- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
12 Countries Sign the Zero Debris Charter
12 Countries Sign the Zero Debris Charter
28-05-2024

12 nations have signed the Zero Debris Charter at the ESA/EU Space Council, solidifying their commitment to the long-term sustainability of human activities in Earth orbit.
- In addition to the 12 countries, the European Space Agency also signed the Zero Debris Charter as an International Organization (IGO).
Background:
- Origin: The Charter, an initiative of the European Space Agency (ESA), was unveiled at the ESA Space Summit in Seville in November 2023.
- Response to Member States' Encouragement: It came in response to ESA Member States' urging the Agency to adopt a "Zero Debris approach" for its missions and encourage partners and other actors to follow suit.
Unique Aspects:
- Unprecedented Collaboration: The Charter is the first initiative of its kind, bringing together a diverse range of space actors worldwide with the shared goal of eliminating debris creation by 2030 and ensuring the long-term viability of space activities.
- Ambitious Objectives: It aims to establish far-reaching guiding principles and ambitious yet feasible technical targets to guide the development of a Zero Debris roadmap, driving global efforts to mitigate and remediate space debris.
Key Features:
- Non-Legally Binding Agreement: The Charter is a non-legally binding agreement that promotes a community of proactive actors working collaboratively towards jointly defined targets for 2030.
- Specific Targets: The Charter sets out several targets, including limiting the probability of a mission generating space debris to below 1 in 1,000 per object.
- Post-Mission Disposal: It establishes a 99% success target for post-mission disposal, potentially involving external means when necessary.
- Information Sharing and Coordination: It encourages transparent information sharing and space traffic coordination to minimize collision risks.
Implementation Strategies:
- Technological Development: ESA will focus on developing groundbreaking technologies for satellite end-of-life disposal, in-orbit servicing, and active debris removal to implement the Charter effectively.
- Regulatory Collaboration: ESA will work closely with institutions responsible for regulatory aspects to ensure alignment with the Charter's objectives.
What is Space Debris?
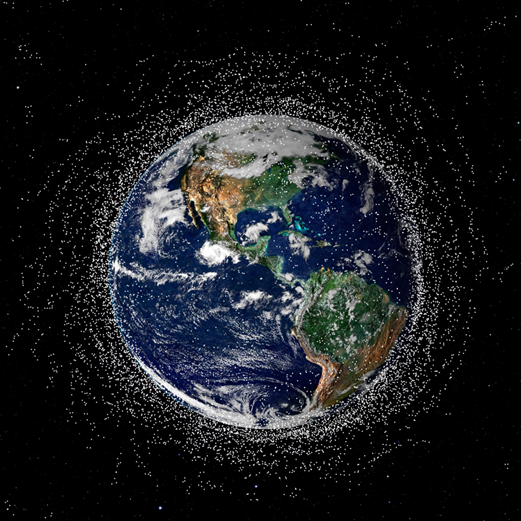
- Space debris is any human-made object in orbit not serving a useful purpose.
- Space debris includes old spacecraft, rocket stages, and micro-debris.
- Much of the debris is in low Earth orbit, within 2,000 km (1,200 miles) of Earth’s surface.
- Some debris can be found in geostationary orbit 35,786 km (22,236 miles) above the Equator.
Must Check: UPSC Coaching Institute In Delhi