- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
The State of the World's Mangroves 2024
The State of the World's Mangroves 2024
02-08-2024
Introduction
- Report title: "The State of the World's Mangroves 2024"
- Released by: Global Mangrove Alliance (GMA)
- Release date: World Mangrove Day (26 July 2024)
- GMA: An alliance of 100+ members focused on mangrove conservation and restoration
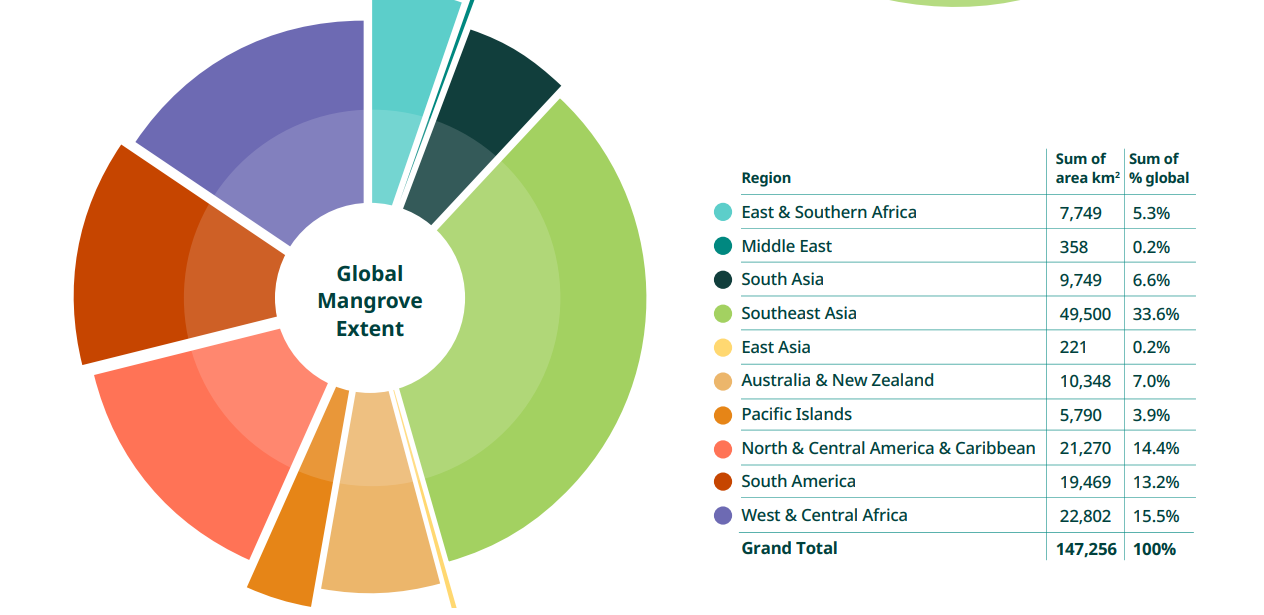
Global Mangrove Status
- Latest world map (GMW v4.0) by Global Mangrove Watch:
- Sixfold improvement in spatial resolution
- Total mangrove area in 2020: 147,256 km²
- Added data for six new territories
- Southeast Asia holds about one-third of the world's mangroves
- Indonesia alone accounts for 21% of global mangroves
Key Benefits of Mangroves:
- Carbon Storage:
- Average: 394 tonnes of carbon per hectare (living biomass and top meter of soil)
- Some areas (e.g., Philippines): Over 650 tonnes per hectare
- Biodiversity:
- Ecotone nature supports diverse species
- Indian mangroves alone: Over 5,700 plant and animal species across 21 phyla
- Flood Reduction:
- Reduce flood depths by 15-20% (over 70% in some areas)
- Crucial in context of climate change-exacerbated flooding
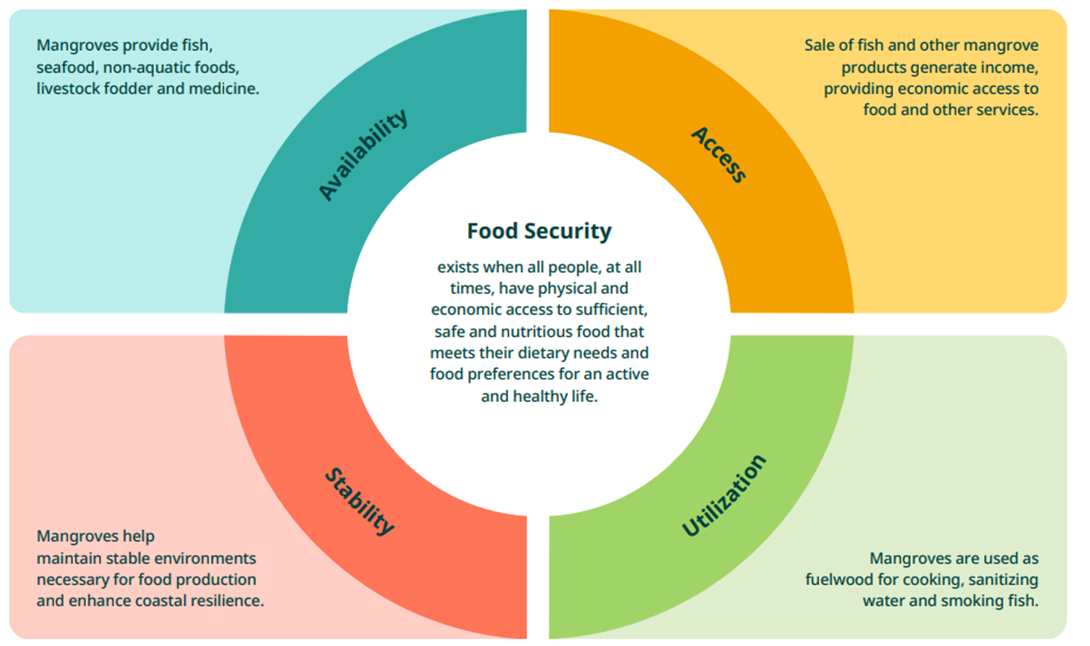
- Food Security:
- Support nearly 800 billion young fish, prawns, bivalves, and crabs annually
- Provide non-aquatic food resources (honey, leaves, fruits)
- Cultural Significance:
- Widely used in traditional medicine
Indian Mangrove Scenario
-
Mangrove Distribution:
- Largest area: West Bengal
- Second largest: Gujarat (Gulf of Kutch and Gulf of Khambhat)
-
Biodiversity:
- Highest recorded biodiversity globally: 5,746 species
- 4,822 species (84%) are animals
-
Threatened Areas:
- Critically Endangered: Southern Indian coast, Lakshadweep archipelago, Tamil Nadu
- Vulnerable: Western coast (Gujarat to Kerala)
- Threats: Rising sea levels, shrimp aquaculture, tropical storms, human activities
-
Conservation Challenges:
- Gulf of Cambay (Khambhat): Severe grazing and lopping during flowering season
-
Government Initiatives:
- Mangrove Initiative for Shoreline Habitats & Tangible Incomes (MISHTI):
- Goal: Augment mangrove cover by 540 sq km across 11 states and 2 Union territories
- Corporate involvement: 6 major corporations to plant mangroves in 30 sq km in Gujarat
- Mangrove Initiative for Shoreline Habitats & Tangible Incomes (MISHTI):
Global Challenges
-
Major causes of mangrove loss (2000-2020):
- Conversion to aquaculture: 26%
- Oil palm plantations and rice cultivation: 17%
