- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
UNDESA releases UN World Economic Situation and Prospects 2025 report
UNDESA releases UN World Economic Situation and Prospects 2025 report
04-02-2025
Recent Context
- Recently, in January 2025, the UN World Economic Situation and Prospects 2025 report was released by the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UN DESA),
- It was prepared in partnership with UN Trade and Development (UNCTAD) and the five UN regional commissions.
- The report comes at the mid-way point of a decade that has been characterized by economic turbulence. However, it shows that the global economy is finally recovering following a sequence of shocks.
|
United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UN DESA)
UN Trade and Development (UNCTAD)
Five regional Commissions
|
What are the key global economic highlights?
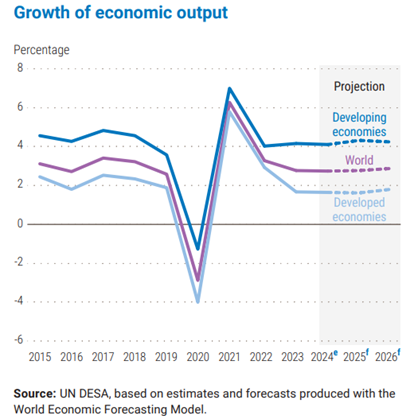
- Economic growth forecast:
- The Report has pegged the global economic growth forecast at 2.8% for 2025 and 2.9% for 2026, largely unchanged from previous years.
- Overall: Slower global growth than the pre-pandemic average of 3.2%
- Slower growth: China and the United States
- Modest Recovery: European Union, Japan, United Kingdom
- Strong Performance: In large developing economies like India and Indonesia.
- Slight improvement in growth for least developed countries (LDCs) in 2025
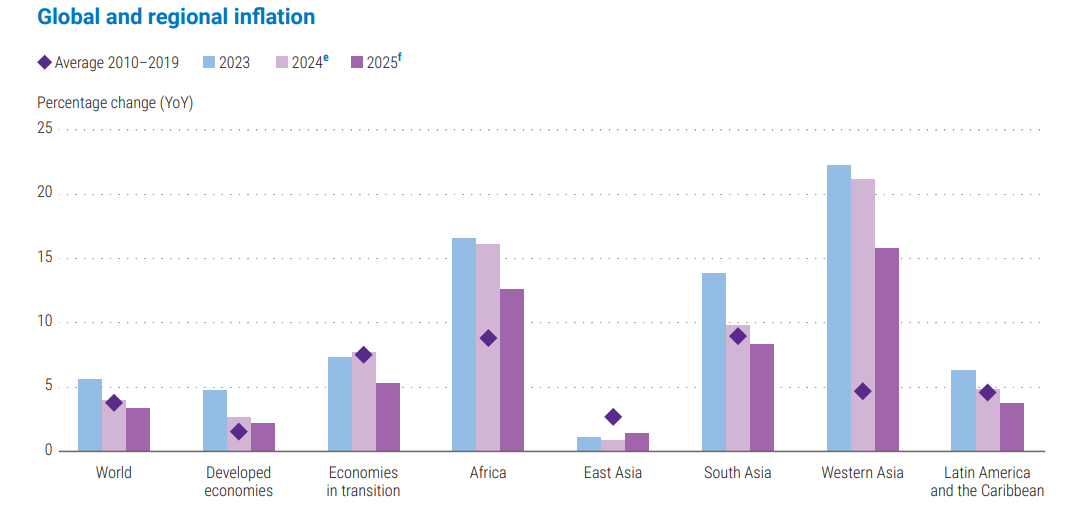
- Global inflation:
- Fall in global inflation from 4% in 2024 to 3.4% in 2025, driven by:
- Easing labour market pressures in developed economies
- Moderating international food and energy commodity prices.
- Fall in global inflation from 4% in 2024 to 3.4% in 2025, driven by:
- US:
- Growth to moderate to 1.9% in 2025 and 2.1% in 2026
- Due to weaker labour market performance, modest income growth, and looming cuts in public spending
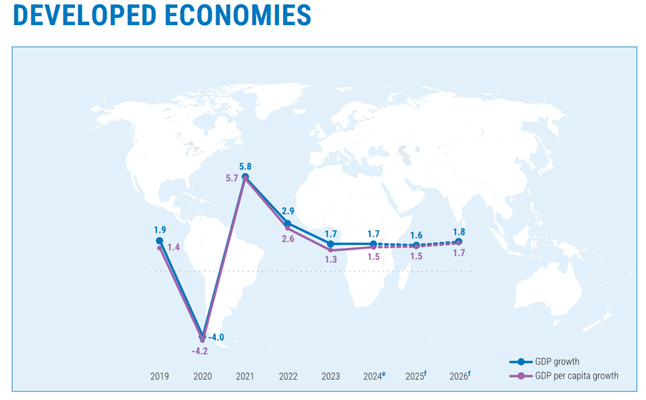
- European Union:
- Growth is forecasted to rise from 0.9% in 2024 to 1.3% in 2025 and 1.5% in 2026.
