- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
New Diseases Among Bees Are Threatening Global Economies
New Diseases Among Bees Are Threatening Global Economies
18-11-2024
- Bees and other insects that help plants to grow by pollinating them are very important for the world’s farming and food production.
- More than 75% of food crops, fruits, and flowering plants need bees, wasps, butterflies, and other pollinators to grow successfully.
- If these insects are harmed, it can affect the economy and food supply around the world.
- Pollinators are important for the global food supply and economic stability.
- In November 2024, these important insects, especially bees, are facing new dangers, including diseases, loss of habitat, pesticides, pollution, and climate change.
- These dangers are becoming bigger problems for economies everywhere.
What is pollination ?
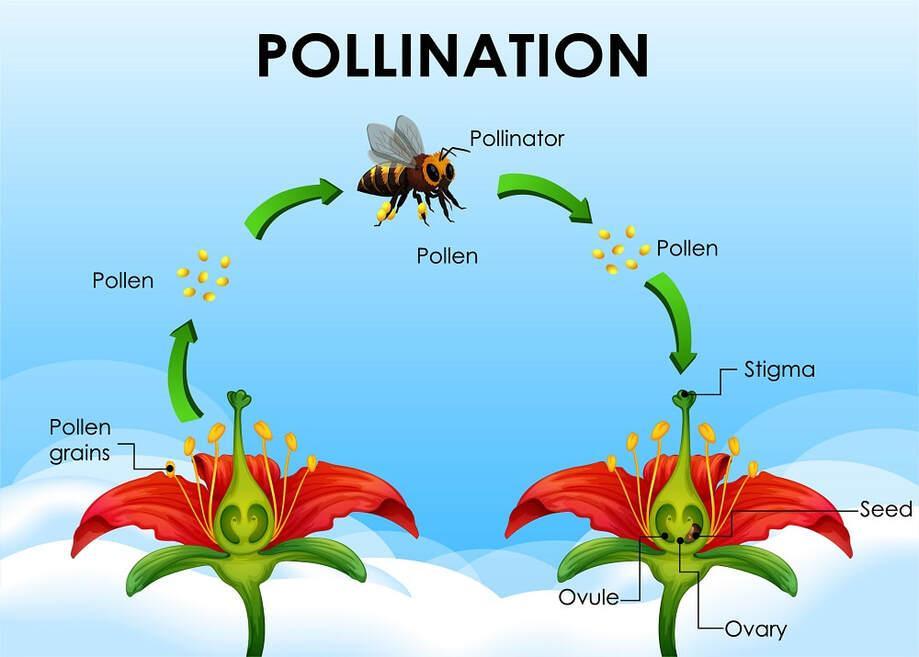
- Pollination is the process of transferring pollen (a powdery substance containing male reproductive cells) from the male part (anther) of a flower to the female part (stigma).
- This process allows plants to reproduce, leading to the formation of seeds and fruits.
- Animals like bees, butterflies, birds, and bats, as well as wind and water, act as pollinators, carrying pollen from one flower to another, ensuring the continuation of plant life and the production of food for humans and other animals.
What is The Importance of Pollinators in Farming ?
- Pollinators are key to growing many crops and plants that make up the world’s food.
- Without bees and other pollinators, the amount of food we produce would be much lower, which could cause big problems for food security.
What are the Rising Threat of Diseases Among Bees ?
- A new danger to bees is the spread of diseases, which is getting worse because of habitat loss.
- The decline in bee populations has already been seen in places like Europe and North America, but there is not much information about bee populations in places with a lot of wildlife, like the Indian subcontinent.
- The Western honey bee (Apis mellifera), which is the most studied bee, can carry diseases that affect both managed bees (bees kept by beekeepers) and wild pollinators.
- This is called pathogen spillover. When these bees live in the same area, diseases can spread between them.
- A study led by Corina Maurer at ETH Zürich in Switzerland found that wild bees in places where they shared flowers with honey bees had much higher levels of diseases like the deformed wing virus and black queen virus.
- The disease levels were 10 times higher in wild bees that shared flowers with honey bees.
- The study showed that habitats with more flowers can lower the risk of spreading diseases between wild and managed bees.
- But when habitats are lost, bees are forced into smaller areas, which increases the risk of disease spreading.
- Axel Brockmann, a retired professor from Bangalore, warned that if wild bees and honey bees are forced to live in the same area because of habitat loss, diseases can spread more easily.
Bee Diversity and Habitat Overlap in India
India is home to over 700 types of bees, including four types of indigenous honey bees:
- Asiatic honey bee (Apis cerana indica)
- Giant rock bee (Apis dorsata)
- Dwarf honey bee (Apis florea)
- Stingless bee (Trigona species)
- Western honey bees were brought to India in 1983 to improve honey production.
- However, these bees have caused some problems, especially with spreading diseases to native bee species.
- One of the biggest dangers to the Asiatic honey bee is the Thai sacbrood virus, which caused the deaths of 90% of honey bee colonies in South India in 1991-1992.
- The virus came back in 2021 in Telangana.
- This virus harms the Asiatic honey bees by killing their larvae, but the same virus affects Western honey bees less severely.
- Scientists still don’t know exactly how the virus spreads between different bee populations, but there is concern that diseases from honey bees can infect wild bees and make the virus more dangerous.
What are the Challenges of Bee Migration and Habitat Loss ?
- Migration of Managed Honey Bees: Beekeepers in India move their honey bee colonies along routes where there are many flowers for the bees.
- This migration can cause problems because wild bees may have to compete for food and space with Western honey bees.
- In places like Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, and Maharashtra, some local bee species have disappeared, possibly because they are competing with migrating honey bees.
- This has led to disease transmission and a decline in local bee populations.
- A 2023 study found that 40% of bumblebee species in the Indian Himalayas could lose 90% of their habitat by 2050, raising worries that Western honey bees might take over their food sources.
- In Kolhapur, Maharashtra, beekeepers noticed that after they brought in Western honey bees, local bee populations were wiped out by disease.
- As a result, the area went from producing 8-10 tonnes of honey to less than 1 tonne.
Need for More Research on Bee Diseases
- More research is needed to understand how diseases spread between managed honey bees and wild pollinators.
- This is especially true in places like India, where we don’t know much about the diseases affecting local bees.
- Sujana Krishnamoorthy, head of the Under the Mango Tree Society, which trains farmers to work with native bees, says more surveys of wild bees and managed honey bees are needed to track disease outbreaks.
- Surveys of honeybee colonies can help reduce the spread of diseases to wild species.
- Maurer and her team emphasize that viral diseases, such as the Thai sacbrood virus, need more attention so that scientists can find ways to stop them from harming bees.
- Axel Brockmann highlighted the importance of understanding how pollinators work in nature, so that we can develop better ways to protect them from threats like climate change, habitat loss, and diseases.
Conclusion
Bees are crucial for farming and food production around the world. New threats, including diseases, are spreading between managed honey bees and wild pollinators, and they are becoming a growing problem for global food security.