- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- NCERT Medieval History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Union Budget 2024-2025
Union Budget 2024-2025
24-07-2024
The Union Budget 2024-25 was presented by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman on July 23, 2024, her seventh consecutive budget.
- The budget is significant as it surpasses the record of six consecutive budgets presented by Morarji Desai.
- This budget presentation is a quinquennial event in India, typically occurring once every five years. Because Union Budget is presented twice:
- first as an interim budget by the outgoing government and,
- Then as a full budget by the newly-formed government.
Constitutional Reference:
- The Budget is referred to as the Annual Financial Statement in the Constitution (Article 112).
- The budget is a statement covering estimated expenditure and receipts for the Government of India in a financial year.
Historical Context:
- The Government of India had two separate budgets (railway and general budget) until 2016.
- The railway budget was merged with the general budget in 2016, scrapping a 92-year-old practice.
Economic Overview
- India's economic growth remains strong despite global uncertainties
- Inflation is low and stable, moving towards the 4% target
- Core inflation (non-food, non-fuel) is at 3.1%
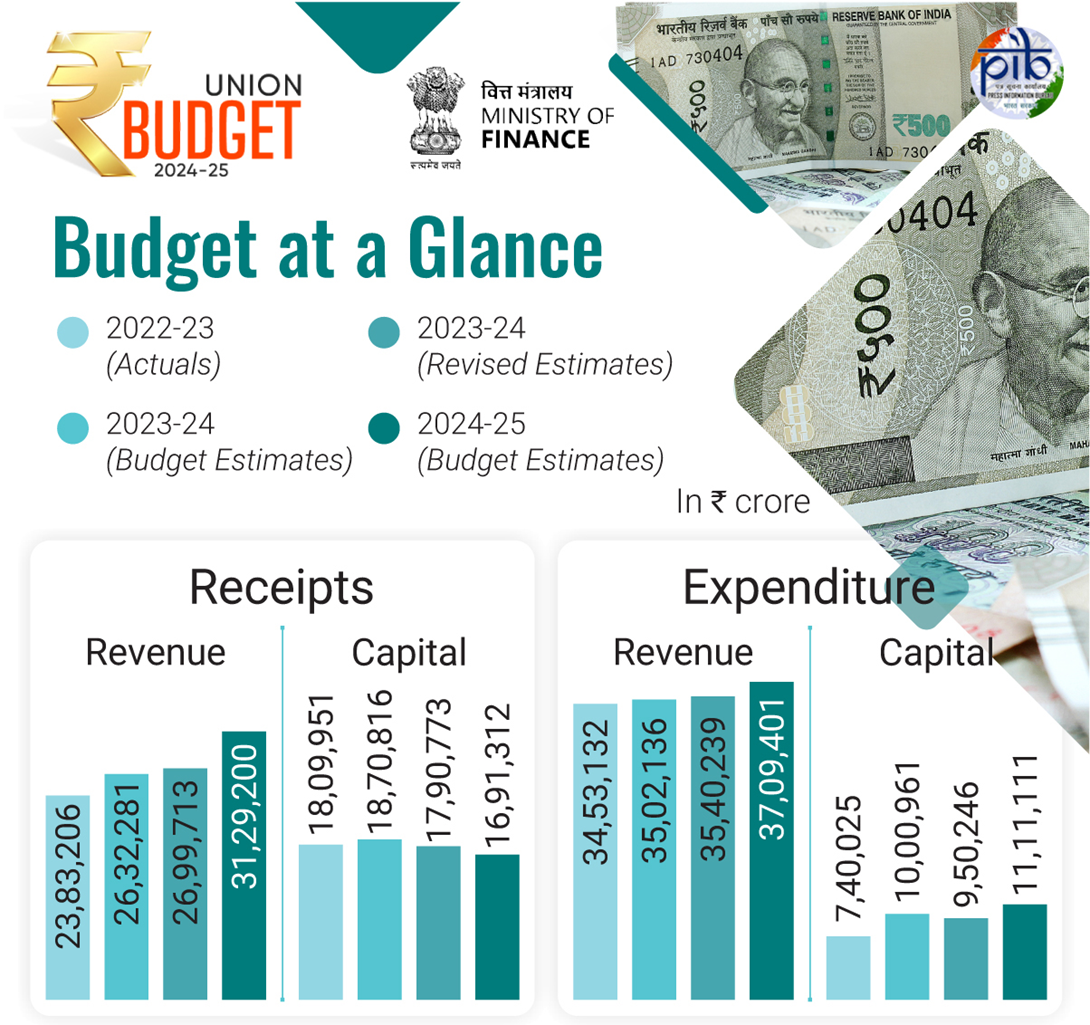
Fiscal Management
- Total receipts (excluding borrowings): ₹32.07 lakh crore
- Total expenditure: ₹48.21 lakh crore
- Net tax receipts: ₹25.83 lakh crore
- Fiscal deficit: 4.9% of GDP
- Gross and net market borrowings through dated securities: ₹14.01 lakh crore and ₹11.63 lakh crore respectively
- Aim to reach deficit below 4.5% by next year
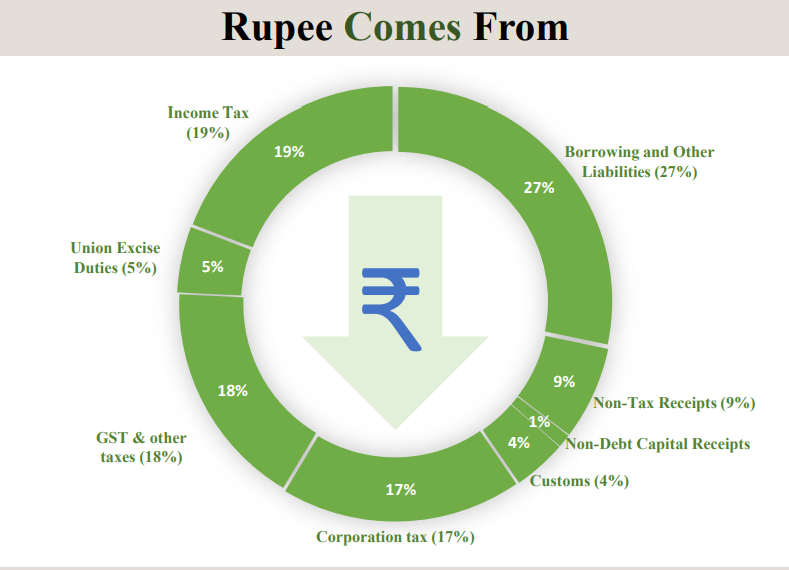
Rupee comes from :
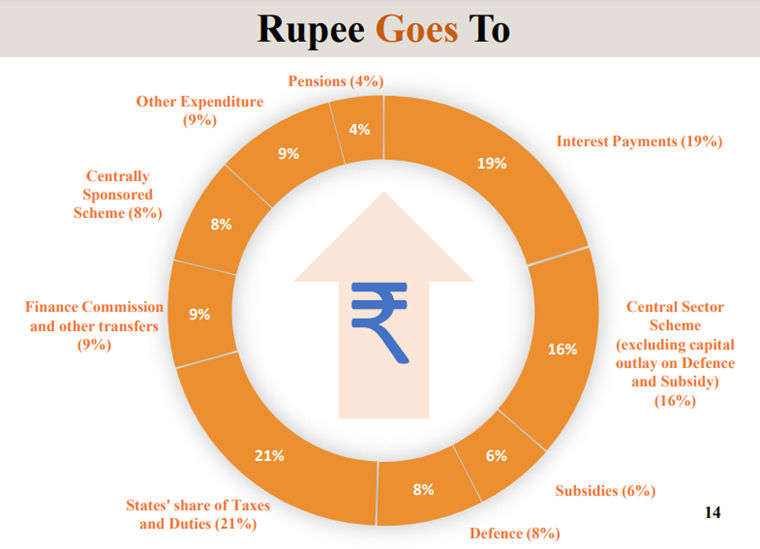
Rupees Goes To:
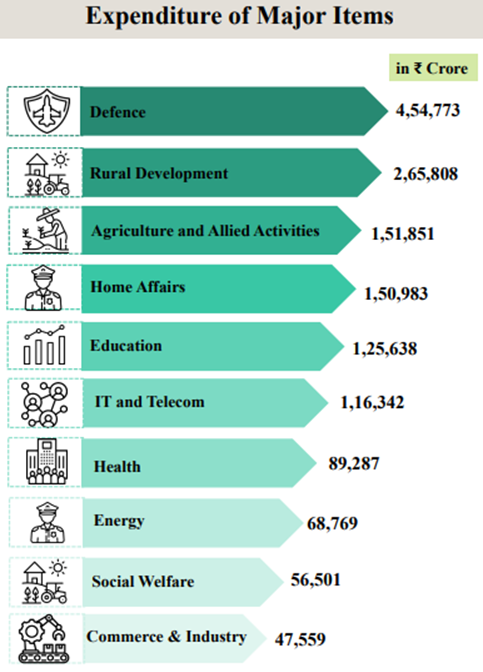
