- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PLACES IN NEWS 27th DECEMBER 2024
PLACES IN NEWS 27th DECEMBER 2024
27-12-2024

Rajaji National Park
Why in news?
- The Supreme Court of India recently remarked that a plea challenging construction activities near Rajaji National Park in Uttarakhand appeared "prima facie sponsored."
- The case concerns allegations of illegal construction and environmental degradation in the ecologically sensitive zone surrounding the park.
About Rajaji National Park:
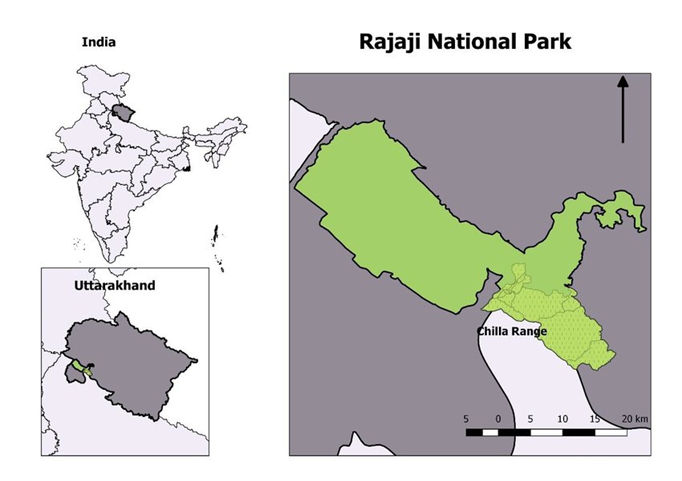
- Geography
- Rajaji National Park, located in the northern state of Uttarakhand, spans the Shivalik Hills in the Himalayan foothills. It stretches across three districts: Dehradun, Haridwar, and Pauri Garhwal, covering an area of 820 square kilometres.
- The park forms an essential corridor between Kedarnath Wildlife Sanctuary and Jim Corbett National Park, making it a significant link for wildlife movement in the Terai Arc Landscape.
- The park derives its name from C. Rajagopalachari, affectionately called Rajaji, who was a prominent freedom fighter and the first Indian Governor-General of India. His contributions to India’s independence and governance inspired the naming of this rich natural reserve.
- Conservation status
- The park was established in 1983 by merging Chilla, Motichur, and Rajaji sanctuaries.
- It attained the status of a tiger reserve in 2015 under the Project Tiger initiative, highlighting its critical role in conserving biodiversity.
- Flora and Fauna
- Rajaji National Park boasts diverse flora and fauna due to its varied topography and climate. The vegetation includes sal forests, riverine forests, broad-leaved deciduous forests, grasslands, and scrublands, supporting a wide range of species.
- The park is home to over 315 bird species, including hornbills, kingfishers, and woodpeckers, making it a birdwatcher's haven.
- The fauna includes iconic species such as tigers, leopards, Asian elephants, sloth bears, wild boars, and striped hyenas. Rajaji’s elephant population is particularly significant, as it serves as a key habitat for this endangered species.
- Reptiles like king cobras and amphibians also inhabit the park. Freshwater species thrive in its rivers, notably the Ganga and its tributaries, which flow through the park, enriching its ecosystem.
- The park’s conservation efforts focus on mitigating human-wildlife conflict, ensuring the safety of both local communities and wildlife. Challenges such as illegal encroachments and developmental activities threaten its fragile ecosystem, necessitating stringent protective measures.
You Can Read Also: PLACES IN NEWS 26th DECEMBER 2024
Cameroon
Why in news?
- In Cameroon, an ancient royal ritual known as "The Trial of a King" plays a pivotal role in promoting peace and unity.
- This traditional practice involves symbolic acts of accountability where tribal leaders and rulers are "judged" for their governance by elders and the community.
