- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PLACES IN NEWS 20th FEBRUARY 2025
PLACES IN NEWS 20th FEBRUARY 2025
21-02-2025

Qatar
Why in news?
- India and Qatar upgraded their relations to a strategic partnership and committed to doubling bilateral trade, aiming to reach nearly $30 billion by 2030.
About Qatar:
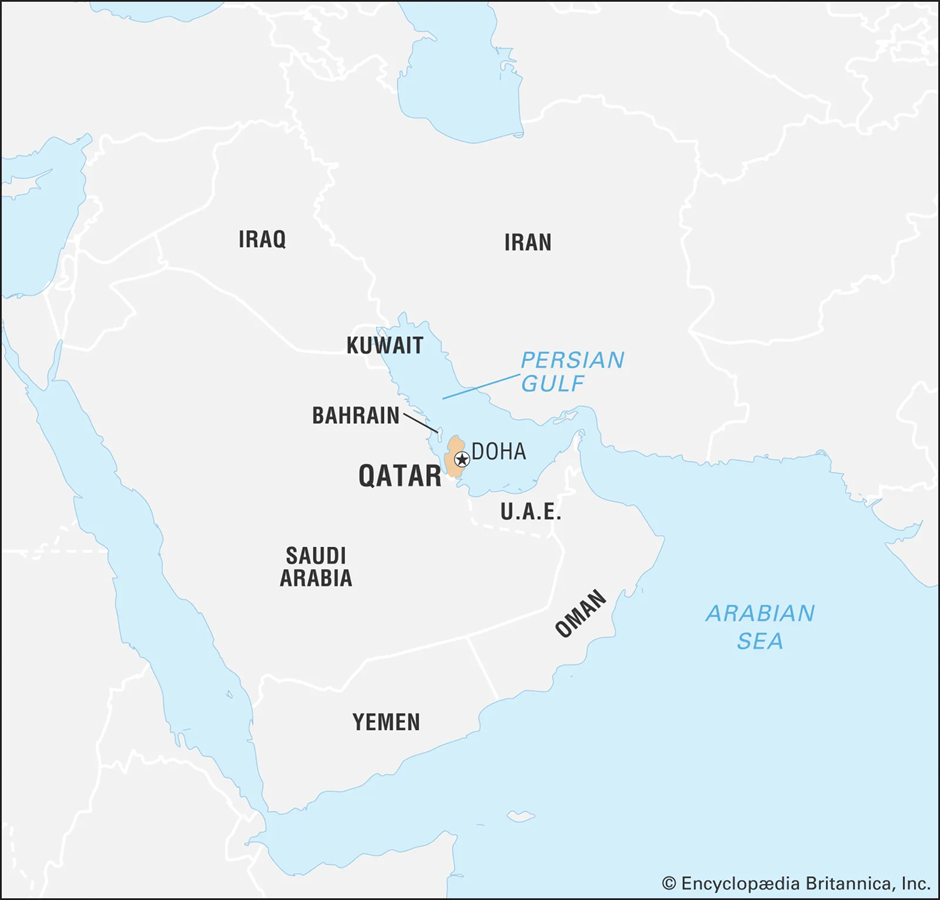
- Location and Geography:
- Qatar is a small nation on the north-eastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula that extends into the Persian Gulf.
- Covering approximately 11,437 square kilometres, its terrain is predominantly flat and arid, with vast stretches of desert.
- It shares land borders with Saudi Arabia to the south and maritime boundaries with Bahrain, the United Arab Emirates, and Iran.
- The country experiences a desert climate, marked by extremely hot summers and mild winters, with scarce rainfall and frequent dust storms.
- Potential Natural Resources:
- Qatar possesses significant oil reserves, estimated at approximately 25 billion barrels, ranking it 13th globally.
- The country is also renowned for its vast natural gas reserves, particularly the offshore North Field, which is among the largest gas fields worldwide.
- The energy sector, especially oil and natural gas, forms the backbone of Qatar's economy, contributing over 70% of government revenue, more than 60% of GDP, and about 80% of export earnings.
- Significance of Qatar for India
- Indian Diaspora: Indians constitute a substantial portion of Qatar's population, forming about 25% of its population, primarily as migrant workers.
- Energy Security: India relies on Qatar for a significant portion of its energy imports, particularly liquefied natural gas (LNG), making Qatar a crucial partner in ensuring India's energy security.