Expenditure of Major Items:
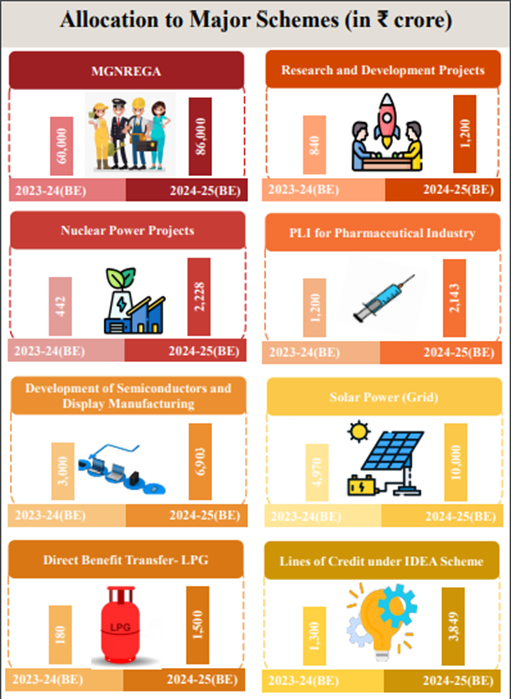
Allocation to Major Schemes:
Budget Focus and Priorities
- Four major castes emphasized:
- 'Garib' (Poor)
- 'Mahilayen' (Women)
- 'Yuva' (Youth)
- 'Annadata' (Farmer)
- Main focus areas:
- Employment
- Skilling
- MSMEs
- Middle class
- Nine priorities for 'Viksit Bharat' (Developed India):
- Productivity and resilience in Agriculture
- Employment & Skilling
- Inclusive Human Resource Development and Social Justice
- Manufacturing & Services
- Urban Development
- Energy Security
- Infrastructure
- Innovation, Research & Development
- Next Generation Reforms
Key Initiatives and Allocations
Agriculture and Allied Sectors
- ₹1.52 lakh crore allocated
- Comprehensive review of agriculture research setup
- 109 new high-yielding and climate-resilient crop varieties
- 1 crore farmers to be initiated into natural farming in next two years
- 10,000 need-based bio-input resource centres to be established
- Focus on self-sufficiency in pulses and oilseeds
- Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) in agriculture to cover farmers and their lands in 3 years
Employment and Skilling
- ₹2 lakh crore package for 4.1 crore youth over 5 years
- ₹1.48 lakh crore allocated for education, employment, and skilling
- Three Employment Linked Incentive schemes
- New centrally sponsored skilling scheme
- 20 lakh youth to be skilled over 5 years
- 1,000 Industrial Training Institutes to be upgraded
- Model Skill Loan Scheme revised (up to ₹7.5 lakh loans)
- Financial support for higher education loans (up to ₹10 lakh)
- Comprehensive scheme for internship opportunities in 500 top companies for 1 crore youth in 5 years
Social Development and Inclusive Growth
- Purvodaya plan for eastern region development (Bihar, Jharkhand, West Bengal, Odisha, Andhra Pradesh)