About Cameroon:
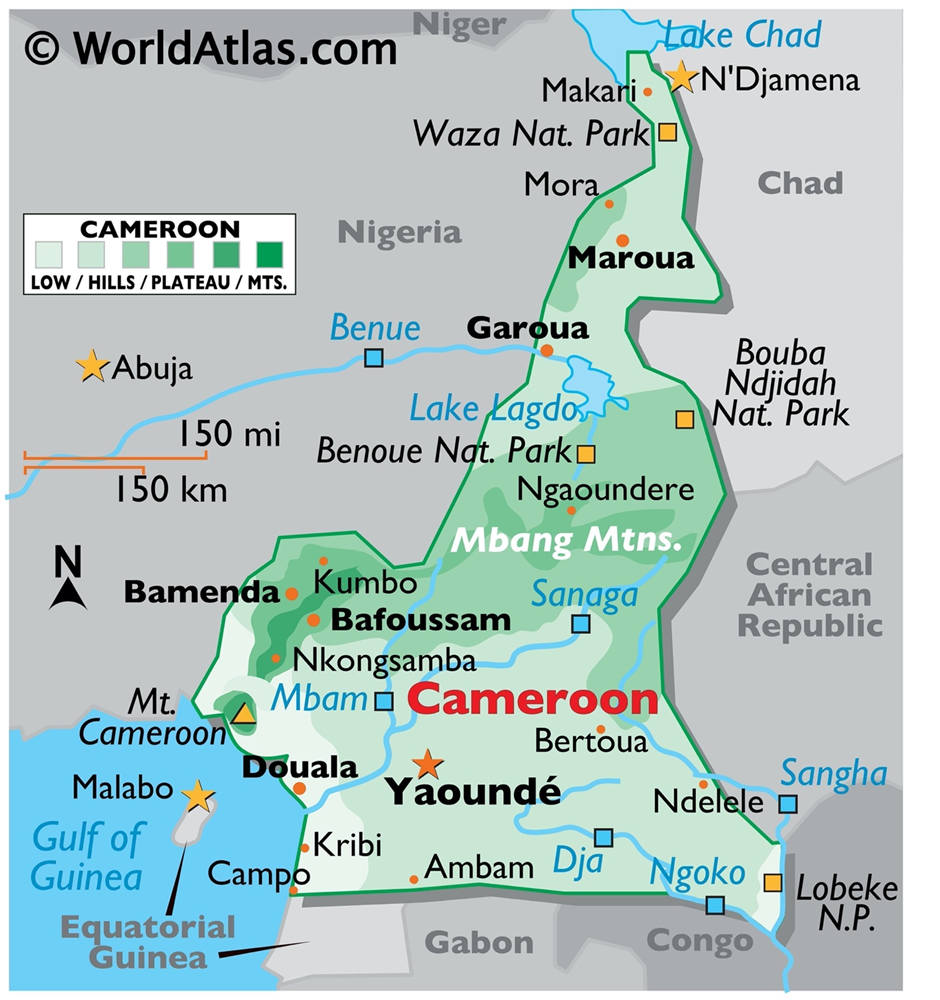
- Geography and Location
- Cameroon, located in Central Africa, spans from the Gulf of Guinea on the Atlantic coast to the Sahel region, covering an area of 475,442 square kilometres.
- Its geography is diverse, ranging from coastal plains and tropical rainforests in the south to savannahs in the north.
- The Adamawa Plateau, which divides the country, serves as a climatic and cultural transition zone.
- The Mount Cameroon volcano, the highest point at 4,095 meters, dominates the southwestern region and is among the most active volcanoes in Africa. Several rivers, including the Sanaga and Benue, provide critical water resources for agriculture and energy.
- Natural resources
- Cameroon is endowed with abundant natural resources, making it one of Africa’s resource-rich nations. Its key resources include petroleum, natural gas, timber, bauxite, and iron ore.
- The fertile soil supports the production of cocoa, coffee, bananas, and palm oil, while rivers offer immense potential for hydropower.
- Despite this wealth, challenges such as inefficient resource management and corruption limit the country’s full economic potential.
- Political status
- Cameroon is a unitary presidential republic, one of the longest-serving heads of state in the world. The country's governance has faced criticism for its authoritarian tendencies, including restrictions on opposition parties and media freedom.
- Cameroon has maintained stability compared to some neighbouring nations but grapples with internal conflicts that threaten its peace.
- Regional issues
- Regional issues significantly impact Cameroon’s development and social harmony. The Anglophone crisis, rooted in grievances of marginalisation by the Francophone majority, has escalated into a violent separatist conflict in the Northwest and Southwest regions.
- Armed separatist groups demand independence for a region they call Ambazonia, leading to thousands of deaths and displacement. Additionally, Cameroon faces threats from the Boko Haram insurgency in the northern regions, affecting the Far North, which borders Nigeria and Chad. Refugee influxes and cross-border tensions further strain resources.
