- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PLACES IN NEWS 30h DECEMBER 2024
PLACES IN NEWS 30h DECEMBER 2024
30-12-2024

Daying Ering Memorial Wildlife Sanctuary (DEMWS)
Why in news?
- Three poachers were recently arrested for killing a sambar deer inside the Daying Ering Memorial Wildlife Sanctuary (DEMWS) in Arunachal Pradesh's East Siang district.
About Daying Ering Memorial Wildlife Sanctuary (DEMWS):
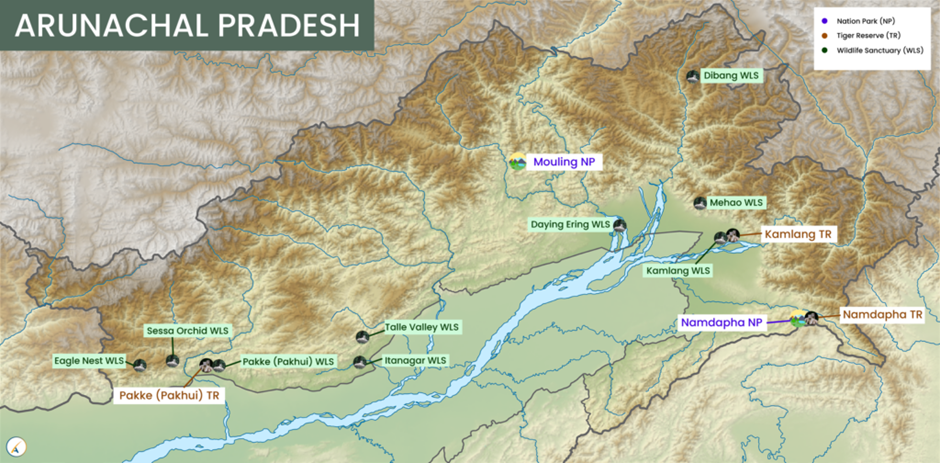
- Geography:
- The Daying Ering Memorial Wildlife Sanctuary (DEMWS), located in Arunachal Pradesh’s East Siang district, spans an area characterised by flat grasslands, riverine forests, and patches of wetlands.
- It is nourished by the Siang River, a tributary of the Brahmaputra, which divides the sanctuary into multiple small islands, making it unique and ecologically significant.
- Flora and Fauna
- The sanctuary hosts diverse flora, including tall grasses, bamboo, and tropical deciduous trees. These ecosystems support the region’s biodiversity while serving as critical habitats for its wildlife.
- In terms of fauna, DEMWS is home to species like the hog deer, sambar deer, wild boar, and various primates. It also harbours an impressive array of bird species, including migratory waterfowl and raptors.
About Sambar deer:
- Sambar deer are widely distributed across the Indian subcontinent, Southeast Asia, and parts of China. In India, they inhabit forests, grasslands, and marshy regions.
- Listed under Schedule III of the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972, they receive significant legal protection. The IUCN Red List categorises the sambar as Vulnerable.
- Additionally, they are included in CITES Appendix I, restricting international trade.
- Conservation measures focus on habitat preservation, anti-poaching initiatives, and awareness campaigns to protect this vital species. Their survival is essential for maintaining ecosystem balance and supporting large carnivore populations dependent on them as prey.
Kamarajar Port
Why in news?
- Minister for Ports, Shipping and Waterways Sarbananda Sonowal said the capacity increased by 87 per cent in the last nine years, with Tamil Nadu’s Kamarajar Port registering a whopping swell of 154 per cent
About Kamarajar Port:
- Kamarajar Port, previously called Ennore Port, is situated about 24 km north of Chennai in Tamil Nadu.
- It is India’s 12th major port and holds the distinction of being the country’s first public company port.
- In March 1999, the port was officially designated as a major port under the Indian Ports Act, 1908.
- Chennai Port Trust owns the port, which complements the operations of the Port of Chennai.
- It is the only corporatised major port in India and operates as a registered company.
- The port follows the landlord port model, blending public ownership with private sector participation.
- In this model, the port authority assumes regulatory and landlord roles, while private companies handle cargo operations.
- Kamarajar Port includes terminals designed for handling coal, LNG, containers, and multipurpose cargo, with coal being the predominant commodity managed.
- The port has experienced remarkable growth in cargo capacity, becoming a vital player in India's maritime trade.
