- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Daily Current Affairs Summary 11th APRIL 2025
Daily Current Affairs Summary 11th APRIL 2025
Japan Constructs 3D-Printed Train Station in Just Six Hours
- In April 2025, the West Japan Railway Company has unveiled what it claims to be the world’s first 3D-printed train station.
- Located in the city of Arida, this innovative infrastructure project was completed in a record time of just six hours, highlighting the immense potential of 3D printing technology in construction and public infrastructure.

3D-Printed Train Station in Japan
Understanding 3D Printing
- What is 3D Printing?
- Also known as additive manufacturing, 3D printing is a process of creating three-dimensional physical objects directly from digital designs.
- It involves the layer-by-layer addition of materials to build the final product, as opposed to traditional subtractive manufacturing methods that remove material from a solid block.
- How Does it Work?
- The process begins with a digital 3D model. Using specialized printers, material—such as plastic, metal, or concrete—is deposited layer by layer until the object is fully formed.
- This additive approach allows for exceptional precision and design flexibility.
Key Advantages of 3D Printing
- Rapid Prototyping & Concept Realization: Designers and engineers can quickly transform digital models into tangible products, enabling faster development cycles and innovation.
- Reduced Workforce Dependency: Particularly beneficial in nations like Japan, where the population is aging and the labor force is shrinking, 3D printing minimizes the need for manual labor.
- On-Demand Customization: Custom items can be produced without the need to overhaul manufacturing lines, making personalization easy and efficient.
- Cost Efficiency: By minimizing material waste and reducing reliance on large inventories, 3D printing leads to significant savings in production and operational costs.
- Enhanced Design Flexibility: Complex geometries and intricate lattice structures, which are difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional methods, are easily created through 3D printing.
- Sustainable and Eco-Friendly: The technology supports localized, on-demand production which lowers transportation emissions, material usage, and overall environmental impact.
Diverse Applications of 3D Printing
- Manufacturing Sector: Widely used in the production of consumer goods like eyewear, as well as industrial tools, functional parts, and prototypes.
- Healthcare Innovations: From tailor-made prosthetics to bio-printing of human tissues and organs (like "organ-on-a-chip" technology), 3D printing is revolutionizing medical care.
- Construction Industry: Enables the rapid creation of architectural models and even full-scale structures, as demonstrated by the Arida train station. It also allows for greater precision and reduced construction time.
- Cultural and Historical Preservation: Assists archaeologists and historians in reconstructing fossils, restoring artifacts, and creating replicas for educational purposes.
- Forensic Science: Used to recreate crime scenes and reconstruct evidence, particularly in forensic pathology.
Modernization of Command Area Development and Water Management
- The Union Cabinet has given its nod to the Modernization of Command Area Development and Water Management (M-CADWM) scheme, a significant sub-scheme under the Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY).
- This initiative is slated to be implemented during the financial period of 2025–2026, with a strong focus on modernizing irrigation infrastructure and enhancing water efficiency in agriculture.
About Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY)
Launched in 2015-16, PMKSY aims to:
- Provide assured irrigation by enhancing physical access to water on farms.
- Improve on-farm water use efficiency.
- Expand the area under sustainable and reliable irrigation systems.
Highlights of M-CADWM Sub-Scheme
Key Objective
To upgrade and modernize the irrigation water delivery systems that bring water from existing canals or other sources to a defined command area or cluster of farms.
Infrastructure Enhancement
- Development of a pressurized underground piped irrigation network to deliver water from the source to the farm gate, covering up to 1 hectare.
- This infrastructure will serve as a strong backend support system for promoting micro-irrigation among farmers.
Integration of Advanced Technologies
- The scheme will incorporate Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems.
- It will also leverage the Internet of Things (IoT) to facilitate accurate water accounting and efficient water management practices.
Expected Outcomes and Benefits
- Higher Water Use Efficiency (WUE): Optimized irrigation at the farm level will lead to better crop yields and higher productivity.
- Sustainable Agricultural Practices: The scheme promotes Irrigation Management Transfer (IMT) to Water User Societies (WUS), empowering them to take charge of irrigation assets.
- These societies will receive dedicated handholding support for five years, enabling them to establish links with Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs) and other agribusiness networks.