- Cameroon’s geographical and cultural diversity make it a microcosm of Africa, often referred to as "Africa in miniature." However, its rich resources and strategic location are overshadowed by political and social challenges.
- To realise its potential, Cameroon must address regional conflicts, promote equitable governance, and utilise its resources sustainably, ensuring peace and prosperity for its people.
You Can Read Also: PLACES IN NEWS 25th DECEMBER 2024
Coral Triangle
Why in news?
- According to a new report, fossil fuel projects are putting the Pacific Coral Triangle’s unique marine ecosystem at risk.
About Coral Triangle:
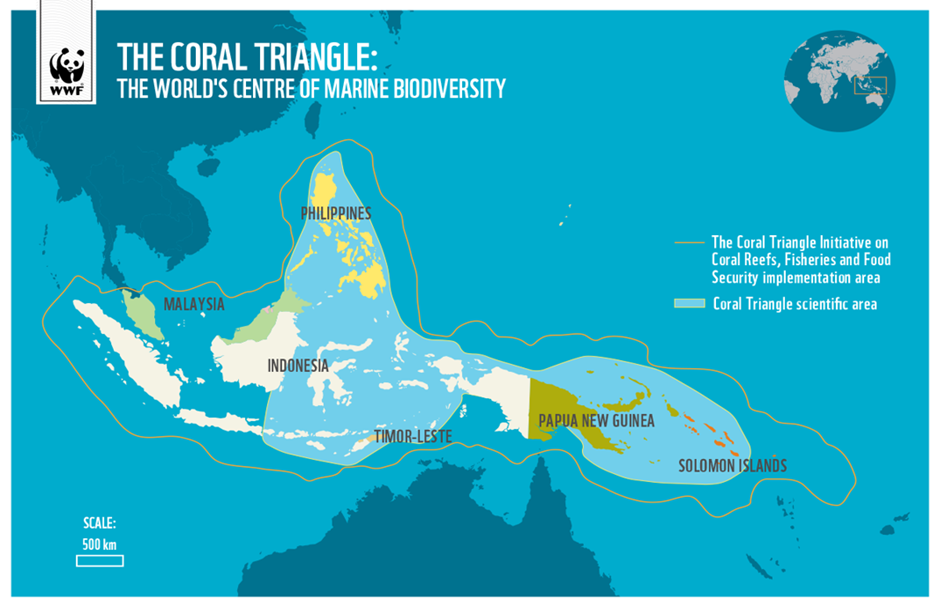
- Geography and Location:
- The Coral Triangle, often referred to as the Amazon of the seas, is a vast marine area located in the western Pacific Ocean, covering parts of Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Papua New Guinea, Timor-Leste, and the Solomon Islands.
- It spans over 6 million square kilometres and is renowned for its extraordinary biodiversity. The region hosts over 75% of the world’s coral species, more than 3,000 species of fish, and countless other marine organisms, making it the most biologically diverse marine area on Earth.
- Its vibrant coral reefs are critical not only for marine life but also for the livelihoods of millions of coastal communities, who depend on fishing and tourism.
- Environmental threat:
- Despite its ecological importance, the Coral Triangle faces significant environmental threats. Climate change poses a severe risk, with rising sea temperatures causing widespread coral bleaching and ocean acidification weakening coral skeletons.
- Overfishing and illegal fishing practices, such as dynamite fishing and cyanide fishing, deplete marine stocks and destroy habitats.
- Coastal development, including infrastructure projects and land reclamation, leads to habitat loss and water pollution, further stressing the delicate marine ecosystems.
- Fossil fuel extraction and associated activities add another layer of threat. Pollution from oil spills, runoff, and industrial waste directly harms marine life, while greenhouse gas emissions accelerate climate change impacts on the reefs.
- Plastic pollution, prevalent in this region, chokes marine species and damages coral structures.
- Protecting the Coral Triangle requires global and regional cooperation, sustainable fishing practices, and climate change mitigation. The health of this marine treasure is not only vital for biodiversity but also for the food security and economic well-being of millions who rely on its resources. Without decisive action, the Coral Triangle's unparalleled ecosystems risk irreversible damage.
East China Sea
Why in news?
- Japanese Foreign Minister recently urged China to address escalating security concerns in the East China Sea.
- Japan highlighted issues such as Beijing’s increasing military presence, territorial disputes, and aggressive actions near the Senkaku Islands in the East China Sea, which Japan administers but China claims.
