- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
SMART CITIES MISSION (SCM)
SMART CITIES MISSION (SCM)
04-05-2023
-1683872390692.jpg)

Latest Context
The deadline for completing projects under the Smart Cities Mission was extended for all 100 participating cities to June 2023 due to the delays caused by COVID-19 and based on a NITI Aayog recommendation in August, according to Housing and Urban Affairs Ministry.
Facts About Smart Cities Mission
- Launched: June, 2015
- Nature: Centrally Sponsored Schemes
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Housing & Urban Affairs
- Aim: To bring about a paradigm shift in the practice of urban development in the country.
- Focus: Sustainable and inclusive development.
- Implemented through: Special Purpose Vehicles (SPVs) at city level.
- Mission Deadline: Extended to June 2023.
- Coverage: Developing 100 selected cities as Smart Cities.
Six Fundamental Principles of SCM
- Community at the Core.
- More from Less.
- Cooperative and Competitive Federalism.
- Integration, Innovation and Sustainability.
- Technology as means not as a goal.
- Convergence.
Pillars of the SCM
- Social Infrastructure.
- Physical Infrastructure.
- Institutional Infrastructure.
- Economic Infrastructure.
Objectives of SCM
- Create employment opportunities.
- Make cities liveable, inclusive and sustainable.
- Provide core infrastructure and give a decent life to their citizens.
Challenges of the SCM
- Slow Progress: Less than 50% of the project had completed.
- Finance Resources: It has difficulty in mobilizing funds, transferring them to SPVs and using them efficiently.
- Digital Security: Vulnerable to hacking by cybercriminals.
- Lack of confidence shown by the citizens: It is a lack of clarity around the benefits.
- Urban Problems: Such as air pollution, broad congestion and the decline in public transport.
- Policy Issues: Hindrance in getting environmental clearances.
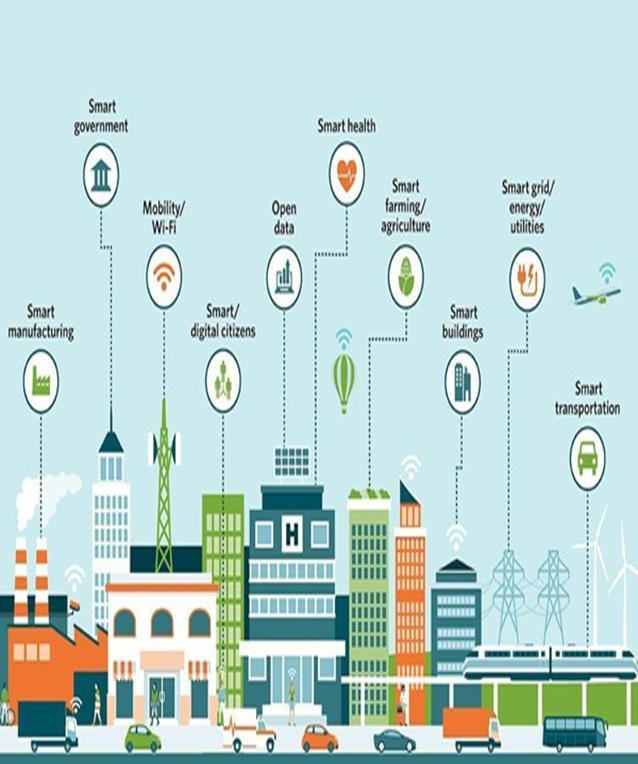
Smart Solutions
- Energy Management: Involves the use of smart grids, renewable energy sources, and energy-efficient buildings to reduce energy consumption and carbon emissions.
- Solid Waste Management: Use of technology to improve waste collection and disposal systems such as smart bin that alert authorities when they are full, waste-to-energy plants, and recycling facilities.
- Transportation: It involves the integration of technology in public transport systems such as real-time traffic monitoring, smart traffic lights, and intelligent public transport systems that provide citizens with the most efficient and cost-effective routes.
- Smart Healthcare: To improve the quality and accessibility of healthcare services such as telemedicine, remote patient monitoring, and smart healthcare facilities.
- Smart Governance: Make them more transparent and efficient such as e-governance portals, citizen feedback mechanism and smart surveillance systems.