Major ports in India:
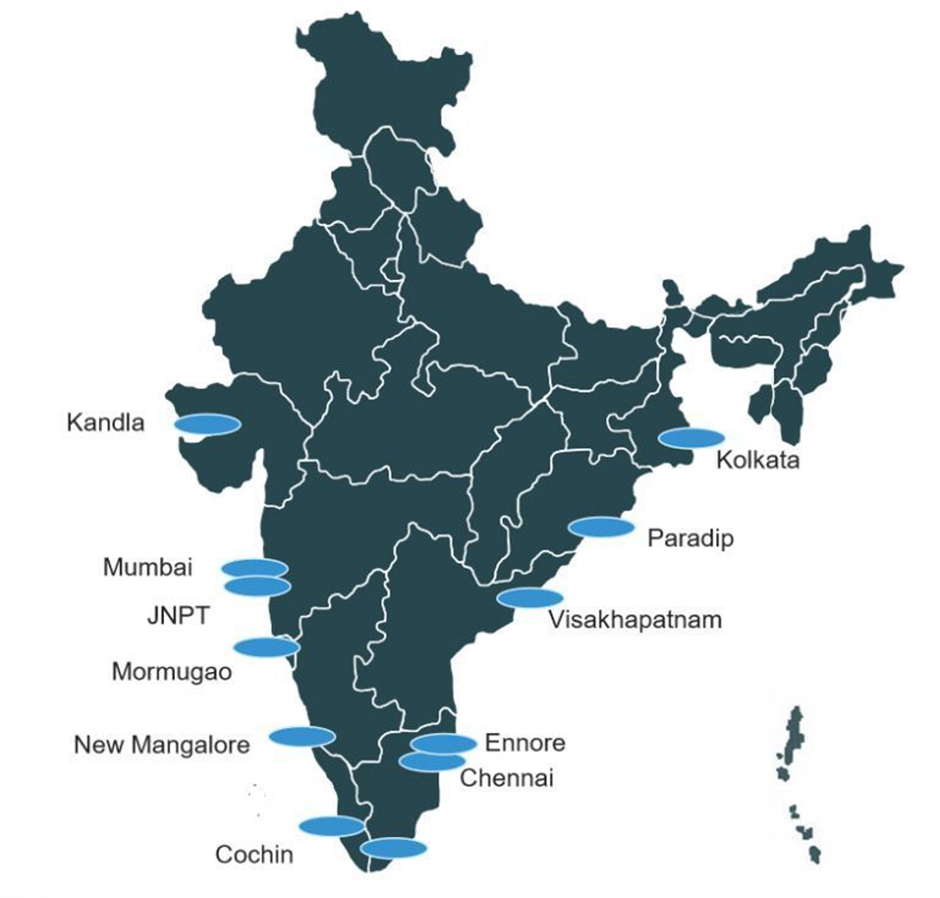
|
Port |
Location |
Key features |
|
Kolkata (Syama Prasad Mookerjee) |
West Bengal |
|
|
Paradip |
Odisha |
|
|
Visakhapatnam |
Andhra Pradesh |
|
|
Chennai |
Tamil Nadu |
|
|
Tuticorin (V.O. Chidambaranar) |
Tamil Nadu |
|
|
Cochin |
Kerala |
|
|
Marmagao |
Goa |
|
|
Mumbai |
Maharashtra |
|
|
Jawaharlal Nehru (Nhava Sheva) |
Maharashtra |
|
|
Kandla (Deendayal) |
Gujarat |
|
|
Ennore (Kamarajar) |
Tamil Nadu |
|
|
Mangalore |
Karnataka |
|
Teesta River
Why in news?
- A massive landslide struck East Sikkim’s Dipu Dara near Singtam on Tuesday morning, causing extensive damage to the 510-MW Teesta Stage V hydroelectric project of NHPC, officials reported.
