- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
WMO forecasts regarding heatwaves in oceans
WMO forecasts regarding heatwaves in oceans
08-09-2023
Latest Context:
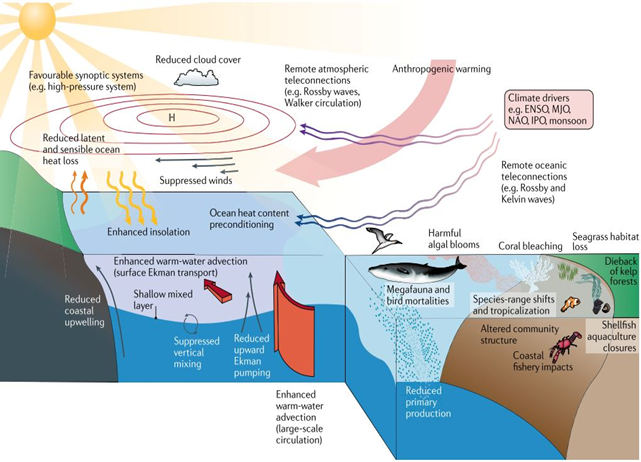
Recently, the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) forecasted that marine heatwaves may extend till 2024.
What are Marine Heatwaves?
- Marine heatwaves are prolonged periods of unusually warm sea surface temperatures in the ocean.
- These events are similar in concept to heatwaves that occur on land.
- Marine heatwaves can last for days, weeks, or even months, and their duration can vary widely depending on the specific event and location.
- The intensity of a marine heatwave is determined by how much warmer the sea surface temperatures are compared to the historical average.
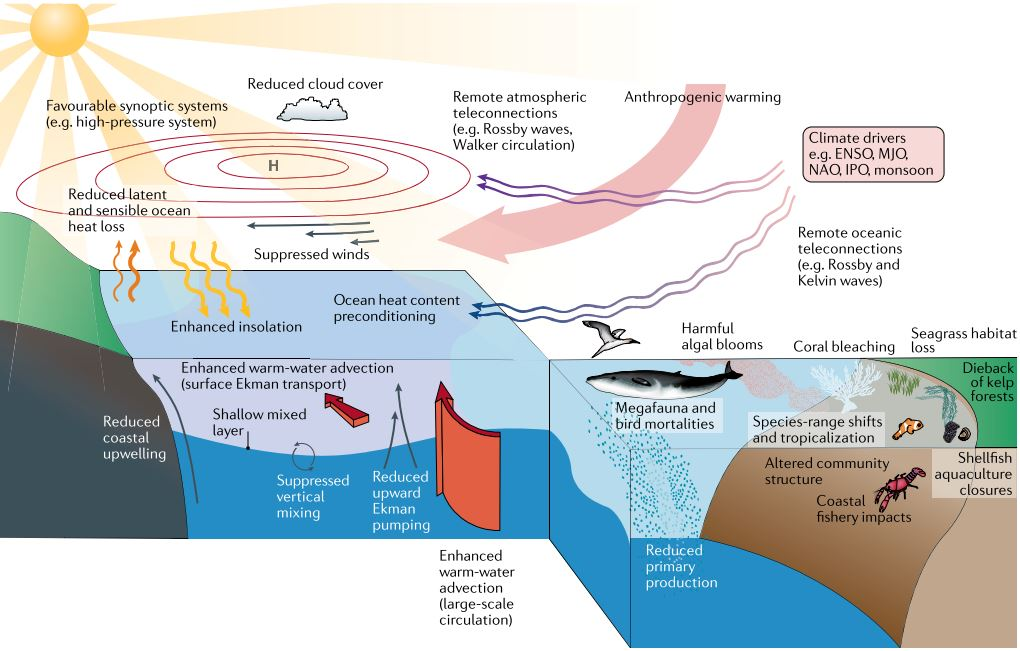
Causes of Marine Heatwaves are:
- Climate Variability: Events like El Niño and La Niña, can contribute to the development of marine heatwaves. El Niño events, for example, are associated with warmer-than-average sea surface temperatures in parts of the Pacific Ocean and can lead to widespread marine heatwaves in affected regions.
- Ocean Currents: Changes in ocean currents can transport warm water masses to regions, where they typically do not occur. When warm water is transported into a particular area, it can lead to increased sea surface temperatures and the development of a marine heatwave.
- Atmospheric Conditions: Weather patterns and atmospheric conditions can play a big role. High-pressure systems and persistent weather patterns can trap heat in a region, leading to prolonged periods of warm sea surface temperatures.
- Climate Change: Long-term climate change, driven by the increase in greenhouse gas emissions, is a significant contributor to the increasing frequency and intensity of marine heatwaves. The overall warming of the planet leads to warmer ocean temperatures.
- Localized Factors: In some cases, local factors can contribute to the development. For example, coastal upwelling, which is the rising of cold, nutrient-rich waters to the surface, can be disrupted, allowing warmer water to dominate the surface layer and lead to elevated temperatures.
Impacts of Marine Heatwaves can be:
- Ecosystem Stress and Disruption: Marine heatwaves can cause stress to marine ecosystems, including kelp forests and seagrass beds. Increased temperatures can lead to reduced growth rate of marine plants, and shifts in the distribution and behaviour of marine species. This disruption can have negative effects throughout the food web.
- Species Mortality: In severe marine heatwaves, many marine species may not be able to tolerate the extreme temperatures, leading to mass mortality events.
- Changes in Species Distribution: Some species may move to different areas in response to the changing temperatures, seeking cooler waters. This can lead to shifts in the distribution of commercially important species and alter the composition of marine communities.
- Harm to Commercial Fisheries: MHWs can harm commercial fisheries by affecting the abundance and distribution of target species. This can result in reduced catches and economic losses for fishing industries. Fisheries management may need to adapt to these changes.
- Coral Bleaching: One of the most well-documented impacts of MHWs is coral bleaching. Increased sea temperatures can cause corals to expel their symbiotic algae (zooxanthellae), which provide them with nutrients and their vibrant colours. Repeated or severe bleaching events can lead to coral mortality and the degradation of coral reefs.
- Economic Impacts: Industries such as tourism, recreational fishing, and coastal real estate can suffer economic losses due to marine heatwaves. Coral reef tourism, for example, can be severely impacted by bleaching events, which deter tourists and damage the tourism industry.
- Oceanographic Consequences: Marine heatwaves can influence ocean circulation patterns and atmospheric conditions, which can have broader climate impacts, including changes in weather patterns and precipitation.
- Reduced Oxygen Levels: Warmer waters can hold less dissolved oxygen, leading to the expansion of low-oxygen zones. Oxygen-depleted waters can harm or displace marine life that relies on oxygen to survive.
- Toxic Algal Blooms: Some harmful algal species that lives in warm water conditions can increase. They release toxins which are harmful to marine life, human health, and seafood industries.