- Strategic Location: Qatar's position in the Middle East offers India strategic advantages, facilitating access to regional markets and serving as a hub for air travel between India and other parts of the world.
- Investment Opportunities: The Qatar Investment Authority's decision to open an office in India reflects growing economic ties and mutual investment interests.
- Challenges in Qatar-India Relations
- Legal and Human Rights Issues: Indian workers in Qatar often face legal challenges, including imprisonment and labour rights concerns.
- Cultural and Religious Sensitivities: Navigating cultural differences requires careful diplomacy to prevent misunderstandings and ensure the welfare of the Indian community in Qatar.
- Labour and Employment Practices: Reports of labour rights violations necessitate continuous dialogue to improve working conditions for Indian expatriates.
- Geopolitical Dynamics: Regional tensions in the Middle East can impact bilateral relations, requiring India to balance its foreign policy to maintain stability and protect its interests.
- Recent Developments
- Strategic Partnership: On February 18, 2025, India and Qatar elevated their ties to a strategic partnership, aiming to double bilateral trade by 2030.
- Investment Initiatives: The establishment of the Joint Task Force on Investments in June 2024 highlights both nations' commitment to exploring investment opportunities and strengthening economic cooperation.
Peppara Wildlife Sanctuary
Why in news?
- The Periyar Tiger Conservation Foundation recently introduced a real-time monitoring and networking system in Peppara Wildlife Sanctuary, located within the Thiruvananthapuram Forest Division.
About Peppara Wildlife Sanctuary:
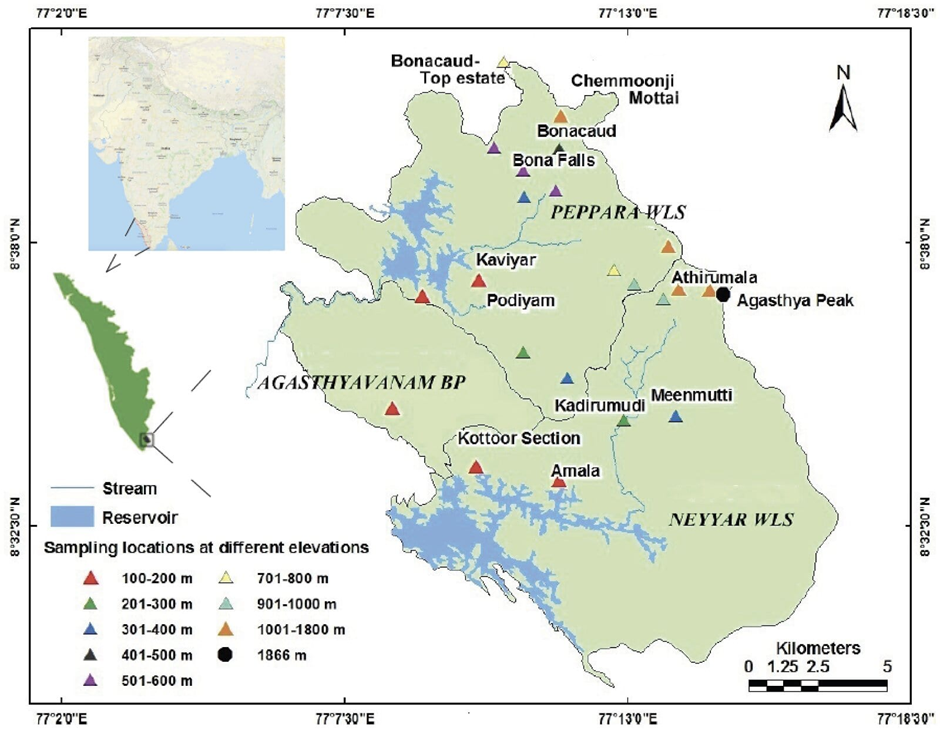
- Location and Key Features
- Peppara Wildlife Sanctuary is a protected area located in the Thiruvananthapuram district of Kerala, covering 53 sq. km.
- It was declared a wildlife sanctuary in 1983 and plays a crucial role in water conservation, as it forms the catchment area of the Peppara Dam, constructed across the Karamana River.
- The terrain varies in altitude from 100 m to 1717 m, with notable peaks like Chemmunjimottai (1717 m) and Athirumalai (1594 m) shaping its diverse topography.
- The Vazhvanthol waterfall, located near the sanctuary, enhances its ecological and tourism significance.
