- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
World-First Cybercrime Index
World-First Cybercrime Index
13-04-2024

An international team of researchers has prepared the first 'World Cyber Crime Index' after 3 years of intensive research.
Insights into the World Cybercrime Index:
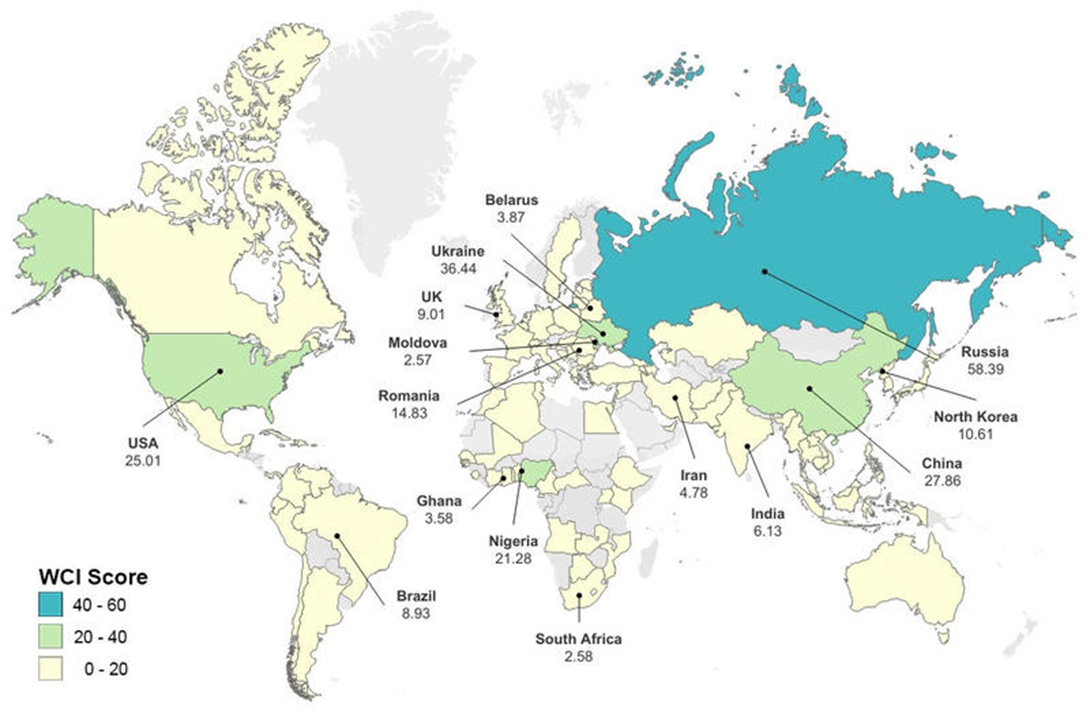
- The index identifies the world's major cybercrime hotspots by ranking the most significant sources of cybercrime at the national level.
- It is a joint partnership between the University of Oxford and UNSW Canberra.
- The data for the index was gathered through a survey of 92 leading cybercrime experts worldwide involved in cybercrime intelligence gathering and investigations.
- The index ranks approximately 100 countries and identifies key hotspots according to various cybercrime categories, including ransomware, credit card theft, and scams.
- Key Findings:
- The threat of cybercrime is not evenly distributed worldwide.
- Russia tops the list, followed by Ukraine, China, the USA, Nigeria, and Romania.
- India is at 10th position in the ranking.
- Researchers also found that certain types of cybercrime were associated with particular countries. For example, the United States was associated with data and identity theft, while those related to technical products or services seemed to often originate from China.
The 5 major categories of cybercrime assessed by the study were:
- Technical products/services (e.g. malware coding, botnet access, access to compromised systems, tool production).
- Attacks and extortion (e.g. denial-of-service attacks, ransomware).
- Data/identity theft (e.g. hacking, phishing, account compromises, credit card comprises).
- Scams (e.g. advance fee fraud, business email compromise, online auction fraud).
- Cashing out/money laundering (e.g. credit card fraud, money mules, illicit virtual currency platforms).
It is estimated that cybercrime cost the world around $9.22 trillion in 2024, expected to grow to $13.82 trillion by 2028.
FAQs:
Q1: What is Ransomware?
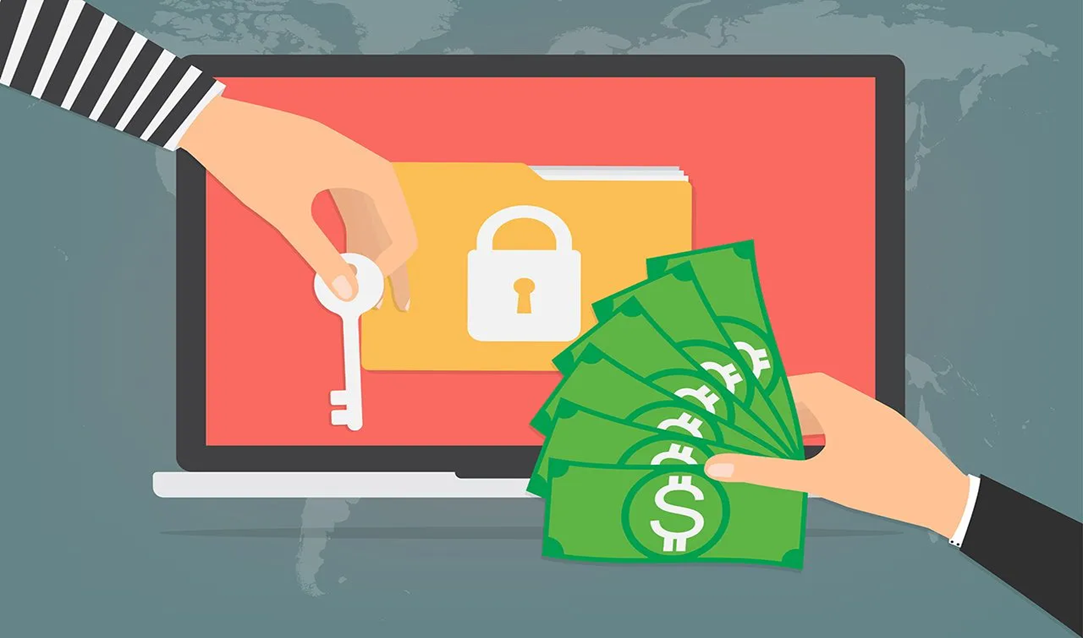

Ransomware is a type of malicious software that prevents users from accessing their computer files, networks, or systems, and demands payment to return them. Ransomware attacks can cause costly disruptions to operations and the loss of critical information and data.
Recent Example: AIIMS Delhi also faced a cyber-attack last year, which brought down its servers and disrupted functioning at AIIMS, including appointments and registrations, billing, laboratory report generation, etc.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi


