- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
US SCIENTISTS ACHIEVED NET ENERGY GAIN IN NUCLEAR FUSION
US SCIENTISTS ACHIEVED NET ENERGY GAIN IN NUCLEAR FUSION
Latest Context
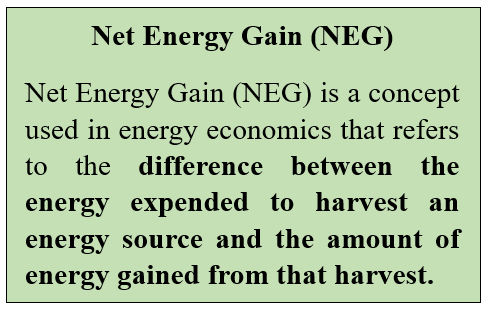
Recently, for the second time, US Scientists have achieved Net Energy Gain (NET) in a fusion reaction.
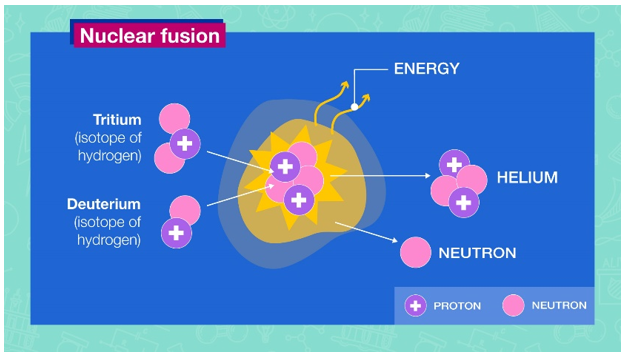
Nuclear Fusion: Nuclear fusion is the process by which two light atomic nuclei combine to form a single heavier one while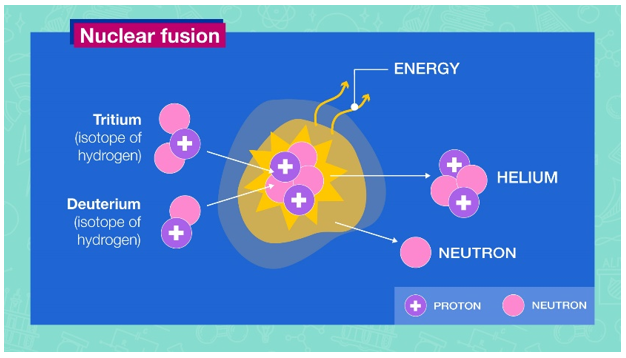 releasing massive amounts of energy. It takes place in a state of matter called plasma — a hot, charged gas made of positive ions and free-moving electrons with unique properties distinct from solids, liquids or gases.
releasing massive amounts of energy. It takes place in a state of matter called plasma — a hot, charged gas made of positive ions and free-moving electrons with unique properties distinct from solids, liquids or gases.
Nuclear Fission: In this process, the nucleus of an atom splits into two or more smaller nuclei. The fission process often produces gamma photons and releases a very large amount of energy even by the energetic standards of radioactive decay
Reasons for Studying Nuclear Fusion
- Fusion could generate four times more energy per kilogram of fuel than fission (used in nuclear power plants) and nearly four million times more energy than burning oil or coal
Benefits of Nuclear Fusion
- No carbon emissions: The only by-products of fusion reactions are small amounts of helium, an inert gas that can be safely released without harming the environment.
- Abundant fuels: Deuterium can be extracted from water and tritium will be produced inside the power station from lithium, an element abundant in the earth’s crust and seawater. Even with the widespread adoption of fusion power stations, these fuel supplies would last for many thousands of years.
- Energy efficiency: One kilogram of fusion fuel could provide the same amount of energy as 10 million kilograms of fossil fuel. A 1-Gigawatt fusion power station will need less than one tonne of fuel during a year’s operation
- Safety: A large-scale nuclear accident is not possible in a fusion reactor. The amounts of fuel used in fusion devices are very small (about the weight of a postage stamp at any one time). Furthermore, as the fusion process is difficult to start and keep going, there is no risk of a runaway reaction which could lead to a meltdown.
- Reliable power: Fusion power plants will be designed to produce a continuous supply of large amounts of electricity. Once established in the market, costs are predicted to be broadly similar to other energy sources.
International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER): It is one of the most ambitious energy projects in the world today.
- In southern France, 35 nations are collaborating to build the world's largest tokamak, a magnetic fusion device that has been designed to prove the feasibility of fusion as a large-scale and carbon-free source of energy based on the same principle that powers our Sun and stars
- India is part of the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) project to demonstrate NEG from fusion reactors
- India has also constructed its indigenous tokamak ADITYA and semi-indigenous Steady State Superconducting Tokamak (SST-1).
Must Check: IAS Coaching Centre In Delhi