About East China Sea:
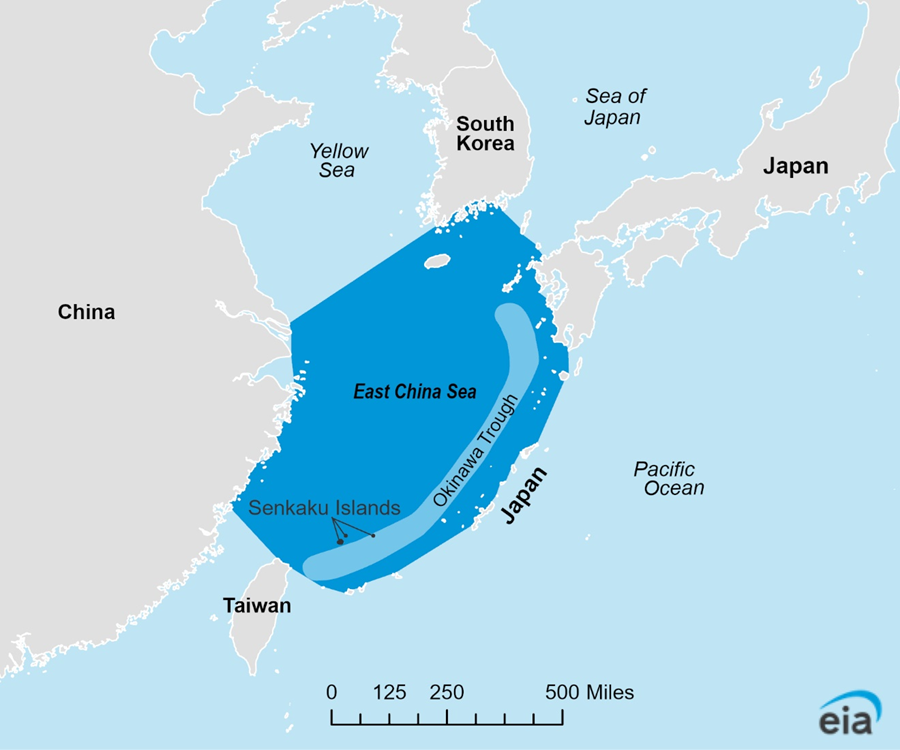
- Geography and Location:
- The East China Sea, a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean, lies between China, Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan.
- It spans approximately 1.25 million square kilometres, connecting to the Yellow Sea in the north and the South China Sea in the south.
- The sea is bordered by the Ryukyu Islands of Japan to the east and the Chinese mainland to the west. Its waters are crucial for international shipping, fisheries, and regional economies.
- Natural resources:
- Rich in natural resources, the East China Sea holds significant deposits of oil and natural gas beneath its seabed, particularly in areas like the Chunxiao gas field.
- These energy reserves have made the sea a focal point for exploration and economic interests.
- Additionally, the sea supports extensive fishing grounds, supplying seafood to surrounding nations and contributing to their economies.
- However, overfishing has become a growing concern, threatening marine biodiversity and the sustainability of fish stocks.
- Regional issues between China and Japan:
- Regional tensions between China and Japan over the East China Sea primarily revolve around territorial disputes and resource control.
- The Senkaku Islands (known as the Diaoyu Islands in China), uninhabited but strategically located, are the central point of contention.
- Japan administers these islands, but China claims historical rights over them. This dispute has led to frequent confrontations, including naval and aerial encounters, heightening security concerns in the region.
- China’s increased military presence and assertive actions in the East China Sea, including the establishment of an Air Defence Identification Zone (ADIZ) in 2013, have further strained relations.
- Japan views these moves as a violation of its sovereignty and a threat to regional stability. Both nations also clash over overlapping claims to exclusive economic zones (EEZs), complicating efforts to exploit undersea resources.
- Efforts to manage these tensions through diplomatic channels, such as bilateral dialogues and agreements on resource sharing, have achieved limited success.
- The East China Sea remains a geopolitical hotspot, symbolising broader power struggles in the Asia-Pacific region. Resolving these disputes requires mutual respect for international norms and sustained dialogue to ensure peace and stability in this strategically and economically vital maritime zone.
UPSC CSE PYQQ. Which one of the following statements best reflects the issue with the Senkaku Islands, sometimes mentioned in the news? (2022)
Answer: Option B
|
|
Also Read |
|