- Peppara Wildlife Sanctuary is part of the Agasthyamalai Biosphere Reserve, which is a part of UNESCO's Man and Biosphere (MAB) Reserves.
- Other protected areas within the biosphere reserve include the Neyyar Wildlife Sanctuary, Shendurney Wildlife Sanctuary, and Kalakad Mundanthurai Tiger Reserve, forming an interconnected habitat for diverse flora and fauna.
- Flora and Fauna
- The sanctuary features tropical evergreen, moist deciduous, semi-evergreen, and Myristica swamp forests, supporting a rich biodiversity.
- Common tree species include teak, ebony, mahogany, ironwood, and silk cotton trees.
- The sanctuary is home to 43 species of mammals, including tiger, leopard, sloth bear, Asian elephant, sambar, barking deer, lion-tailed macaque, Nilgiri langur, and Nilgiri tahr.
- The avian diversity is remarkable, with 233 bird species, while 46 reptile species, 13 amphibians, and 27 fish species further enrich its ecosystem.
Sariska Tiger Reserve (STR)
Why in news?
- The forest department recently announced its decision to designate the eco-sensitive zone (ESZ) around Sariska Tiger Reserve (STR) to enhance conservation efforts and regulate activities in the surrounding areas.
About Sariska Tiger Reserve (STR):
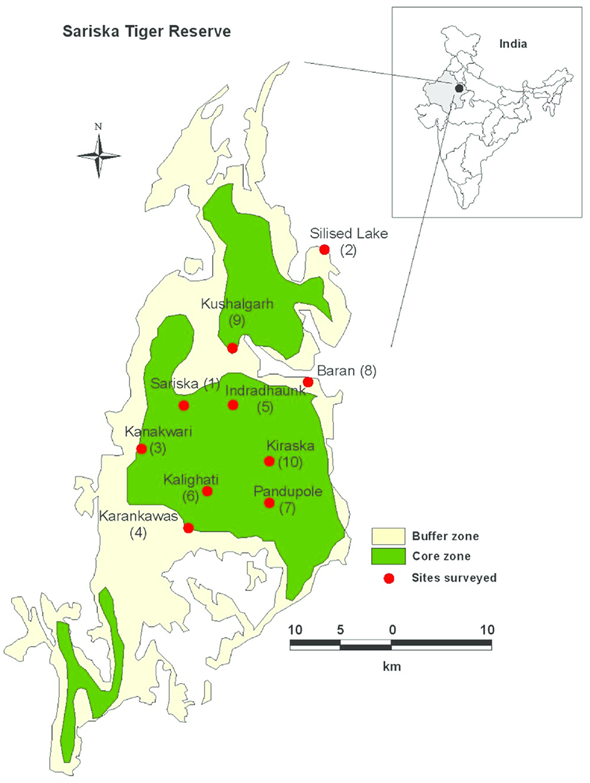
-
- Location and Key Features
- Location and Key Features
- Sariska Tiger Reserve is a protected area located in Rajasthan, spanning 800 sq. km.
- It is situated in the Aravalli mountain range, which is one of the oldest mountain ranges in the world.
- Initially, it served as a hunting ground for the Maharaja of Alwar before being declared a natural reserve in 1955 and later a national park in 1979.
- It is the first reserve in the world to successfully relocate tigers, marking a milestone in tiger conservation efforts.
- Apart from its rich biodiversity, Sariska is known for its historical sites, including Pandu Pol, Bhangarh Fort, Ajabgarh, Pratapgarh, Siliserh Lake, and Jai Samand Lake, which add cultural significance to the region.
- Flora and Fauna
- Flora and Fauna
- The topography of Sariska consists of rocky landscapes, scrub thorn arid forests, grasslands, hilly cliffs, and semi-deciduous woodlands, supporting a diverse range of flora and fauna.
- The vegetation is categorized under Northern Tropical Dry Deciduous Forests and Northern Tropical Thorn Forests, which thrive in the arid climatic conditions of Rajasthan.
- The forest is primarily covered with dhok trees, along with other species like salar, kadaya, gol, ber, banyan, gugal, bamboo, kair, and adusta.
- Sariska is home to a variety of wildlife species, including Bengal tigers, leopards, sambar deer, chital, nilgai, four-horned antelope, and wild boar, making it an important habitat for predator-prey dynamics
Caspian Sea
Why in news?
- Russia reported a 30-40% reduction in oil flows through the Caspian Pipeline Consortium (CPC), a key Caspian Sea export route, following a Ukrainian drone attack on a pumping station.
