- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
U.K. TO HAND SOVEREIGNTY OF CHAGOS ISLANDS TO MAURITIUS, INDIA WELCOMES UK-MAURITIUS TREATY
U.K. TO HAND SOVEREIGNTY OF CHAGOS ISLANDS TO MAURITIUS, INDIA WELCOMES UK-MAURITIUS TREATY
24-05-2025
Why in the News?
After a long span of 60 years, Britain returned the sovereignty of Chagos Island to Mauritius in May 2025.
Historical Background of Chagos Island:
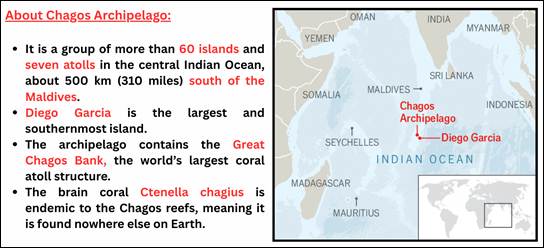
- The Chagos Islands in the Indian Ocean, have been under British control since 1814.
- In 1965, shortly before granting Mauritius independence, the UK separated the Chagos Islands to form the British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT).
- It retained control over the islands while Mauritius became independent in 1968.
- The UK later expelled the Chagossian residents from the Chagos islands to make way for a US military base on Diego Garcia, the largest island in this group.
-
- Mauritius has long contested the legality of the UK's continued administration of the Chagos Islands.
- It argued that the separation violated International law of Sea Tribunal and the Right to self-determination.
- Finally, in 2017, the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) requested an advisory opinion from the International Court of Justice (ICJ) on the legal consequences of the separation of the Chagos Archipelago from Mauritius.
- In February 2019, the ICJ delivered its advisory opinion with a decisive 13–1 ruling. The court found:
-
- The separation of the Chagos Islands from Mauritius in 1965 was not based on the free and genuine expression of the will of the people concerned that reflects “Unlawful Separation”.
-
-
- The process of decolonization of Mauritius was not lawfully completed yet.
- The Court stated that the UK is “under an obligation to bring to an end its administration of the Chagos Archipelago as rapidly as possible”.
-
-
- In fact, the ICJ called on all UN member states to cooperate with the United Nations to complete the decolonization of Mauritius.
-
-
- This was supported by UN members in majority.
- The UNGA resolution significantly increased international pressure on the UK and strengthened Mauritius’s claim.
-
- The case became a landmark in the Global Movement for Decolonization and the Right to self-determination.
- The ICJ opinion, though advisory and not legally binding, clarified the legal status of the Chagos Islands and the obligations of the UK under international law.
- The ruling highlighted the ‘Human rights’ of displaced Chagossians and the need for their resettlement.
What are the key highlights of the New UK-Mauritius Agreement?
- The agreement was briefly delayed by a UK court ‘injunction’ after two Chagossian women, displaced from the islands decades ago, raised concerns about their right to return.
- Injunction refers to a court order that temporarily stopped or delayed the signing of the agreement. However, the injunction was lifted on 22nd May 2025, and the signing proceeded.
- This ends more than 200 years of British rule and decades of legal and diplomatic disputes over the islands.
- Some of the major provisions include:
- Mauritius regains sovereignty over the Chagos Islands.
- Diego Garcia and Financial Terms: The UK and US will retain control and operational oversight of the crucial military base on Diego Garcia, the largest island in the archipelago, through a 99-year lease agreement.
- This base is strategically important for defense and intelligence operations in the Indian Ocean.
- The UK will pay Mauritius an annual fee (reported as £101 million or about €120 million per year) for the lease.
- Chagossian Rights: The agreement establishes a £40 million trust fund to support Chagossians, the original inhabitants who were forcibly displaced in the 1960s and 1970s.
What is India’s stance?
- India welcomed the 2025 UK-Mauritius treaty as a “milestone achievement” and a positive regional development.
- This stance is rooted in India’s principled position on decolonization, respect for sovereignty, and the territorial integrity of nations.
-
- India has actively backed Mauritius in international forums, making both written and oral submissions before the International Court of Justice (ICJ) and UNGA resolutions that called for the UK to return the islands to Mauritius.
- What are India's Strategic and Regional interests?
-
- India views the Indian Ocean as a strategic priority and sees the resolution of the Chagos issue as vital for regional stability and maritime security.
- India has carefully balanced its relations with the UK and the US, acknowledging the strategic importance of the Diego Garcia military base for Indo-Pacific security and QUAD cooperation.
- What are India’s broader Geopolitical Calculations?
-
- India’s stand reinforces its image as a Global leader which respects the sovereignty and decolonization in the Global South.
- By supporting Mauritius, India also ensures to prevent Chinese influence.
PYQ Relevance:
- What problems were germane to the decolonization in the Malay Peninsula? (UPSC CSE 2017)
|
Also Read |
|