- Pradhan Mantri Janjatiya Unnat Gram Abhiyan for tribal communities (63,000 villages, 5 crore tribal people)
- 100 new India Post Payment Bank branches in North East
- ₹2.66 lakh crore for rural development
- More than ₹3 lakh crore allocated for schemes benefiting women and girls
MSMEs and Manufacturing
- New self-financing guarantee fund (up to ₹100 crore per applicant)
- Mudra loan limit increased to ₹20 lakh from ₹10 lakh
- 50 multi-product food irradiation units
- 100 food quality and safety testing labs with NABL accreditation
- E-Commerce Export Hubs in PPP mode
Urban Development
- PM Awas Yojana Urban 2.0: ₹10 lakh crore investment for 1 crore families
- Water supply, sewage, and waste management projects for 100 large cities
- Development of 100 weekly 'haats' or street food hubs annually for five years
Energy and Infrastructure
- PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana for rooftop solar (1 crore households, free electricity up to 300 units monthly)
- Focus on nuclear energy for future energy mix
- ₹11,11,111 crore allocated for capital expenditure (3.4% of GDP)
- PMGSY Phase IV for rural road connectivity to 25,000 rural habitations
- Irrigation and flood mitigation projects (₹11,500 crore for Bihar and support for Assam, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, and Sikkim)
Innovation and Research
- Anusandhan National Research Fund for basic research and prototype development
- ₹1 lakh crore financing pool for private sector-driven research and innovation
- ₹1,000 crore venture capital fund for space economy
- Goal to expand space economy 5 times in the next 10 years
Tax Reforms
Direct Taxes
- Standard deduction increased to ₹75,000 from ₹50,000 for new tax regime
- Deduction on family pension increased to ₹25,000 from ₹15,000
- Angel tax abolished for all classes of investors
- Corporate tax rate on foreign companies reduced to 35% from 40%