About Teesta River:
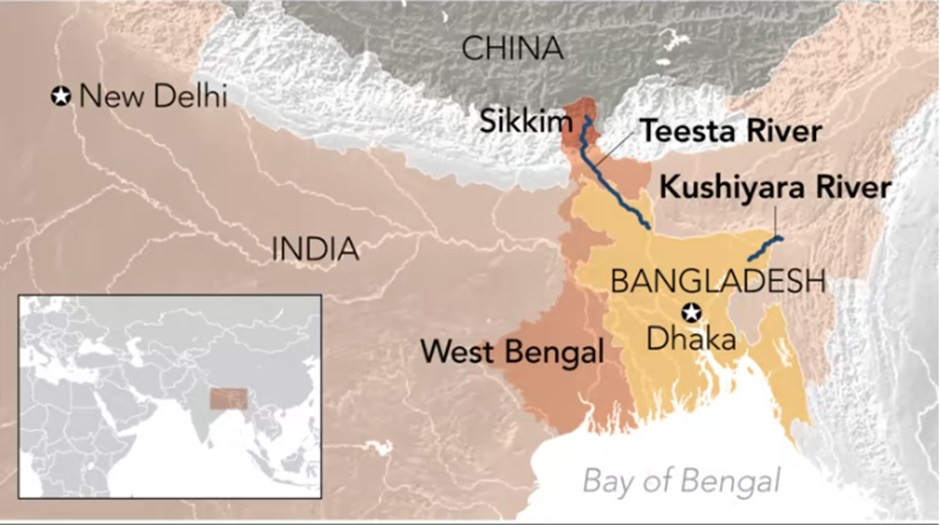
- The Teesta River originates as Chhombo Chhu from the glacial lake Khangchung Chho at an elevation of 5,280 meters in the northeastern corner of Sikkim. Some sources also identify the Teesta Khangse Glacier and Chho Lhamo Lake as its origin points.
- Flowing southward, the river traverses through Sikkim, carving deep valleys and gorges, and enters West Bengal near the town of Rangpo. It then flows through the plains, enriching the fertile Terai region, before crossing into Bangladesh.
- In Bangladesh, the Teesta merges with the Brahmaputra River, locally known as the Jamuna, near Fulchhari. This confluence significantly contributes to the river systems of the region, supporting agriculture and livelihoods.
- Tributaries of the River include Rangit, Rangpo, Lachung, Talung, and Rangeet, contributing to its flow across Sikkim and West Bengal.
- Geographically, the Teesta creates a dynamic landscape marked by steep gradients in the upper reaches and alluvial plains downstream. Its tributaries and seasonal flows make it vital for irrigation, hydropower, and drinking water.
Challenges associated:
- The river faces challenges such as glacial retreat due to climate change, which threatens its flow and seasonal patterns. Intense monsoon rains often lead to flash floods and landslides, causing loss of life and property.
- Human interventions, including hydropower projects, dams, and excessive sand mining, disrupt the river’s ecosystem and aquatic biodiversity. In the plains, agricultural runoff and pollution degrade water quality, impacting flora and fauna.
- Conflicts over water sharing between India and Bangladesh add a geopolitical dimension to the challenges, complicating conservation efforts.
You Can Read Also: PLACES IN NEWS 28th DECEMBER 2024
Rooppur nuclear power plant
Why in news?
- Bangladesh's Anti-Corruption Commission is investigating alleged $5 billion financial irregularities in the $12.65 billion Rooppur nuclear power plant project, built with Russian assistance.
