- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
THE SOUTHERN OCEAN HAS THE EARTH’S CLEANEST AIR
THE SOUTHERN OCEAN HAS THE EARTH’S CLEANEST AIR
07-04-2024

The Southern Ocean, also known as the Antarctic Ocean, is famous for its remarkably clean air, yet the reasons behind this phenomenon have long remained a mystery.
- Geographical Overview:
- The Southern Ocean, one of Earth's five major ocean basins. The Southern Ocean basin is made up of the parts of the Global Ocean (made up of the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian ocean basins) and surrounding Antarctica below 60° S.
- It was formed about 34 million years ago when Antarctica and South America separated, creating the Drake Passage.
- Distinctive Features:
- The Southern Ocean experiences strong winds, intense storms, and dramatic seasonal changes, resulting in cooler temperatures.
- The Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC) is the largest ocean current, transporting more water around the world than any other current.
- The ACC is a deep current that flows clockwise around Antarctica, from west to east. It's also known as the West Wind Drift
- Air Quality:
- The Southern Ocean has the cleanest air on Earth due to several factors:
- Its remote location minimizes human-induced air pollution.
- Cold temperatures and strong winds promote efficient dispersion of air pollutants.
- The lack of large surrounding landmass limits the input of continental aerosols.
- The Southern Ocean has the cleanest air on Earth due to several factors:
- Biodiversity:
- The Southern Ocean supports a diverse range of marine life, with many species dependent on the abundant phytoplankton produced in the Antarctic Convergence.
- Notable marine animals include whales, penguins, orcas, and seals, which thrive in the cool, nutrient-rich waters.
Conclusion:
The Southern Ocean remains a fascinating and mysterious region, characterized by its clean air quality and unique biodiversity. Understanding the complex interactions within this ecosystem is important to maintain its delicate balance and securing its continued ecological importance.
FAQs:
Q1: What are Ocean currents?
- Ocean currents are the continuous, predictable, directional movement of seawater driven by gravity, wind (Coriolis Effect), and water density. Ocean water moves in two directions: horizontally and vertically.
- Horizontal movements are referred to as currents, while vertical changes are called upwellings or downwellings.
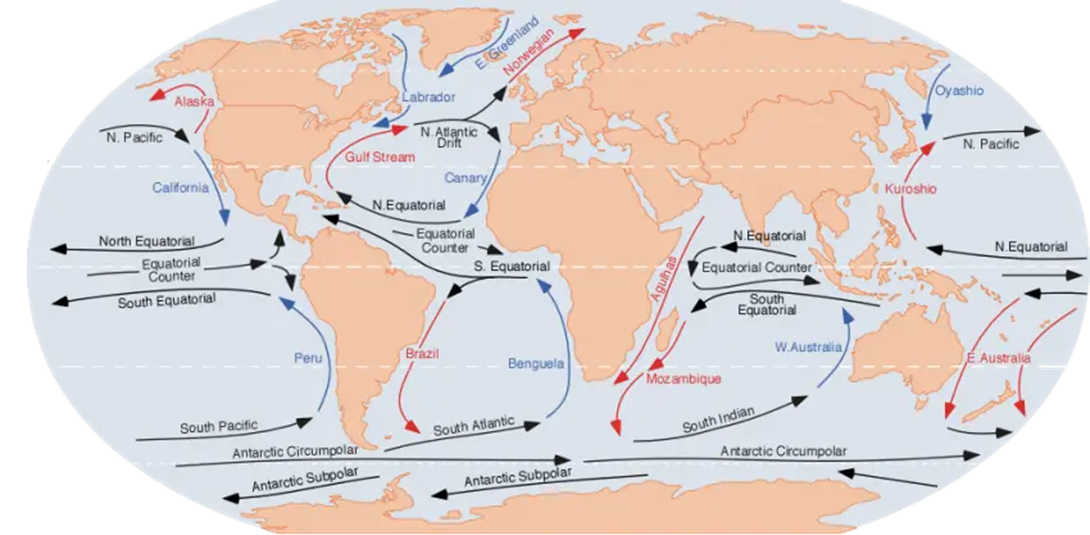
Here are some types of ocean currents:
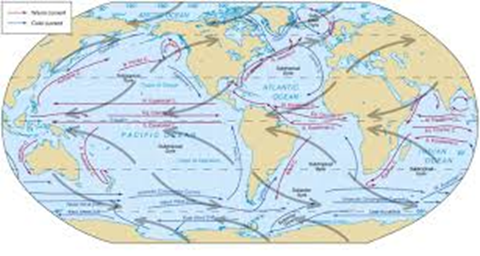
- Surface currents
- currents flow near the surface of the ocean and are primarily driven by wind. They help distribute heat around the planet and moderate the Earth's temperature.
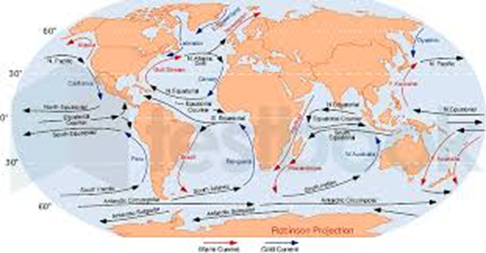
- Equatorial currents
- Equatorial Counter Current is a narrow and shallow current that flows eastward along the equator. It can be found in the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian oceans.

- Antarctic Circumpolar Current
- deep ocean current circles around Antarctica, carrying cold water from the Southern Ocean to the north.