- Youth Engagement in Agriculture: By integrating modern irrigation techniques, the scheme aims to attract younger generations to farming.
|
Command Area Development and Water Management (CAD&WM) Programme
Key Components of CAD&WM 1. Structural Interventions
2. Non-Structural Interventions
|
NHRC Takes Suo-Motu Cognisance of Prisoners’ Plight
- The National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) has taken suo-motu cognisance of the ongoing hardships faced by prisoners across India.
- Responding to reports highlighting the deteriorating conditions in jails, the NHRC has issued notices to the Chief Secretaries of all States and Union Territories, seeking detailed reports on challenges such as overcrowding, inadequate healthcare, and the lack of basic facilities in prisons.
Legal Framework: Prisons as a State Subject
- Under Schedule VII of the Indian Constitution, the management and regulation of prisons fall under the jurisdiction of State Governments, categorized under List II (State List).
- As such, the responsibility for ensuring humane conditions within prisons rests primarily with individual states.
Key Challenges Faced by Prisoners in India
1. Overcrowding and Basic Facilities
- Indian jails are operating beyond capacity, with an average occupancy rate of 131.4%.
- Undertrial prisoners form the majority of the prison population, accounting for 75.8% as of 2022.
- Access to essential amenities remains poor:
- Fewer than 40% of prisons provide sanitary napkins.
- Only 18% have dedicated facilities for women inmates.
2. Concerns Regarding Women Prisoners
- Many women inmates are subject to violations of dignity and safety, leading to mental trauma and emotional distress.
- There are no explicit provisions in many state jail manuals that recognize a woman prisoner’s right to reproductive health and choice.
3. Prisoners on Death Row
- The justice process for those sentenced to death is marked by excessive delays.
- From 2006 to 2022, the execution rate stood at a mere 0.3%, as per NCRB data.
4. Discrimination Within Prison Walls
- Caste-based roles are often assigned in prison labour.
- Instances of manual scavenging persist.
- Inmate classification is sometimes influenced by social status, contributing to unequal treatment and discrimination.
|
Legal and Policy Provisions for Protecting Prisoners’ Rights Provisions in India
International Guidelines
|
India Approves Purchase of 26 Rafale Marine Fighter Jets for the Navy
- The Indian government has given the green light to a landmark defence deal for the acquisition of 26 Rafale Marine (M) fighter jets from France.
- These advanced aircraft will be inducted into the Indian Navy and are set to operate from INS Vikrant, India's first indigenously built aircraft carrier. This procurement marks a significant step in bolstering India’s maritime security and power projection capabilities.
- Currently, the Indian Air Force (IAF) already operates a fleet of 36 Rafale jets, which have significantly enhanced India's air combat capabilities since their induction.
|
About Rafale Fighter Aircraft
|
Global Context: The Race for Sixth-Generation Fighter Jets
While India enhances its fourth-plus generation capabilities, the global race to dominate sixth-generation fighter technology is heating up, especially between the United States and China.
United States:
- The U.S. has announced the development of a next-generation stealth fighter, currently known as the F-47.
- This aircraft is part of the U.S. Air Force's push toward future-ready air dominance platforms.
China:
- In a notable advancement, China successfully conducted flight tests for two sixth-generation prototypes—the J-36 and J-50—in December 2024.
- These aircraft are expected to challenge U.S. air superiority in the Asia-Pacific region.
Key Features of Sixth-Generation Fighter Jets
These futuristic aircraft are expected to go far beyond the capabilities of their predecessors, with defining features including:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration: For enhanced decision-making and autonomous operations.
- Hypersonic Speed: Enabling unmatched speed and maneuverability.
- Unmanned or Manned-Unmanned Teaming (MUM-T): Allowing them to operate with or without a pilot, and coordinate with unmanned drones in combat scenarios.
Comparative Overview: Fighter Jet Generations
|
Generation |
Key Features |
Examples |
|
Fourth Generation (1970s–80s) |
Traditional fighters with basic air-to-air and air-to-ground roles |
MiG-29, F-16, Mirage-2000 |
|
4.5 Generation |
Added stealth features, radar-absorbent material, better avionics, swing-role capabilities |
Eurofighter Typhoon, Rafale |
|
Fifth Generation |
Advanced stealth, supercruise, sensor fusion, internal weapons |
F-22 Raptor, Chengdu J-20 |
|
Sixth Generation (In Development) |
AI integration, hypersonic speed, unmanned ops, advanced networking |
F-47 (US), J-36 & J-50 (China) |
Jevons Paradox: Understanding the Counterintuitive Impact of Efficiency
Microsoft CEO Satya Nadella recently referred to the concept of Jevons Paradox while discussing the accelerating global adoption of Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies.