About Caspian Sea:
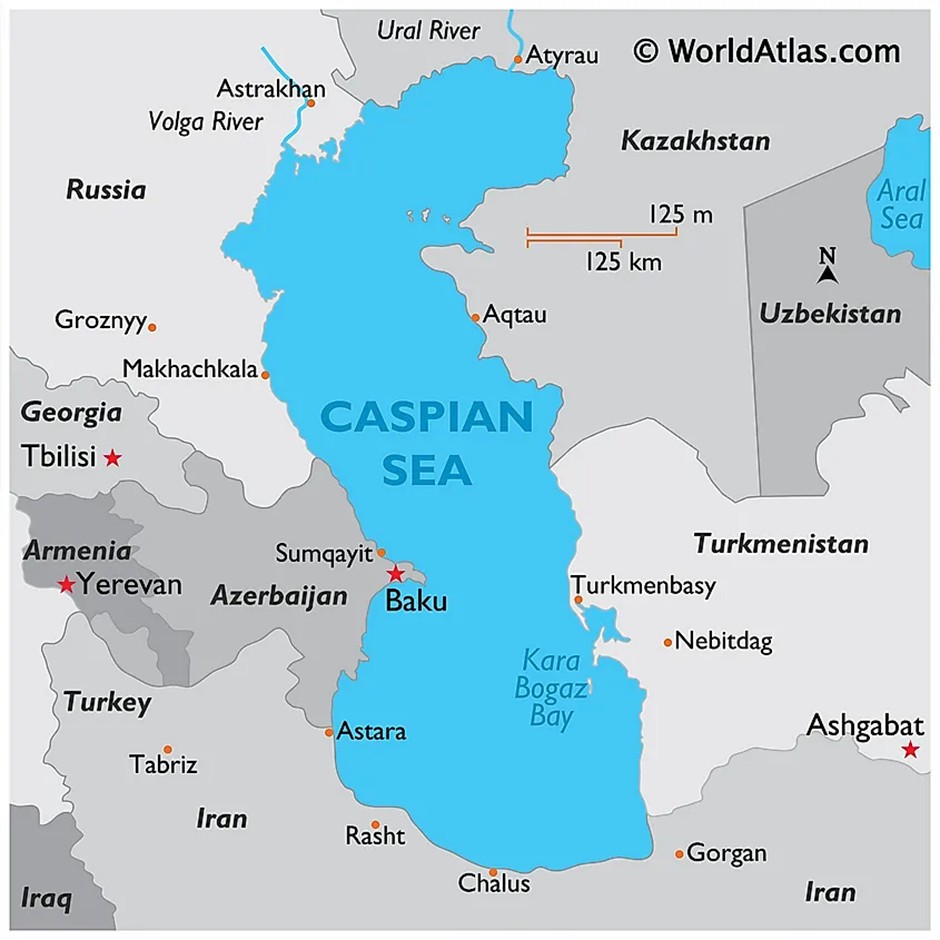
-
- Location:
- Location:
- The Caspian Sea, the largest enclosed inland body of water, lies between Europe and Asia, bordered by Russia, Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan, Iran, and Azerbaijan.
- It covers approximately 371,000 sq. km, with a length of 1,200 km and a maximum depth of about 1,025 meters.
- Though termed a sea, it lacks an outlet to the world's oceans, leading to disputes over whether it should be classified as a lake or a sea, influencing legal rights over its resources.
- The Volga River, the largest river in Europe, along with the Ural River and several others, drains into the Caspian Sea.
- Natural Resources:
- Natural Resources:
- The Caspian region is rich in oil and natural gas, making it a crucial energy hub. Vast offshore oil fields are found in Kazakhstan’s Kashagan field, Azerbaijan’s Azeri-Chirag-Gunashli complex, and Turkmenistan’s offshore blocks.
- The Caspian Sea is estimated to hold over 40 billion barrels of oil and around 8.7 trillion cubic meters of natural gas, significantly contributing to the global energy market.
- International Importance:
- International Importance:
- The Caspian Sea plays a vital role in regional geopolitics, trade, and security. Its strategic location connects Central Asia, Russia, and the Middle East, influencing energy transportation and economic policies.
- The Caspian Convention (2018) attempted to resolve disputes over resource sharing and military presence. It is also crucial for fisheries, particularly sturgeon, a key source of caviar, though overfishing and pollution threaten its ecosystem.
