- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT- First Ladder
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PLACES IN NEWS 18th MARCH 2025
PLACES IN NEWS 18th MARCH 2025
18-03-2025

Bhadra River
Why in news?
- Two youths from Rajasthan drowned in the Bhadra River recently.
About Bhadra River:
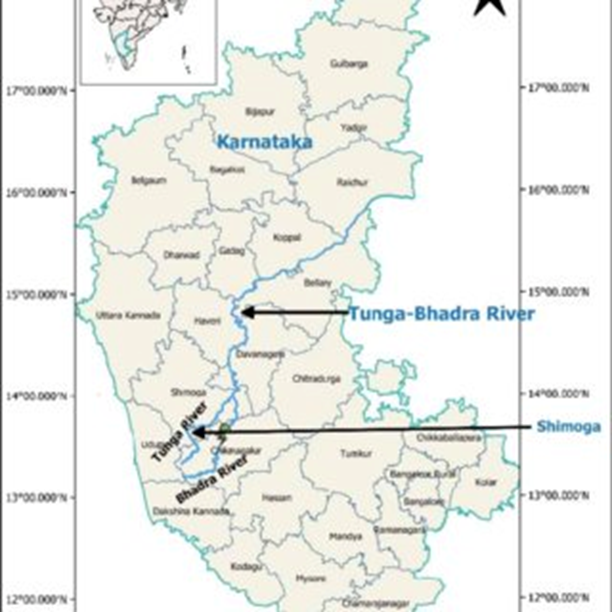
- Location and Geography:
- The Bhadra River is a significant river in Karnataka, originating in Gangamoola near Kudremukha in the Western Ghats (Sahyadri range).
- The river flows eastward across the southern Deccan Plateau, passing through towns like Kudremukh, Kalasa, Horanadu, Haluvalli, Balehonnur, Balehole, and Narasimharajapura.
- It is joined by tributaries such as Somavahini (near Hebbe), Thadabehalla, and Odirayanahalla.
- The Bhadra River eventually merges with the Tunga River at Koodli, near Shivamogga, forming the Tungabhadra River, a key tributary of the Krishna River that drains into the Bay of Bengal.
- Hydropower and Irrigation Projects:
- The Bhadra Dam, located at BRP (Bhadravathi), Karnataka, was built to control the river’s flow and support irrigation and power generation.
- The dam forms the Bhadra Reservoir (186 ft), which is crucial for agriculture and drinking water supply.
- The Bhadra Hydroelectric Project contributes to power generation in Karnataka.
- Cultural and Environmental Significance:
- The river flows near Kudremukh National Park, a biodiversity hotspot, supporting unique flora and fauna.
- Several temples and pilgrimage sites along its course, such as Horanadu and Kalasa, add to its religious significance.
- The river sustains agricultural activities, especially rice and arecanut cultivation in the region.
Yemen
Why in news?
- The U.S. recently conducted airstrikes on Houthi-controlled regions in Yemen, targeting key Houthi bases, missile defense systems, and leadership positions to counter their military capabilities and strategic influence.