- Natural retraction (climate change, sediment shifts, sea-level rise): 26%
- Logging for timber and charcoal
- Oil spills: 8.2% (e.g., Niger Delta)
-
Climate Change Impacts:
- Sea-level rise threatening mangrove habitats
- Increasing frequency and intensity of cyclonic storms
-
Protection Status:
- Only 40% of world's mangroves in protected areas
- Some countries (e.g., Malaysia, Myanmar) have less than 5% protection
-
IUCN Red List:
- Half of the world's mangrove provinces are threatened
-
Financial Challenges:
- Securing adequate financing for conservation

Recommended Steps for Mangrove Protection
-
Six Guiding Principles for Successful Mangrove Restoration:
- Safeguard nature and maximize biodiversity
- Employ best information and practices
- Empower people and address their needs
- Align to the broader context – operate locally and contextually
- Design for sustainability
- Mobilize high-integrity capital
-
Expand Protected Areas:
- Global Mangrove Alliance goals by 2030:
- Halt mangrove loss
- Restore half of the world's lost mangroves
- Double protection (aim for 80% protected)
- Global Mangrove Alliance goals by 2030:
-
Implement Other Effective Area-Based Conservation Measures (OECMs):
- Integrate biodiversity into sectors like food and water security
-
Innovative Financial Tools:
- Develop carbon credits and mangrove insurance
-
Community Involvement:
- Encourage community-led restoration projects (examples from Philippines, Colombia, Kenya)
-
International Policy Frameworks:
- Leverage frameworks like Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework
Conclusion:
The successful conservation of the world's mangroves will require coordinated efforts at local, national, and international levels. It will necessitate balancing human development needs with ecological conservation, and recognizing the long-term value of healthy mangrove ecosystems. As we face the dual crises of climate change and biodiversity loss, the protection and restoration of mangroves emerge as a critical nature-based solution that can yield multiple benefits for both people and the planet.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi
UPSC Prelims Result 2024 Out: Expected Cut Off & Other Details, UPSC Prelims 2024 Answer with Explanation, Daily Prelims Quiz, Daily Current Affairs, MONTHLY CURRENT AFFAIRS TOTAL (CAT) MAGAZINE, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Karol Bagh, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Delhi, Daily Mains Question Answer Practice, ENSURE IAS UPSC Toppers, UPSC Toppers Marksheet, Previous Year Interview Questions, UPSC Syllabus