What is Jevons Paradox?
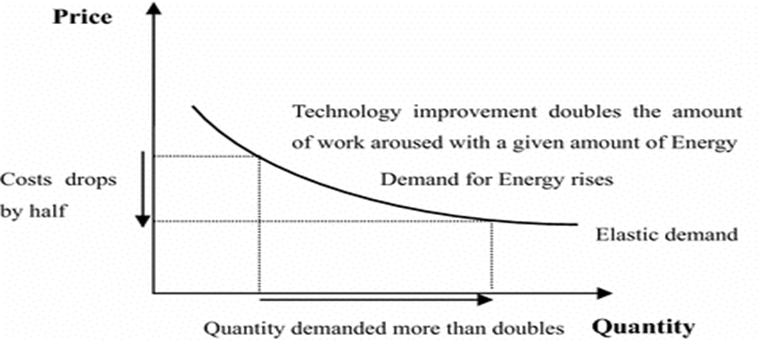
The Jevons Paradox refers to a situation where increasing the efficiency of using a particular resource doesn't reduce its overall consumption—in fact, it may do the opposite.
- Definition: As technology makes the use of a resource more cost-effective or efficient, it often leads to an increase in demand for that resource, resulting in higher overall consumption.
Jevons Paradox
Historical Origin
This idea was first introduced by British economist William Stanley Jevons in 1865.
- In his analysis of coal consumption in the UK, Jevons argued that the invention of more efficient steam engines—rather than reducing coal usage—actually led to greater reliance on coal, as efficiency made it more economically attractive to use steam power in more industries.

William Stanley Jevons (1835-1882)
Relevance in the Age of AI
The paradox is particularly relevant today as AI systems become:
- More powerful and capable of handling complex tasks,
- Cheaper to deploy, and
- More accessible across sectors and geographies.
While these advances suggest we might use less computing power or energy per task, the total demand for AI is expected to increase significantly due to broader usage—spanning everything from healthcare and education to entertainment and defense.
Why It Matters
Understanding Jevons Paradox is crucial in the modern tech landscape because it:
- Challenges the assumption that efficiency alone leads to sustainability,
- Highlights the need for policy and infrastructure planning, especially concerning energy use, and
- Encourages a more holistic view of the impact of emerging technologies like AI on resource consumption.
River Mandovi: Goa’s Lifeline Gets a Digital Push
In a significant step towards modernizing inland waterway development, the first No Objection Certificate (NOC) has been granted through the newly launched Digital Portal for National Waterways. This approval paves the way for the construction of a jetty at Malim, located along the banks of the River Mandovi.
Mandovi River
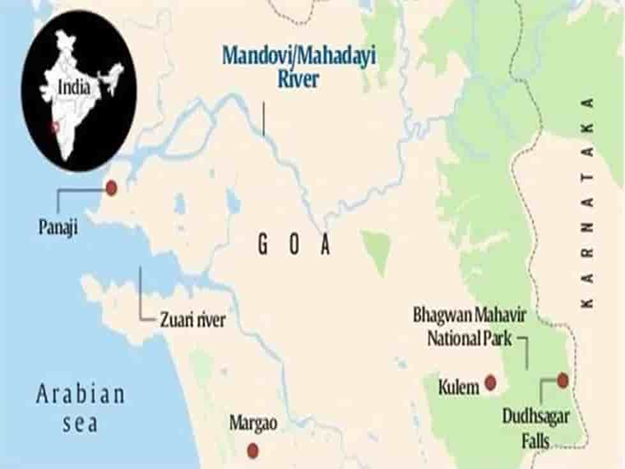
About River Mandovi
Also referred to as the Mahadayi or Mhadei, the Mandovi River holds immense ecological and economic importance, earning it the title of “lifeline of Goa.”
Key Features:
- Origin: The river originates from the Bhimgad region in the Western Ghats, specifically from a group of about 30 springs in Belagavi district, Karnataka.
