- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
World Bank Makes Appointments Under the Indus Water Treaty (IWT)
World Bank Makes Appointments Under the Indus Water Treaty (IWT)

- Recently, the World Bank appointed Neutral Expert on IWT backed India's stance on its competence regarding a dispute over 2 hydroelectric projects in Jammu and Kashmir.
- Complaint & Dispute Resolution: Pakistan filed a complaint in 2015, triggering dual-track dispute resolution through:
- Neutral Expert (India's request)
- Permanent Court of Arbitration (Pakistan's request)
- Disputed Projects:
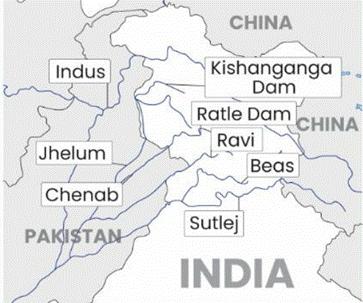
- Kishenganga Project (330 MW, inaugurated in 2018) on the Jhelum River
- Ratle Project (850 MW, under construction) on the Chenab River
- Pakistan's Objections: Pakistan argues that these run-of-river projects could
affect its water flow and agricultural lands.
About the Indus Water Treaty (IWT)
- Signed in 1960 between India and Pakistan, mediated by the World Bank.
- Water Usage Rights:
- Eastern Rivers (Ravi, Beas, Sutlej) allocated to India for unrestricted use.
- Western Rivers (Indus, Jhelum, Chenab) allocated to Pakistan, with India permitted specific non-consumptive uses like navigation, timber floating, flood protection, and hydroelectric power generation.
- India gets about 30% of the Indus River System’s water, while Pakistan gets 70%.
- Implementation: Both countries must appoint Permanent Indus Commissioners for communication and treaty implementation.
Dispute Resolution Mechanism
- Three-Level Graded Mechanism:
- Permanent Indus Commission (PIC): Resolves disputes about treaty interpretation or violations.
- Neutral Expert: Technical disputes that cannot be settled by PIC, appointed by the World Bank or jointly by India and Pakistan.
- Court of Arbitration: A 7-member tribunal for legal adjudication if earlier levels fail.
Challenges and Way Forward regarding the Indus Water Treaty (IWT):
|
Challenges |
Way Forward |
|
|
Pakistan's Opposition to Indian Projects : Pakistan opposes Indian projects like Kishenganga and Ratle hydroelectric projects, questioning their compliance with the treaty's technological criteria. |
Integrated Water Management & Climate Adaptation: Focus on sustainable water use, conservation, and flood management through joint river basin management approaches. |
|
|
Environmental Concerns : Climate change and the rapid melting of Himalayan glaciers are altering river flow and water availability in the Indus system. |
Modernization and Renegotiation: Renegotiate the treaty to incorporate technological advancements, new data on river flow, and the changing environmental conditions. |
|
|
India's Growing Water Needs : India's growing population, agricultural expansion, and energy demands are putting pressure on water resources. |
Adopt Principles of International Water Law: - Reevaluate water usage rights using principles like Equitable and Reasonable Utilization (ERU) and the No Harm Rule (NHR) to ensure fairness in allocation. |
|
|
Security & Political Tensions : Water is being seen as a strategic asset and has been linked to political tensions, especially in light of cross-border terrorism (e.g., Uri attack 2016). The use of water as a political tool (e.g., "blood and water cannot flow together") increases security concerns. |
Transparency & Data Sharing: Establish transparent, real-time satellite-based monitoring and data-sharing systems for water flow, dam operations, and flood management to reduce tensions. Promote dialogue and cooperation between India and Pakistan to address security-related water issues and foster mutual trust. |
|
International Principles on Transboundary Water Sharing
- Helsinki Rules (1966): Governs the use of shared rivers and groundwater, encouraging dispute resolution through negotiation and international courts.
- Helsinki Convention (1992): Legal framework to prevent and control transboundary water pollution, requiring parties to follow the precautionary principle.
- UN Watercourses Convention (1997): Establishes rules for cooperation between watercourse states, emphasizing equitable and reasonable use and no significant harm to neighbors
|
Also Read |
|
| FREE NIOS Books | |