- The region is witnessing growing geopolitical competition among bordering nations and external players like China and the European Union, as control over energy routes and resources directly impacts global energy security.
About Caspian Pipeline Consortium (CPC):
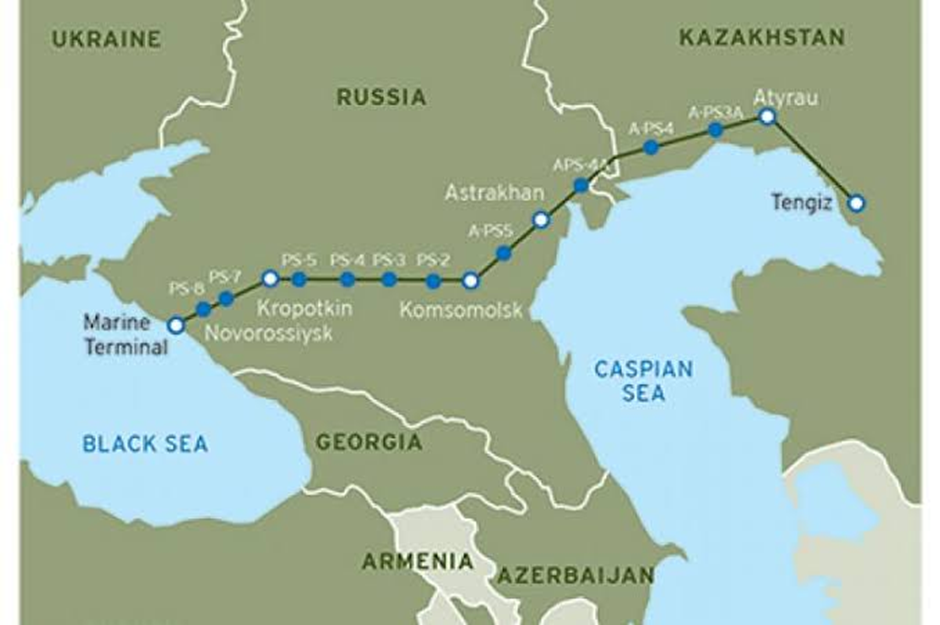
- The Caspian Pipeline Consortium (CPC) is a crude oil pipeline network that transports oil from Kazakhstan's Tengiz oil field to the Russian Black Sea port of Novorossiysk.
- Spanning 935 miles (1,505 km), it serves as a critical East-West energy corridor, facilitating the export of oil from the Caspian Sea region to international markets.
- Construction of the CPC pipeline began in 1999, and it became operational in 2001. A major expansion project worth $5.1 billion was completed in 2018, significantly increasing its capacity.
- The pipeline currently handles 1.4 million barrels of oil per day, contributing to 2.3% of global seaborne oil trade. Notably, it accounts for nearly two-thirds of Kazakhstan’s oil exports, highlighting its economic and strategic importance.
- The CPC consortium includes the governments of Russia and Kazakhstan, alongside major Western energy corporations such as Chevron, ExxonMobil, and Shell.
- This multinational participation underscores its geopolitical significance, as the pipeline strengthens energy cooperation between Central Asia, Russia, and global markets.
Tungabhadra River
Why in news?
- Karnataka’s proposed bridge-cum-barrage on the Tungabhadra River has sparked a dispute with Andhra Pradesh over water sharing, environmental concerns, and alleged violations of the Krishna Water Disputes Tribunal award.