About Yemen:
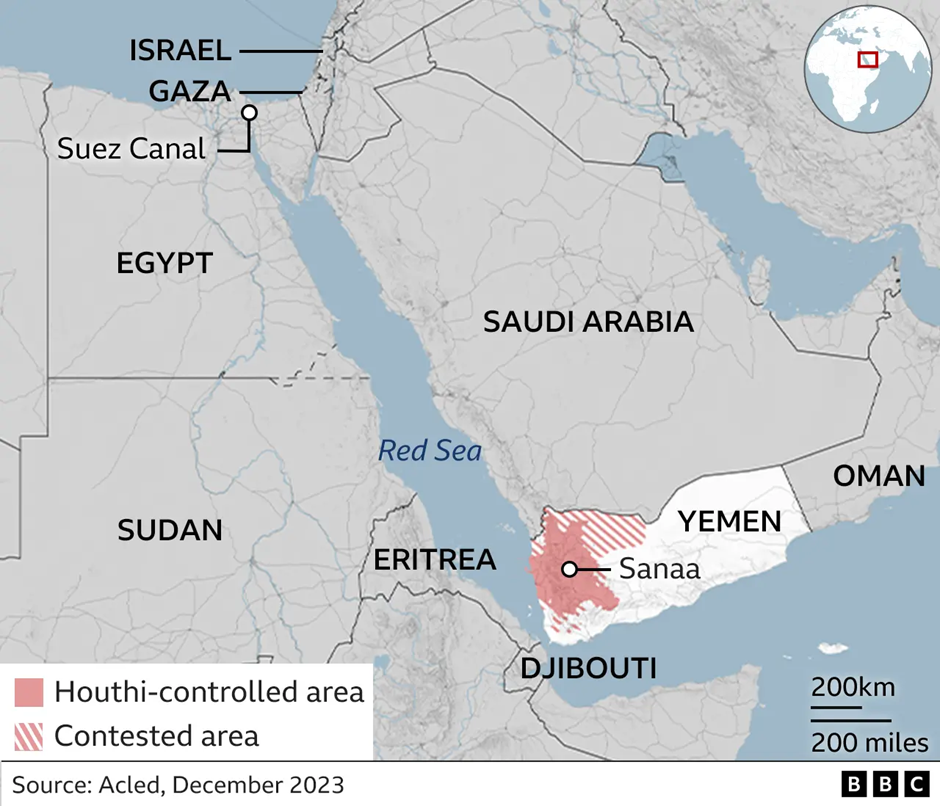
- Location and Strategic Importance:
- Yemen is located in the Middle East, at the southern tip of the Arabian Peninsula, bordering Saudi Arabia (north) and Oman (east).
- It has a strategic coastline along the Red Sea (west), Gulf of Aden, Arabian Sea, and Guardafui Channel (south).
- Yemen controls the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait, a crucial maritime chokepoint connecting the Indian Ocean to the Red Sea via the Gulf of Aden.
- This strait is vital for global oil trade and international shipping, making Yemen geopolitically significant.
- The Houthis:
- The Houthis are a Zaidi Shia sect primarily based in north-western Yemen, particularly in Sa’dah province.
- The group emerged in the 1990s as a rebellion against then-Yemeni President Ali Abdullah Saleh.
- The Houthis control large parts of western and north-western Yemen, including the capital, Sana’a.
- They are backed by Iran and are part of "The Axis of Resistance", an anti-Western and anti-Israel alliance.
- Recent Airstrikes:
- On Sunday, the United States launched airstrikes targeting Houthi-controlled areas in Yemen.
- The strikes targeted Houthi bases, missile defence systems, and leaders, killing at least 53 people, including civilians.
- The Houthis responded by threatening to "meet escalation with escalation" and claimed to have launched attacks on the USS Harry S. Truman carrier strike group.
- Regions Targeted in Airstrikes:
- The U.S. airstrikes focused on key Houthi strongholds, including Sana’a (capital) and Sa’dah, near the Saudi Arabian border.
- Other affected areas included Houthi-controlled military sites that posed a threat to maritime trade in the Red Sea and Gulf of Aden.
- The strikes were carried out in response to Houthi attacks on international shipping routes, which have disrupted trade and freedom of navigation.
Kyushu Island
Why in news?
- Japan's government recently revealed plans to explore deploying long-range missiles on Kyushu, a southwestern island, to enhance regional defence capabilities.