- Confluence and Outflow: The Mandovi merges with the Zuari River, and together they drain into the Arabian Sea, forming the strategic Mormugao harbour.
- Tributaries: One of the most prominent tributaries of the Mandovi is the Mapusa River, which plays a vital role in supporting the river’s flow and surrounding ecosystems.
- Notable Waterfalls:
- Dudhsagar Falls: One of India’s tallest and most spectacular waterfalls, located along the river’s course.
- Varapoha Falls: Another scenic spot that adds to the river’s natural charm.
Vizhinjam Port Welcomes One of the World's Largest Container Ships
Recently, one of the world’s largest container ships, MSC Türkiye, docked at Vizhinjam International Seaport, marking a milestone in the journey of India’s first deepwater transshipment port.
About Vizhinjam International Seaport
The Vizhinjam Port is a strategically important maritime project located near Thiruvananthapuram, the capital city of Kerala. It is designed to handle large-scale transshipment and multi-purpose cargo operations.
Key Highlights:
- Governing Body: The project is managed by Vizhinjam International Seaport Limited (VISL), a fully state-owned company under the Government of Kerala.
- Type of Port: Vizhinjam is a natural deepwater port, enabling it to handle ultra-large container vessels without the need for extensive dredging.
- Primary Objective: The port is primarily intended for container transshipment, along with handling multi-purpose and break bulk cargo operations.
Development Model
The port is being developed under a Landlord Port Model, incorporating a Public-Private Partnership (PPP) component. The arrangement follows the Design, Build, Finance, Operate, and Transfer (DBFOT) model.
- Landlord Model Explained: In this approach, the port authority retains ownership of the infrastructure and plays the role of regulator and landlord, while private operators manage port operations, investments, and services.
Strategic Importance
Vizhinjam's location along the international shipping route and its natural deep draft make it an ideal hub for transshipment. As it becomes operational, it is poised to:
- Reduce India's dependence on foreign ports for transshipment,
- Strengthen regional trade connectivity,
- Position India as a significant maritime hub in the Indian Ocean region.
Aravali Range: NGT Steps In to Curb Illegal Mining
The National Green Tribunal (NGT) has recently directed the State of Haryana to take stringent action against illegal mining activities in the Aravali Range, emphasizing the need to protect this ecologically vital and geologically ancient mountain system.
Map of prominent mountain ranges in India, showing Aravalli in north-west India
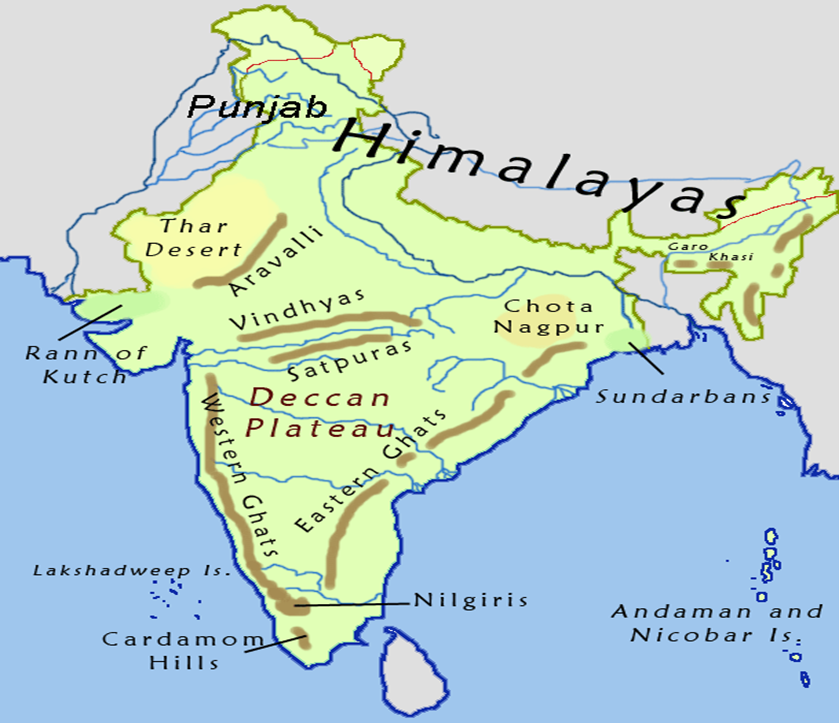
About the Aravali Range
The Aravalis are among the oldest mountain ranges in the world, formed through folding millions of years ago. This range has played a crucial role in shaping the geography, climate, and ecology of northwestern India.