- Simplified tax regime for charities and TDS
- Assessments can be reopened up to 5 years (from 3 years) if escaped income is more than ₹50 lakh
Indirect Taxes
- GST simplification and rationalization planned
- Custom duties revised for various sectors
- Exemptions and reductions for:
- Cancer treating medicines (Trastuzumab Deruxtecan, Osimertinib, Durvalumab)
- X-ray machines, tubes, and flat panel detectors
- Mobile phones, PCBAs, and chargers (15% BCD)
- 25 rare earth minerals (including lithium)
- Capital goods for manufacturing solar panels
- Seafood export-related items
- Increased duties on certain items (e.g., ammonium nitrate, PVC flex banners)
Other Tax Measures
- Vivad se Vishwas Scheme 2024 for resolving income tax disputes
- Increased monetary limits for tax appeals (₹60 lakh for High Courts, ₹2 crore for Supreme Court, ₹5 crore for tribunals)
- Expansion of safe harbour rules
- Streamlined transfer pricing assessment procedure
Other Important Initiatives
- NPS Vatsalya: New pension plan for minors
- Review of New Pension Scheme (NPS) in progress
- Comprehensive review of Income Tax Act to reduce disputes and simplify
- Digitalization of remaining services of Customs and Income Tax
- Economic Policy Framework to be formulated for next generation reforms
- Labour-related reforms: Integration of e-shram portal, revamping of Shram Suvidha and Samadhan portals
- Development of taxonomy for climate finance
Conclusion
The Union Budget 2024-2025 focuses on inclusive growth, with emphasis on agriculture, employment, skilling, and social development. It introduces significant tax reforms and aims to boost various sectors of the economy while maintaining fiscal prudence. The budget sets ambitious targets for infrastructure development, energy security, and innovation, laying the groundwork for India's vision of becoming a developed nation.