About Rooppur nuclear power plant:
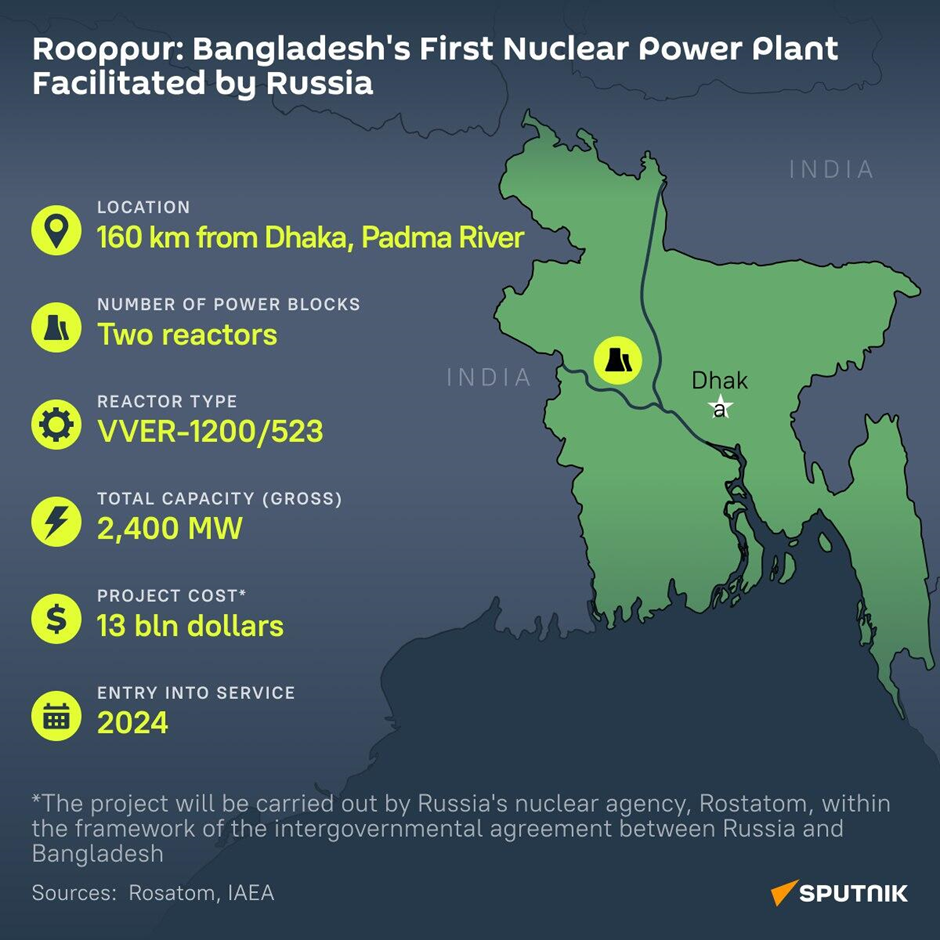
- The Rooppur Nuclear Power Plant, Bangladesh's first nuclear power project, is located in Pabna district on the eastern bank of the Padma River, approximately 160 km northwest of Dhaka.
- Its strategic location was chosen to meet the growing energy demands of Bangladesh, aiming to provide a stable and sustainable electricity supply to the region.
- The plant is being constructed with Russian assistance under an agreement with Rosatom, a state-owned Russian nuclear energy corporation. It comprises two VVER-1200 (Vodo-Vodyanoi Energetichesky Reaktor, or Water-Water Power Reactor) reactors with a combined generation capacity of 2,400 MW.
- Currently, the project is facing significant issues. An investigation by Bangladesh's Anti-Corruption Commission has revealed alleged financial irregularities amounting to $5 billion in the $12.65 billion project.
- Concerns have been raised about mismanagement and lack of transparency in the allocation and utilisation of funds. These allegations cast doubt on the governance and oversight mechanisms of the project, which has been under development for more than a decade.
- Additionally, geopolitical tensions, including international sanctions on Russia, pose potential challenges to the timely delivery of materials and technology.
- Environmental and safety concerns have also been raised, given the plant's location near the Padma River, which is crucial for water resources and ecosystems in the region. Addressing these issues is critical for the project's success and public trust.
You Can Read Also: PLACES IN NEWS 27th DECEMBER 2024
Denmark Strait Cataract
Why in news?
- The Denmark Strait Cataract, the world’s largest underwater waterfall, is a marvel hidden beneath the ocean’s surface. Situated between Greenland and Iceland, it plunges an astonishing 3,505 meters, far exceeding any terrestrial waterfall.