Key Facts:
- Mountain Type: Folded mountains—among the oldest on Earth.
- Length & Spread: Extends over approximately 670 kilometers, running southwest from Delhi, cutting across southern Haryana and Rajasthan, before finally reaching Gujarat.
- Highest Peak: Guru Shikhar, located in Rajasthan, rises to 1,722 meters above sea level.
Rivers Originating from the Aravalis
- Several important rivers have their origin in or flow through the Aravali range, including: Banas River, Sahibi River and Luni River
- These rivers are significant for the water systems and agriculture in the arid and semi-arid regions they pass through.
Rich in Mineral Resources
The Aravalis are also known for their mineral wealth, which includes: Copper, Zinc, Lead and Marble.
- These minerals have historically contributed to local economies, but unchecked mining has raised serious environmental concerns.
Why Protection is Essential
The Aravali Range serves as a natural barrier against desertification from the Thar Desert and plays a vital role in recharging groundwater, regulating temperature, and preserving biodiversity. The NGT’s intervention highlights the urgent need to preserve these mountains from environmental degradation caused by illegal mining and unregulated development.
Malabar Grey Hornbill Conservation Efforts Recognized
A team of researchers from Kerala has been honored with the Future Conservationist Award by the Conservation Leadership Programme (CLP) for their work on the conservation of the Malabar Grey Hornbill.
- The CLP is a collaboration between Fauna & Flora International, BirdLife International, and the Wildlife Conservation Society.
- The award is designed to support emerging conservationists with less than five years of professional experience. It provides funding and mentorship to help them lead effective conservation projects.
About the Malabar Grey Hornbill
- Endemism: This species is endemic to the Western Ghats in India.
- Habitat Range: Found at elevations starting from around 50 meters above sea level, including areas close to the coast.
- Conservation Status: Classified as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List, indicating a high risk of extinction in the wild.
GEAC Approves Import of GM Alfalfa Hay from the US
- The Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC) has granted approval for the import of genetically modified (GM) alfalfa hay from the United States. However, the final clearance is still pending from India’s Ministry of Agriculture.
- This development has gained attention as the US has raised concerns related to the import during ongoing trade discussions with India.
About Alfalfa
- Classification: Alfalfa belongs to the legume family, though it is also widely recognized as a herb.
- Origin: It is believed to have originated in South and Central Asia, but has been cultivated globally for centuries.
- Uses:
- Primarily used as animal feed due to its high nutritional value.
- It also has a long-standing history of use in traditional medicine for humans.
Soil Moisture Found Crucial in Predicting Severe Storms: Study on Mesoscale Convective Systems
A recent study on Mesoscale Convective Systems (MCS) has revealed that soil moisture levels may play a significant role in forecasting intense storm events. This finding could improve early warning systems and disaster preparedness.
What is a Mesoscale Convective System (MCS)?
- An MCS is a large, organized cluster of thunderstorms that behaves as a single weather system.
- These systems can cover areas as large as an entire state and often persist for over 12 hours.
- They are typically associated with heavy rainfall, which can lead to severe impacts on human life, livestock, and infrastructure.
Regions Prone to MCS Events
MCSs are most frequently observed in the following regions: West and Central Africa, Northern India, Argentina, China and The Great Plains of the United States.
Tripura to Host Jatra Utsav
The state of Tripura is set to organize a Jatra Utsav, celebrating one of the most iconic traditional theatre forms of eastern India.
About Jatra
- Jatra is a widely popular folk theatre tradition originating from Bengal and Odisha.
- Its roots go back to the 16th century, closely linked to the spread of Vaishnavism and the Bhakti Movement, led by Sri Chaitanya Mahaprabhu.
- This art form is known for being multifaceted, combining music, dance, dramatic performance, and narration into a single theatrical experience.
- Jatra showcases a broad range of themes—from mythological tales and secular stories to elements of humor, heroism, and melodrama.
|
Also Read |
|
| Public Administration Optional | |
| UPSC Monthly Magazine | Question Answer Practice For UPSC |