- But it faces constraints such as geopolitical uncertainties, and structural challenges like population ageing and weak productivity.
- China
- Growth to moderate from 4.9% in 2024 to 4.8% in 2025
- Public sector investments and strong export performance are partly offset by subdued consumption growth and continued weakness in the property sector.
- Africa
- Growth to improve from 3.4% in 2024 to 3.7% in 2025 and 4% in 2026,
- Driven by recovery in the region’s largest economies—Egypt, Nigeria, and South Africa.
- Least Developed Countries
- Economic growth in the least developed countries (LDCs) is projected to rise to 4.6% in 2025, up from the 4.1% growth estimated for 2024.
- But still well below the 7% Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) target.
|
What are Least Developed Countries (LDCs)?
|
- Hurdles for developing countries
- Finance mobilization challenges: To invest in critical infrastructure, technology, and human capital, and in moving up manufacturing and services value chains.
- Limited benefit of green transition: The benefits of the green transition and technological advancements are projected to remain disproportionately concentrated in developed economies.
- Debt issues: High borrowing costs and debt sustainability challenges leading to high risks of debt distress.
What are the key highlights for South Asia and India?
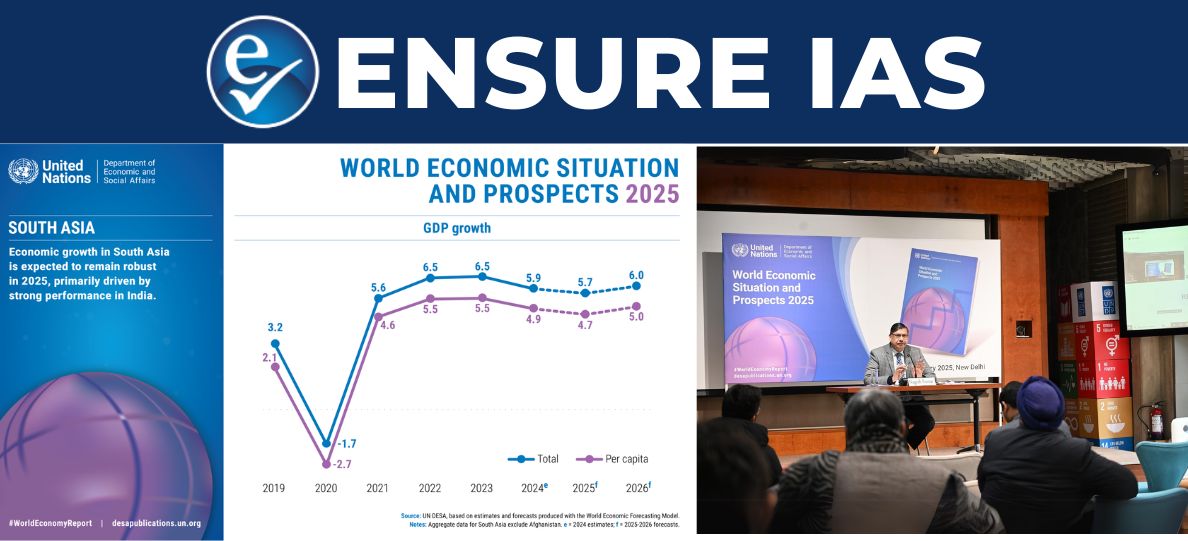
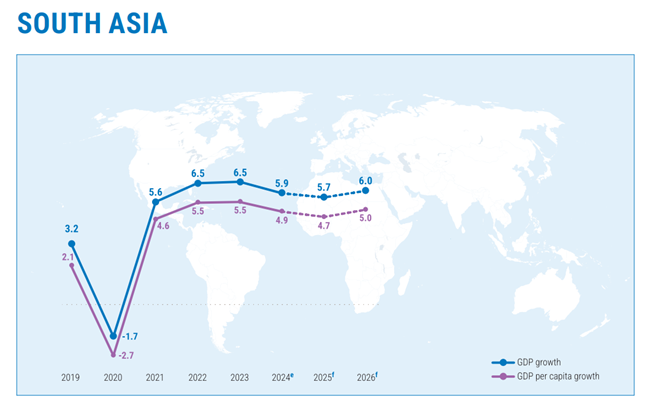
- South Asia
- Robust economic growth expected this year mainly driven by the "strong performance" in India and recovery in Bhutan, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.
- Growth projection: 5.7% in 2025 and 6% in 2026.
- Easing of Depreciation of currencies: As monetary loosening in the United States has increased the attractiveness of both direct and portfolio investments in the region’s economies.
