- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
What is an Aphelion?
What is an Aphelion?
06-07-2024
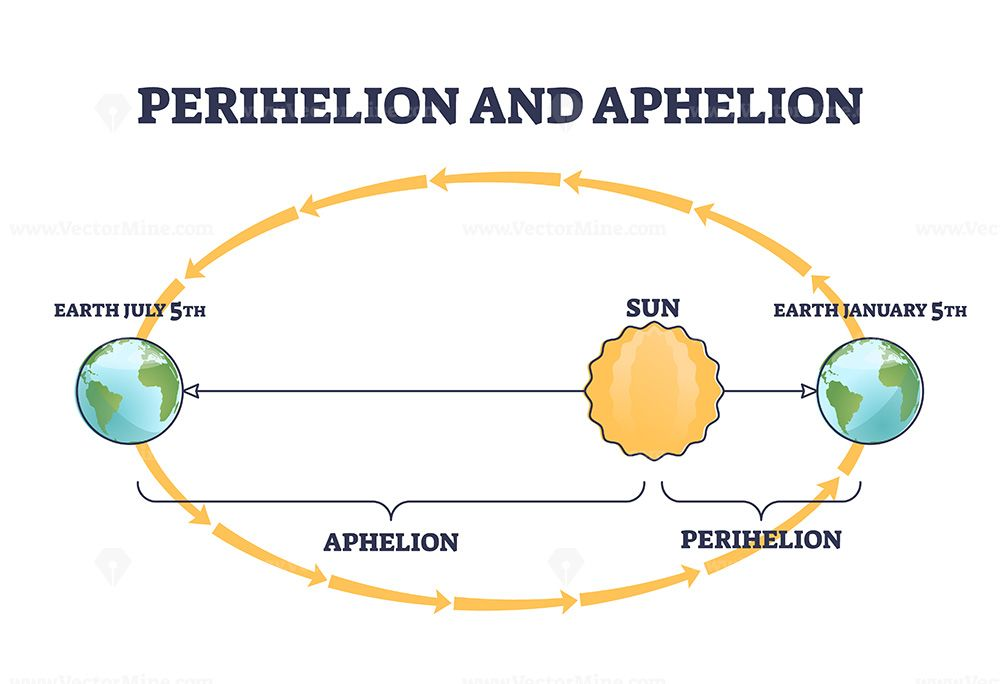
At aphelion, Earth’s distance from the Sun is about 152.1 million km.
Aphelion refers to the point in the Earth's orbit where it is farthest from the Sun. Earth reaches aphelion every July. This year it did so on Friday.
Elliptical Orbits and Gravity
- The orbits of all planets in the solar system, including Earth, are elliptical rather than circular.
- This is due to the gravitational influence of other planets, particularly Jupiter, which is the most massive planet in our solar system.
- The gravitational pull of other planets causes the orbits to deviate from perfect circles, resulting in elliptical shapes.
Eccentricity and its Effects
- Eccentricity measures how much an orbit deviates from a perfect circle.
- The higher the eccentricity, the more elliptical the orbit.
- Earth's eccentricity is 0.017, which means its orbit is relatively close to a perfect circle.
- Other bodies in the solar system, such as Mars and Pluto, have more pronounced eccentricities, resulting in more elliptical orbits.
Distance from the Sun at Aphelion
- At aphelion, Earth's distance from the Sun is approximately 152.1 million kilometers.
- This is about 5 million kilometers farther than its average distance from the Sun.
- Six months later, in early January, Earth reaches perihelion, its closest point to the Sun, with a distance of roughly 147.1 million kilometers.
Impact on Temperatures and Seasons
- A common misconception is that Earth's varying distance from the Sun causes the seasons.
- In reality, the tilt of Earth's axis is the primary factor in determining the seasons.
- However, the varying distance from the Sun does have a minor effect on temperatures.
- At aphelion, the Northern Hemisphere receives about 7% less sunlight, resulting in slightly milder summers and winters.
- This effect is offset by the tilt of Earth's axis, which means that the hemispheres are either closer to or farther from the Sun at different points in the orbit.
Consequences of a Perfectly Circular Orbit
- If Earth's orbit were a perfect circle, the seasons would be exactly the same length.
- However, this would not have a significant impact on the planet's climate or habitability.
Consequences of a More Eccentric Orbit
- If Earth's orbit became more eccentric, the consequences could be catastrophic.
- Seasons in the Southern Hemisphere would become extreme, with unbearably hot summers and intolerably cold winters.
- This could lead to crop failures and freezes, making advanced civilization impossible.
- Fortunately, Earth's orbit is currently in a "sweet spot," allowing for a relatively stable and habitable climate.
Key Takeaways:
- Aphelion is the point in Earth's orbit where it is farthest from the Sun, occurring every July.
- Elliptical orbits are a result of gravitational influence from other planets, particularly Jupiter.
- Eccentricity measures the deviation of an orbit from a perfect circle, with higher eccentricity resulting in more elliptical orbits.
- The varying distance from the Sun has a minor effect on temperatures, but the tilt of Earth's axis is the primary factor in determining the seasons.
- A more eccentric orbit could have catastrophic consequences for the planet's climate and habitability.
- Earth's current orbit is in a "sweet spot," allowing for a relatively stable and habitable climate.



