- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
India’s Renewable Power Capacity: IEA Report
India’s Renewable Power Capacity: IEA Report
India’s Renewable Power Capacity: IEA Report
Recently, a report released by the International Energy Agency (IEA) stated that India will almost double its renewable power capacity in the next 5 years.
What is Renewable Energy?
Renewable energy is energy derived from natural sources that are replenished (produced) at a higher rate than they are consumed. Sunlight and wind are the examples of Renewable Energy.
Key Points of the Report are:
Renewable energy will comprise 90 percent of global electricity capacity expansion in the next 5 years and much of it will be in India.
In the world, Renewable energy’s installed power capacity addition will grow to 2,400 gigawatts (GW) between 2022 and 2027.
This expansion will be 85 percent faster than the previous 5 years.
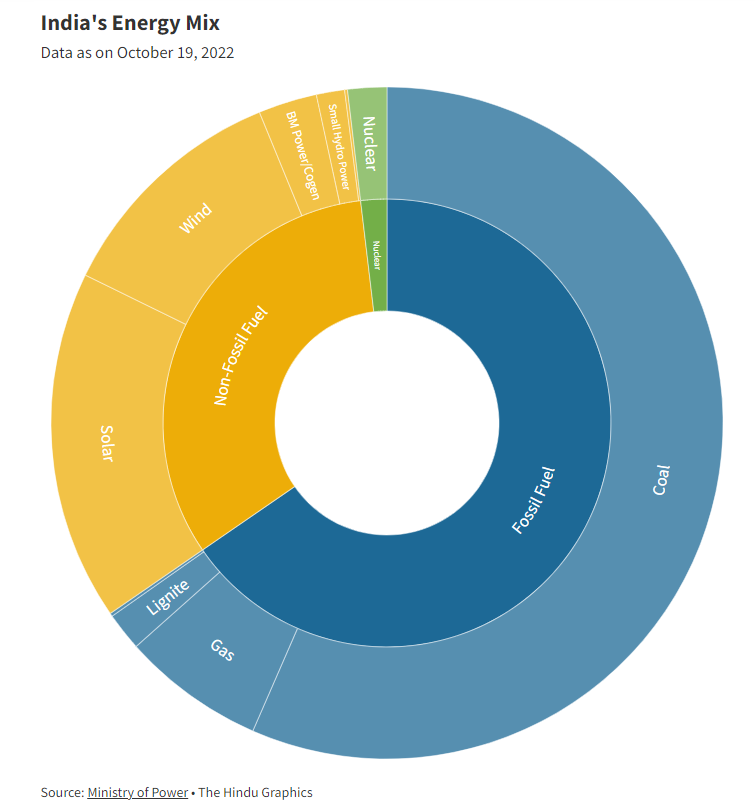
In India, with the addition of 145 gigawatt (GW) of renewable energy, India will almost double its renewable power capacity over 2022-2027. Solar photovoltaic (PV) will account for 75% of this growth, followed by onshore wind with 15 percent and hydropower providing almost all the rest.
China, the European Union and the United States will be the other 3 contributing majorly to this upward trend of renewable energy besides India.
Renewable Energy in India
India has announced a target of 500 GW of renewable energy by 2030 through sources such as solar photovoltaic (PV) energy, wind and hydropower. Currently, projects worth almost $197 billion are underway in India.
As part of its international climate commitments, India has said that it will source roughly half its energy needs from non-fossil fuel sources by 2030.
In 2021, after India increased its subsidy on solar PV installations, the country’s rooftop PV market has shown a record high.
Recently, India extended its national solar production programme, which provides incentives to domestic and international companies for setting up battery manufacturing plants.
Financing the energy transition of developing countries such as India is among the hottest geo-political issues, with India having said multiple times at United Nations climate conferences that “trillions of dollars” will be required.
Renewable-energy generation is only available for a limited time every day, the government is aiming to install battery storage capacity worth 51.5 GW by 2030 to provide “round-the-clock power to end-consumers.
The installed electricity-generating capacity in the country at present is 409 GW, including 173 GW from non-fossil fuel sources, which is about 42% of the total.
|
Initiatives Taken by Indian Government in this regard are: |
|
|
PM-KUSUM |
It was launched by the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) to support installation of off-grid solar pumps in rural areas and reduce dependence on grid, in grid-connected areas. |
|
Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme |
Production Linked Incentive Scheme “National Programme on High Efficiency Solar PV Modules” was introduced with an outlay of Rs. 4500 crores to support and promote manufacturing of high efficiency solar PV modules, including the upstage vertical components like cells, wafers, ingots and polysilicon in India and thus reduce the import dependence in Solar PhotoVoltaic (PV) sector. |
|
Solar Parks Scheme |
To facilitate large scale grid connected solar power projects, a scheme for “Development of Solar Parks and Ultra Mega Solar Power Projects” is under implementation with a target capacity of 40 GW capacity by March 2022. |
|
Roof Top Solar programme Phase-II |
It provides for financial assistance of upto 4 GW of solar roof top capacity to the residential sector and there is a provision to incentivise the power distribution companies for incremental achievement over the previous year. |
|
Central Public Sector Undertaking (CPSU) Scheme |
A scheme for setting up 12 GW Grid- Connected Solar PV Power Projects by Central Public Sector Undertakings with domestic cells and modules is under implementation. Viability Gap Funding support is provided under this scheme. |
|
Hydrogen Mission |
The Prime Minister announced the launch of the National Hydrogen Mission and stated the goal to make India a global hub for Green Hydrogen production and export. |
|
International Solar Alliance |
The ISA is an intergovernmental treaty-based organisation with a global mandate to catalyse solar growth by helping to reduce the cost of financing and technology. Recently, the United States of America has become the 101st member country to join the ISA. |
|
OSOWOG |
The OSOWOG was jointly released by India and UK at the COP26 Climate Meet in Glasgow. |
|
National Wind-Solar Hybrid Policy |
The main objective of the National Wind-Solar Hybrid Policy, 2018 is to provide a framework for promotion of large grid connected wind-solar PV hybrid systems for optimal and efficient utilization of wind and solar resources, transmission infrastructure and land. |
|
National Offshore Wind Energy Policy |
The National Offshore wind energy policy was notified in October 2015 with an objective to develop the offshore wind energy in the Indian Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) along the Indian coastline of 7600 km. |
|
Other Renewables for Power Generation |
Programme on Energy from Urban, Industrial and Agricultural Wastes/Residues Scheme to support Promotion of Biomass based cogeneration in sugar mills and other industries Biogas Power (Off-Grid) Generation and Thermal application Programme (BPGTP) New National Biogas and Organic Manure Programme (NNBOMP) |
Additional Information
International Energy Agency (IEA)
It’s an autonomous Intergovernmental Organisation established in 1974 in Paris, France.
It was established in the wake of the oil crisis of 1973-1974, to help its members respond to major disruptions in oil supply.
The IEA is made up of 30 member countries.
India became an Associate member of IEA in March 2017 but it was in engagement with IEA long before its association with the organization.
It mainly focuses on its energy policies which include economic development, energy security and environmental protection. These policies are also known as the 3 E’s of IEA.
What is REN21?
REN21 is the only global renewable energy community that brings together people from science, governments, NGOs and industry that keep track of global development in renewable sector.
Goal: enable decision-makers to make the shift to renewable energy.
Created: It was created in 2004 as an outcome of the ‘International Conference on Renewable Energy’ held in Bonn, 2024.

![img-PSYCHOLOGICAL WARFARE [PSYWAR]](https://i.filecdn.in/755esias/PSYCHOLOGICALWARFAREPSYWAR-1747206772505.jpg)