About Kyushu Island:
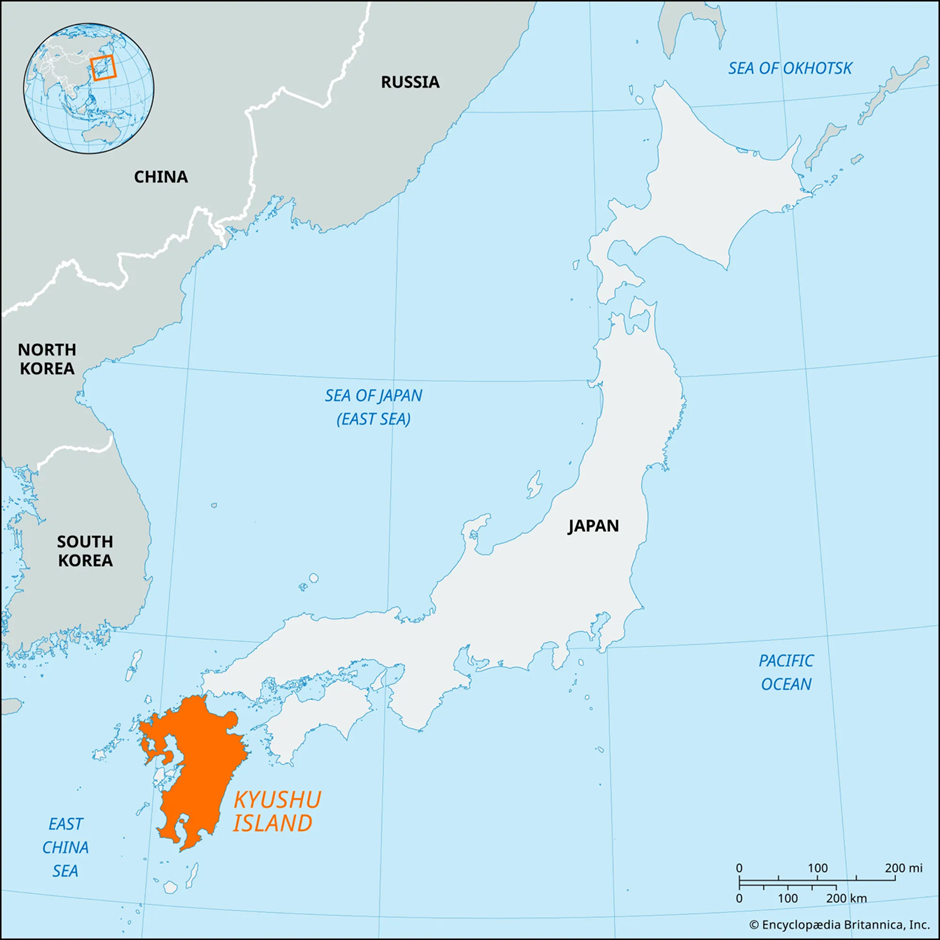
- Location and Strategic Importance:
- Kyushu is the third-largest island of Japan, located in the southwestern part of the country.
- It is bordered by the East China Sea (west) and the Pacific Ocean (east) and is separated from Honshu by the Kanmon Straits.
- Major cities on the island include Fukuoka, Nagasaki, Kumamoto, and Kagoshima, making it a key economic and military region.
- Due to its proximity to China, Taiwan, and the Korean Peninsula, Kyushu holds strategic significance in Japan’s national security framework.
- Reason Behind Missile Deployment:
- The Japanese government is considering deploying long-range missiles on Kyushu to strengthen its defence posture against regional threats.
- China’s increasing military assertiveness, especially around the Senkaku Islands (Diaoyu Islands in Chinese) in the East China Sea, has raised security concerns for Japan.
- North Korea’s frequent missile tests, some of which have flown over Japanese territory, have further heightened Japan’s need for enhanced deterrence.
- Rising tensions in the Taiwan Strait have also prompted Japan to reinforce its southwestern defence line, as any potential conflict involving Taiwan could directly impact Japan’s security.
- Regional Disputes and Strategic Implications:
- Japan has an ongoing territorial dispute with China over the Senkaku Islands, which China also claims.
- The U.S.-Japan alliance plays a crucial role in countering threats from China and North Korea, with Kyushu being a vital base for U.S. military operations.
- The missile deployment would serve as a deterrent against regional aggressors, ensuring Japan’s territorial integrity and maritime security.
- This move aligns with Japan’s recent military expansion policies, emphasising counterstrike capabilities to defend against possible attacks.
Mudumal
Why in news?
- Telangana's Mudumal Megalithic Menhirs were recently included in India’s tentative UNESCO World Heritage list, emphasizing their archaeological and historical importance.