About Denmark Strait Cataract:
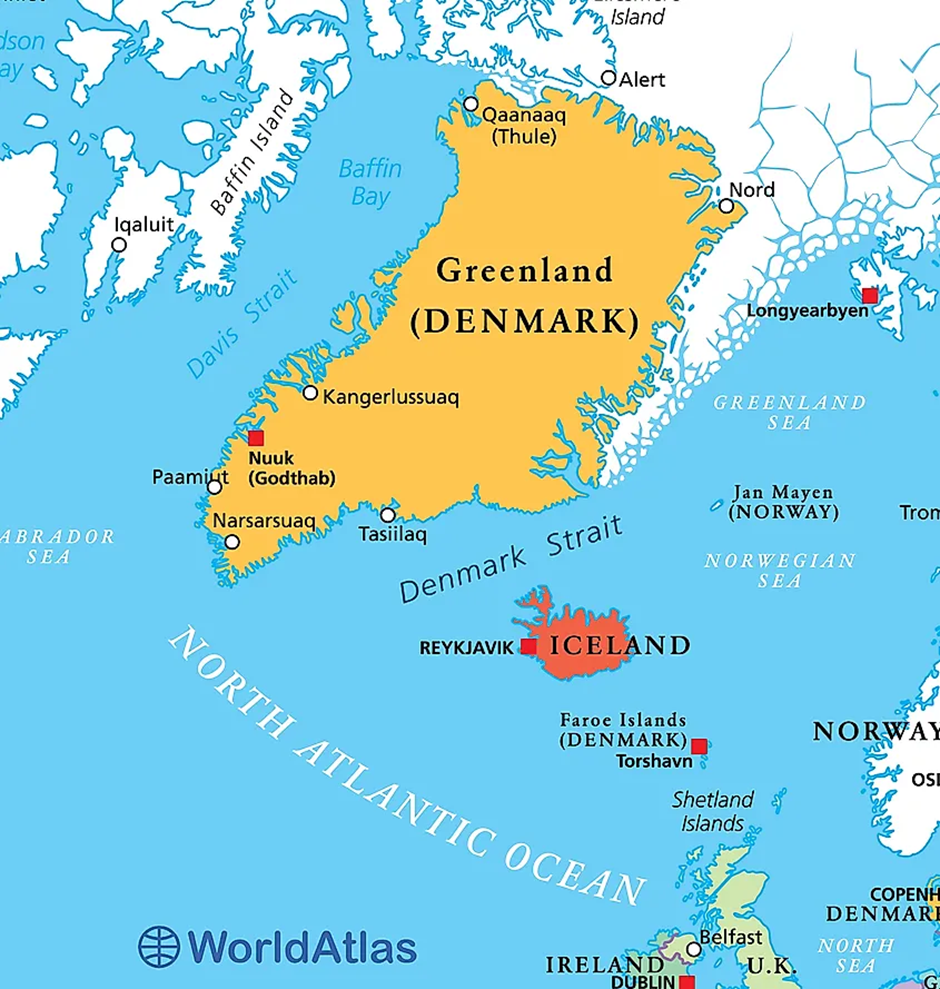
- Geographical Features
- The Denmark Strait Cataract is located between Greenland and Iceland in the North Atlantic Ocean.
- It holds the distinction of being the world's largest underwater waterfall, with water plunging over 3,505 meters (11,500 feet), significantly deeper than Angel Falls, the tallest terrestrial waterfall.
- This phenomenon occurs beneath the ocean surface, where cold, dense water from the Arctic Ocean meets warmer, lighter water from the Atlantic Ocean.
- The unique geography of the Denmark Strait, with its narrow channel and varying depths, facilitates this massive cascade.
- Influence on Global Ocean Circulation
- The Denmark Strait Cataract drives a crucial component of the thermohaline circulation, also known as the global conveyor belt.
- Cold Arctic water sinks as it flows southward, displacing the warmer Atlantic water that moves northward. This continuous exchange is a key part of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC).
- The AMOC regulates the distribution of heat across the planet, ensuring the transport of warm water to higher latitudes and the return flow of cooler water to the tropics.
- By influencing this circulation, the cataract maintains temperature gradients essential for weather patterns and marine ecosystems.
- Role in Climate Change
- The Denmark Strait Cataract plays a vital role in mitigating climate change by supporting the natural heat transfer process.
- A stable AMOC, driven in part by the cataract, prevents extreme climate variations. Disruptions to this circulation, caused by excessive ice melt or warming waters, could weaken the cataract’s flow.
- If the AMOC slows down, it could lead to drastic consequences, such as harsher winters in Europe, rising sea levels along the eastern U.S. coast, and disrupted monsoon patterns.
- The cataract also influences carbon sequestration by enabling the deep ocean to store atmospheric carbon, contributing to long-term climate regulation.
- Ecological Significance
- The constant mixing of waters fosters rich biodiversity, supporting various marine species by transporting nutrients across ocean layers.
- It sustains complex food webs and underpins the health of marine ecosystems in the North Atlantic region.
|
UPSC CSE PYQ Q1. With reference to river Teesta, consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (2017)
Answer: Option B Q2. Consider the following pairs :
How many of the pairs are correctly matched? (2023)
Answer: Option B |
|
Also Read |
|