- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- NCERT Medieval History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PLACES IN NEWS 8th JULY 2025
PLACES IN NEWS 8th JULY 2025
08-07-2025

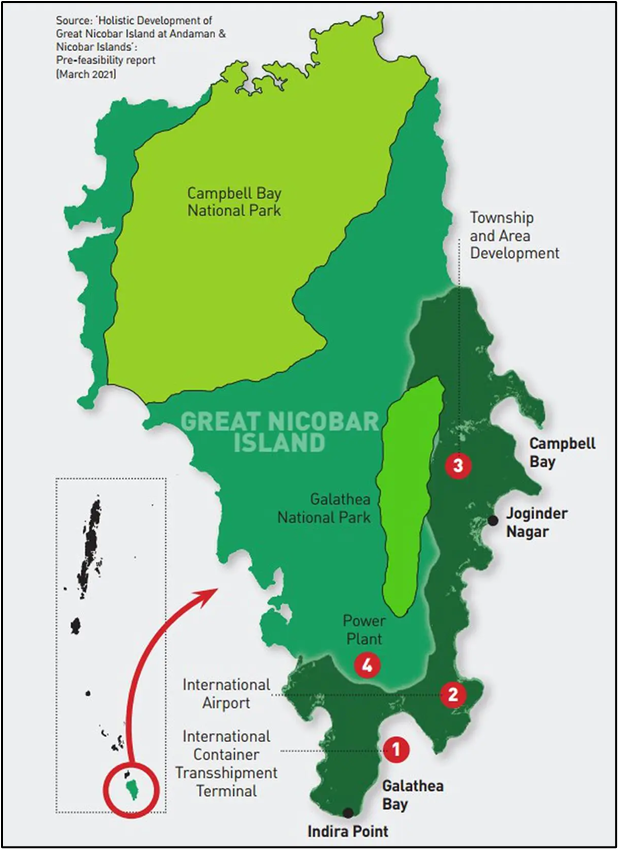
Great Nicobar
Why in the News?
- The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) has submitted a High-Powered Committee (HPC) report to the National Green Tribunal (NGT) on the Great Nicobar Island project.
- The NGT is reviewing it due to concerns over environmental impacts on coral reefs, forests, and wildlife.
- These concerns were raised by activists and researchers citing possible violations of environmental rules.
What are the Key Highlights?
- Geographical Location:
- Country: India
- Union Territory: Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Latitude & Longitude: Between 6°45′N to 7°15′N and 93°30′E to 94°10′E
- Location: Southernmost island of the Nicobar group in the Bay of Bengal
- Indira Point:
- Located on the southern tip of Great Nicobar Island
- Southernmost point of India
- Lies at 6°45′10″N latitude
- Submerged during the 2004 tsunami but later restored with a lighthouse
- Physical Features:
- Area: About 910 square kilometers
- Highest Peak: Mount Thullier (642 meters above sea level)
- Coastline: Rich in mangroves, sandy beaches, and coral reefs
- Seismic Zone: Earthquake-prone area; near the 2004 tsunami epicenter
- Ecological Importance:
- Home to Great Nicobar Biosphere Reserve, part of UNESCO’s Man and Biosphere Programme
- Rich biodiversity with endemic species like the Nicobar megapode and saltwater crocodile
- Dense tropical rainforests, coral reefs, and turtle nesting sites
- National Parks:
- Campbell Bay National Park:
- This National Park is located in the northern part of Great Nicobar Island, which is part of the Union Territory of Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India.
- It was established in 1992 to protect the rich biodiversity of the region.
- Galathea National Park:
- It is located in the southern part of Great Nicobar Island.
- This park was established in 1992.
- It covers an area of about 110 square kilometers and includes both land and coastal ecosystems, making it very important for conservation.
- Campbell Bay National Park:
- Tribes and Population:
- Inhabited by Shompens (a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group - PVTG) and Nicobarese tribes
- Population is sparse and mostly found in small villages
- Strategic Importance:
- Location is geopolitically significant, close to the Malacca Strait
- Plans for a transshipment port, International airport, and defense infrastructure to boost maritime presence
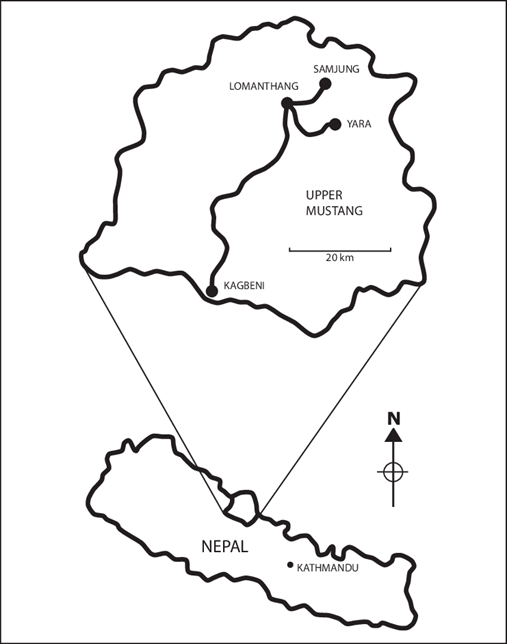
Samjung, Nepal
Why in the News?
- Samjung, a remote Himalayan village in Nepal, has come into focus due to the severe impacts of climate change.
- Residents are being forced to abandon their ancestral homes as snowfall declines, rainfall intensifies, and vital water sources vanish.
About the Place
- Location:
- Samjung is situated in the high-altitude Himalayan region of Nepal.
- Significance:
- Part of the Hindu Kush Himalaya (HKH) range.
- This range spans from Afghanistan to Myanmar.
- It contains the largest volume of ice outside the polar regions.
- Environmental Importance:
- Glaciers in this region feed major rivers.
- These rivers sustain over 240 million people in the mountains and 1.65 billion downstream.
- Climate Impact:
- According to the International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD), high-altitude areas like Samjung are warming faster than the lowlands.
- This is leading to glacier retreat, thawing permafrost, and erratic snowfall patterns.