About Mudumal:
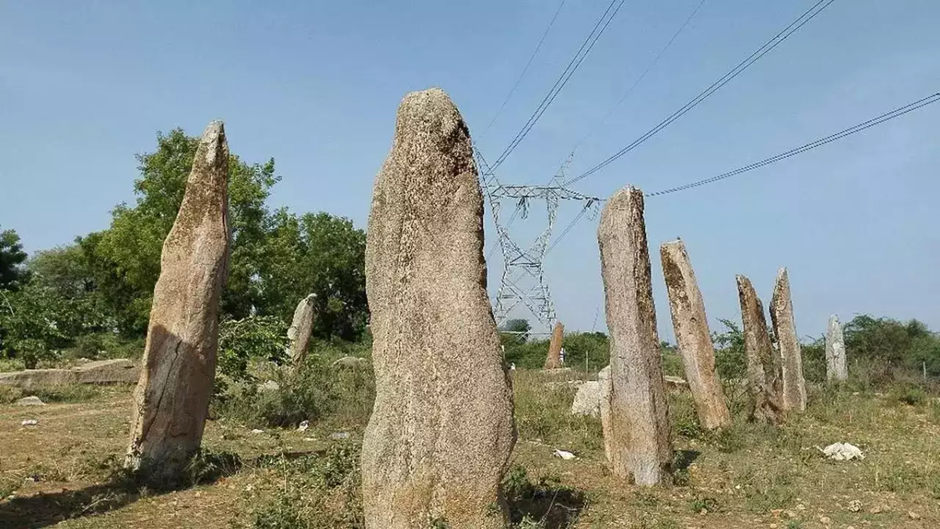

- Location and Historical Significance:
- Mudumal Megalithic Menhirs are located in Telangana, India, and are considered one of South India’s largest megalithic burial sites.
- The site spans 80 acres and consists of around 80 menhirs (10-14 feet high) and 3,000 alignment stones, possibly linked to ancient funerary rites.
- Dating back 3,500–4,000 years, these megaliths reflect advanced prehistoric knowledge of astronomy and mathematics, making them a crucial archaeological site.
- Megalithic Burials and Their Types:
- Megaliths are stone structures used as burial sites or commemorative memorials, mostly from the Iron Age (1500–500 BCE) in India.
- Types of megalithic burials include:
- Dolmenoid Cists: Box-shaped burial chambers made of stone slabs.
- Cairn Circles: Circular arrangements of stones marking graves.
- Capstones: large mushroom-shaped burial chambers, mainly found in Kerala.
- Menhirs: upright standing stones, often serving as memorials or astronomical markers.
- The Mudumal site likely served both funerary and astronomical purposes, with its menhirs aligning with equinoxes and solstices.
- Cultural and Religious Significance:
- Some Mudumal menhirs are worshipped by locals, referred to as "Niluralla Thimmappa" (Thimmappa of the Standing Stones).
- A unique cup-marked menhir at the site is believed to be South Asia’s earliest depiction of a constellation (Ursa Major/Saptarshi Mandal).
- One particular menhir is revered as Goddess Yellamma, showcasing a blend of prehistoric and living traditions.
5. UNESCO Recognition and Future Prospects:
- Telangana has one existing UNESCO World Heritage Site, Ramappa Temple (inscribed in 2021).
- The Mudumal Menhirs were included in the UNESCO Tentative List in 2025, along with other significant sites such as:
- Kanger Valley National Park (Chhattisgarh).
- Ashokan Edict Sites (Multiple States).
- Chausath Yogini Temples (Madhya Pradesh & Odisha).
- Gupta Temples (Multiple States).
- Palace-Fortresses of the Bundelas (Madhya Pradesh & Uttar Pradesh).
Balochistan and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa
Why in news?
-
- Pakistan witnessed a 73% rise in terrorism-related deaths, with Balochistan and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa being the most affected regions, according to a recent report highlighting escalating security concerns.
- Pakistan witnessed a 73% rise in terrorism-related deaths, with Balochistan and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa being the most affected regions, according to a recent report highlighting escalating security concerns.
