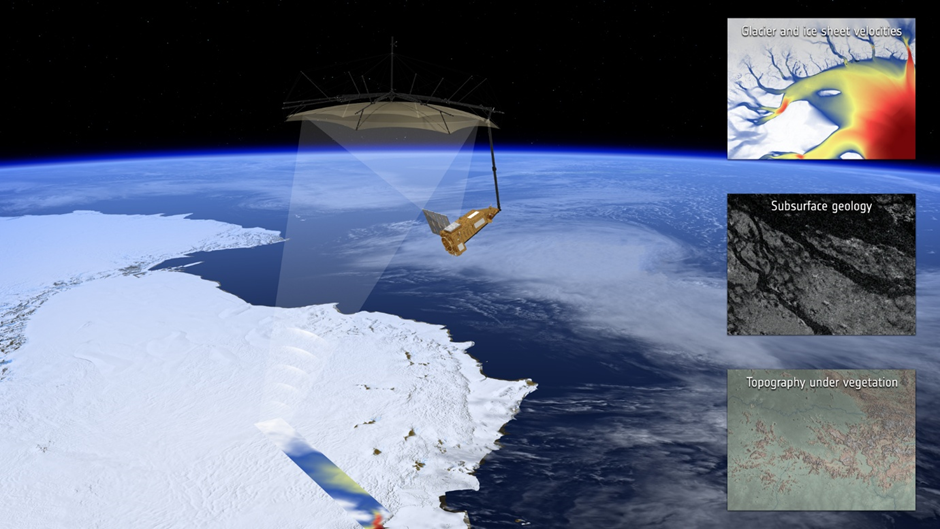

ESA's Biomass mission: Tracking the world's forests
Key Features of the Biomass Mission
- The mission will be based on a single satellite platform operating in Low Earth Orbit (LEO).
- This satellite will carry a Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) instrument as its primary payload.
- Biomass is the first satellite to feature a P-band SAR, a powerful radar capable of deep forest penetration.
- The P-band SAR can measure woody components of forests—trunks, branches, and stems—which store most of the carbon.
Mission Objectives and Significance
- The satellite will map global forests and provide the first-ever comprehensive dataset of forest biomass.
- It will also deliver critical insights into the amount of carbon stored in forests across the world.
- This data is crucial for understanding carbon cycles, supporting climate action, and informing forest conservation policies.
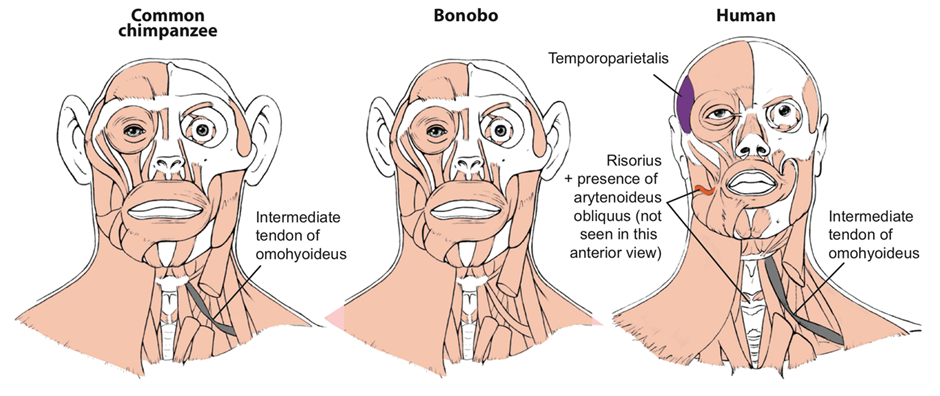
Bonobos: New Study Reveals Human-Like Communication Traits
- Recent studies reveal that Bonobos exhibit vocal communication with compositionality, a feature also found in human language.
- Compositionality is the ability to combine meaningful sound units into larger vocal structures, where the overall meaning depends on both the parts and their arrangement.
Bonobos - revealing just-so stories on human evolution
About Bonobos
- Bonobos and chimpanzees share 98.7% of their DNA with humans, making them our closest living relatives.
- Compared to chimpanzees, bonobos are slightly smaller, leaner, and have darker physical features.
- Bonobo societies are known for being more peaceful and are typically female-led, displaying unique social dynamics.
- They are endemic to the forests of the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) in Central Africa.
- On the IUCN Red List, Bonobos are currently classified as Endangered, facing threats from habitat loss and hunting.
Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE): Strengthening Energy Standards Enforcement
BEE is ramping up enforcement of its Standards & Labelling (S&L) Program by cracking down on fake star ratings in the market.
About BEE
- The Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) is a statutory body established under the Energy Conservation Act, 2001.
- It operates under the administrative control of the Ministry of Power, Government of India.
- The primary objective of BEE is to reduce the energy intensity of India’s economy through regulatory and promotional measures.
Key Regulatory Functions
- BEE sets minimum energy performance standards for a wide range of appliances and equipment under the Standards and Labelling (S&L) scheme.
- It also formulates energy efficiency standards for commercial buildings to promote sustainable construction.
- Additionally, BEE establishes energy consumption norms for Designated Consumers, including large industrial and commercial energy users.
Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary: New Site for Cheetah Relocation
The Cheetah Project Steering Committee has approved the transfer of some cheetahs from Kuno National Park to Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary.
Key Facts About Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary
- Location: Situated in the eastern region of Madhya Pradesh, covering parts of Mandsaur and Nimach districts.
- This area falls within the traditional Nimar region of the state.
- Forest Type: The sanctuary's vegetation is part of the Khathiar-Gir dry deciduous forest biome.
- River System: The Chambal River flows through the sanctuary, enriching its biodiversity.
- Water Body: The protected area surrounds the backwaters of the Gandhi Sagar Dam.
Flora and Fauna
- Dominant Tree Species: Includes Salai, Kardhai, Dhawda, Tendu, and Palash trees.
- Wildlife Species: Home to Wild Dogs (Dholes), Chinkara, Leopards, Otters, and Mugger Crocodiles.
Cultural and Historical Significance
The sanctuary encompasses the renowned Chaturbhuj Nala rock shelters, noted for their ancient rock art.
|
Also Read |
|
| NCERT Books For UPSC | |
| UPSC Monthly Magazine | Best IAS Coaching in Delhi |