- Risks:
- Deceleration in external demand
- Ongoing debt challenges
- Social unrest in parts of South Asia
- Highly vulnerable to the impact of climate hazards
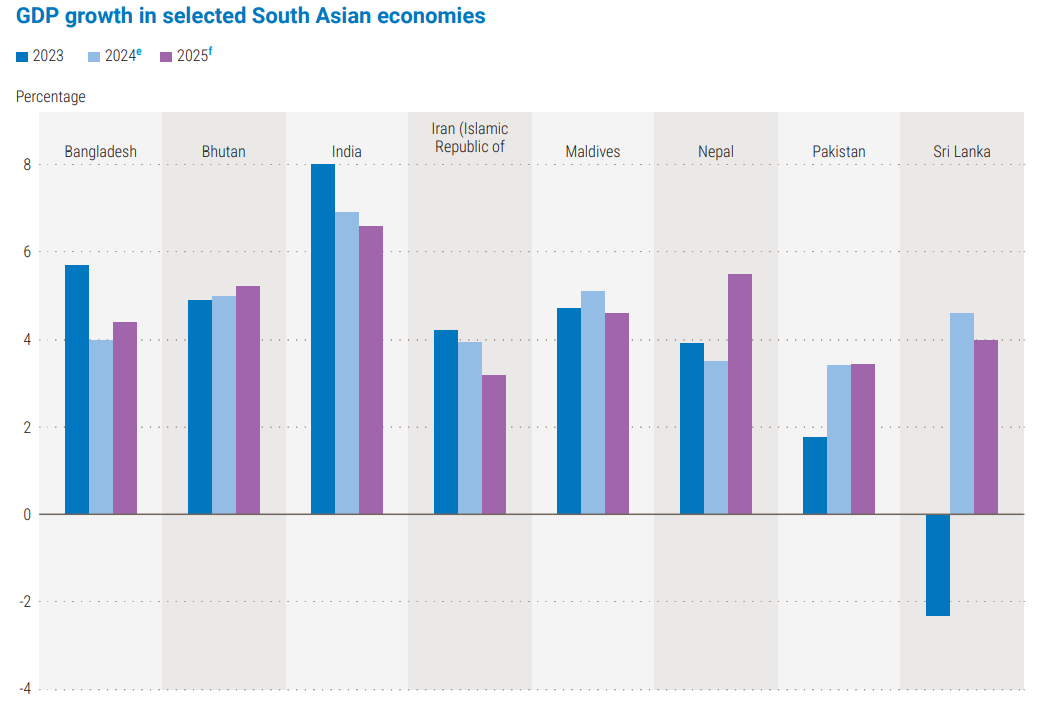
- Indian Economic Growth forecast:
- A growth of 6.6% for India in 2025, following an estimated expansion of 6.9% in 2024.
- Key Drivers: Strong private consumption and investment
- Strengths in the Indian Economy
- Capital expenditure: Capital expenditure on infrastructure development can have strong multiplier effects on growth in the coming years.
- Manufacturing and Services sectors: Expansion in these sectors will continue to drive the economy.
- Strong Export growth: In services and certain goods categories, such as pharmaceutical and electronics.
- Favourable monsoon rains in 2024: This has improved summer-sowing areas for all major crops, boosting agricultural output expectations for 2025.
- Decrease in Consumer price inflation: It would decrease from an estimated 4.8% in 2024 to 4.3% in 2025, staying within the 2–6% medium-term target range set by the RBI.
- Strong Employment indicators: For instance, the labour force participation is at near record highs.
- However, substantial gender gaps remain despite progress in female labour market participation in India.
- Untapped reserves of critical minerals: As per the report, India has vast reserves of rare earth elements but currently accounts for only a small share of global production.
What are the suggestions offered?
- Supporting developing countries:
- With priority given to technology transfer, skills development, and institutional capacity-building.
- Focus on establishing transparent governance frameworks and building basic public sector capabilities.
- Sustainable extraction of critical minerals: It must be backed by comprehensive regulatory frameworks, equitable benefit-sharing, and investments in building productive capacities.
- International cooperation:
- For strengthening multilateral trade cooperation under the World Trade Organization (WTO) and similar frameworks.
- For tackling illicit financial flows as well as enhancing market transparency.
- For ensuring more predictable investment environment and unlocking greater private sector financing opportunities.
- Essential for accelerating growth and progress towards the Sustainable Development Goals.
Conclusion
In an interconnected global economy, shocks on one side of the world can have ripple effects across the world. The UN Secretary General thus emphasises that as every country is affected by connected global issues, every country must also be part of the solution. Together, it is possible to put the world on track for a prosperous, sustainable future for all.
|
Also Read |
|
FREE NIOS Books |
UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
UPSC Monthly Mgazine |
Previous Year Interview Questions |
Free MCQs for UPSC Prelims |
UPSC Test Series |
ENSURE IAS NOTES |
Our Booklist |