About Balochistan and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa:
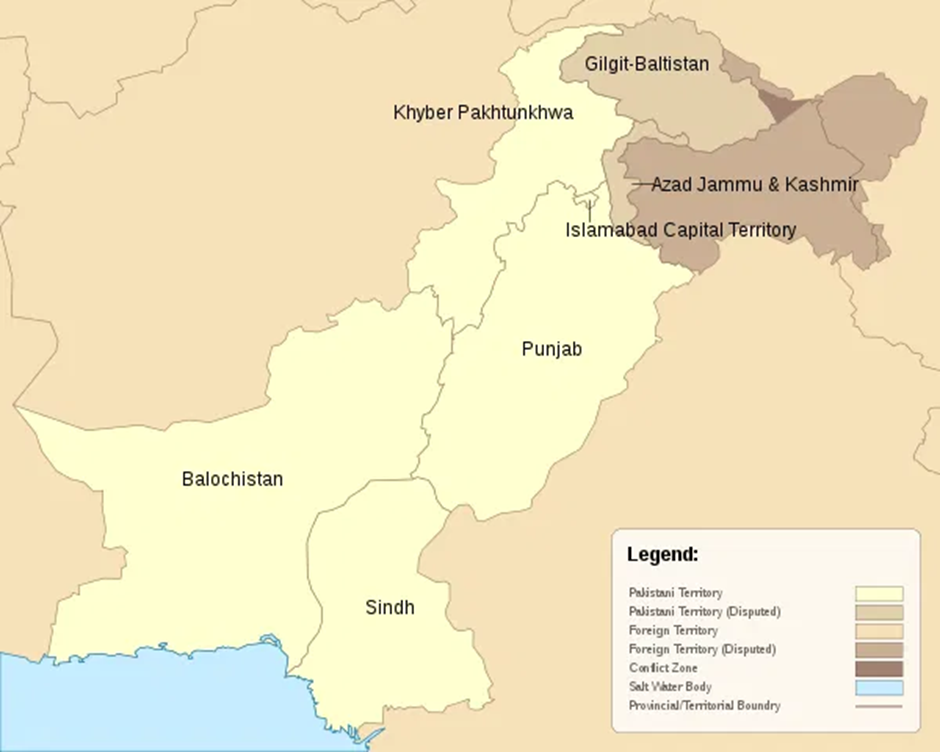
- Location and Geography:
- Balochistan is the largest province of Pakistan by area, located in the southwest of the country.
- It shares borders with Iran (west), Afghanistan (northwest), Punjab and Sindh (east), and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (northeast), along with a coastline along the Arabian Sea (south). The province is largely arid and mountainous, with sparse population density.
- Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (KP) lies in northwestern Pakistan, bordering Afghanistan through the historically significant Durand Line.
- It is known for its rugged terrain, tribal belt, and mountain ranges, including the Hindu Kush. The province includes the Khyber Pass, a strategic route connecting South Asia to Central Asia.
- Reasons Behind the Surge in Terrorist-Related Deaths:
- Resurgence of Tehrik-i-Taliban Pakistan (TTP): The TTP, an umbrella group of militant factions, has intensified attacks, particularly in KP and Balochistan, following the collapse of a ceasefire with the Pakistani government in late 2022.
- Ethno-Nationalist Insurgencies in Balochistan: Separatist groups such as the Balochistan Liberation Army (BLA) and Balochistan Liberation Front (BLF) have escalated attacks against security forces, infrastructure, and Chinese interests due to long-standing grievances over economic marginalisation and resource exploitation.
- Cross-Border Militancy: The Afghan Taliban’s return to power (2021) has emboldened militant groups, providing them safe havens in Afghanistan, leading to increased cross-border attacks in KP and Balochistan.
- Sectarian and Religious Extremism: Groups like ISIS-Khorasan (ISIS-K) and Lashkar-e-Jhangvi (LeJ) have carried out targeted attacks against Shia Muslims, particularly in Quetta (Balochistan) and parts of KP.
- China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) Attacks: Baloch separatists oppose CPEC projects, particularly in Gwadar, targeting Chinese nationals and infrastructure, citing exploitation of local resources without benefits to native Baloch communities.
- Weak Governance and Security Vacuum: The Pakistani state's inability to fully control tribal areas and address socio-economic grievances has allowed militant groups to operate freely.
- Hotspot Regions of Terrorist Activities:
- Balochistan:
- Quetta (provincial capital): frequent bombings and sectarian violence.
- Gwadar: CPEC-related attacks targeting Chinese nationals.
- Turbat and Panjgur: hubs of Baloch separatist insurgencies.
- Chaman: a key border town with cross-border militant movement.
- Khyber Pakhtunkhwa:
- North Waziristan & South Waziristan: strongholds of TTP and Haqqani Network.
- Swat Valley: resurgence of militant activity despite past military operations.
- Peshawar: frequent bombings, including attacks on police and military.
- Khyber District & Bajaur: cross-border infiltration zones with Afghan militants.
|
UPSC CSE PYQs Q1. Which one of the following statements best reflects the issue with Senkaku Islands, sometimes mentioned in the news? (2022)
Answer: Option B Q2. Consider the following pairs:
Which of the above pairs is/ are correctly matched?
Answer: Option A |
|
Also Read |
|
| FREE NIOS Books | |