About Tungabhadra River:
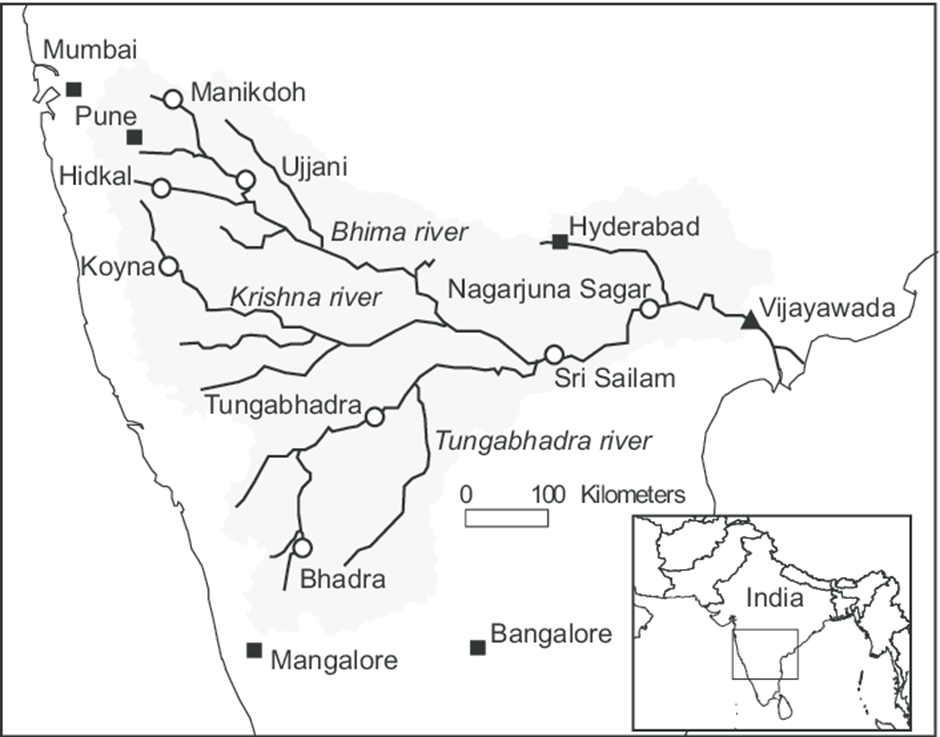
- Location and Origin:
- The Tungabhadra River is a significant tributary of the Krishna River, flowing through the Indian states of Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh.
- It originates from the confluence of two rivers, the Tunga and the Bhadra, both of which rise in the Western Ghats of Karnataka.
- The Tunga River originates in the Chikmagalur district, while the Bhadra River originates in the Shimoga district. These two rivers merge at Koodli, near Shivamogga (Shimoga), to form the Tungabhadra River.
- The Tungabhadra River traverses a course of approximately 531 kilometres before joining the Krishna River near Sangamaleshwaram in Andhra Pradesh. Its total catchment area spans about 71,417 square kilometres.
- Varada, Vedavathi (Hagari), and Handri rivers are major tributaries contributing to the Tungabhadra's flow.
2. Historical and Cultural Significance:
- The banks of the Tungabhadra River have been the cradle of ancient civilisations, most notably serving as the lifeline for the Vijayanagara Empire in the 14th to 16th centuries.
- The empire's capital, Hampi, now a UNESCO World Heritage Site, was strategically established along the river, utilising its waters for agriculture, sustenance, and as a natural defence barrier.
- The Tungabhadra River holds profound religious significance, often being identified with the Pampa River mentioned in the Ramayana.
- It is believed that Lord Rama met Hanuman and Sugriva on its banks during his quest to rescue Sita. This association has made the Tungabhadra a sacred river, with numerous temples and shrines adorning its banks.
- Architectural marvels from the Vijayanagara period, such as the Virupaksha Temple, are situated along the Tungabhadra, reflecting the river's integral role in the region's cultural and spiritual life.
- The river's presence has influenced local traditions, festivals, and the overall way of life for communities residing along its course.
|
UPSC CSE PYQs
Q1. Consider the following pairs:
|
|
Rivers |
Flows into |
|
Andaman Sea |
|
Irish Sea |
|
Caspian Sea |
|
Indian Ocean |
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched? (2020)
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 3 and 4 only
- 1, 2, and 4 only
Answer: Option C
Q2. Consider the following pairs:
|
Famous place |
River |
|
Chandrabhaga |
|
Cauvery |
|
Malaprabha |
Which of the pairs given above are correctly matched? (2019)
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Answer: Option A
Q3. Which of the following are in Agasthyamala Biosphere Reserve? (2019)
- Neyyar, ldl Peppara, and Shendurney Wildlife Sanctuaries; and Kalakad Mundanthurai TigerReserve.
- Mudumalai, Sathyamangalam, and Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuaries; and Silent Valley National Park.
- Kaundinya, Gundla Brahmeswaram, and Papikonda Wildlife Sanctuaries; and MukurthiNational Park.
- Kawal and Sri Venkateswara Wildlife Sanctuaries; and NagarjunasagarSrisailam Tiger Reserve.
Answer: Option A
|
Also Read |
|

![img-PSYCHOLOGICAL WARFARE [PSYWAR]](https://i.filecdn.in/755esias/PSYCHOLOGICALWARFAREPSYWAR-1747206772505.jpg)

