- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT- First Ladder
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Self-Reliance in Cybersecurity
Self-Reliance in Cybersecurity
31-10-2023

Why in News?
Recently, During the 7th edition of the India Mobile Congress, the Prime Minister of India emphasized the significance of Self-Reliance in Cybersecurity.
What is Self-Reliance in Cybersecurity? 
-
About:
- Self-reliance in cybersecurity refers to a nation's ability to develop and maintain its own capabilities and technologies to protect its digital infrastructure and information systems without relying on foreign technology or external assistance.
- The focus is on fostering the development and implementation of indigenous cybersecurity solutions, thereby reducing reliance on external sources for tools and expertise.
-
Need for Self-Reliance in Cyber Security:
- National Security: Digital technology is crucial for critical infrastructure systems like energy grids, transportation networks, and communication systems in many nations.
- Modern military operations are heavily reliant on digital technology.
-
Geopolitical Considerations:
- Over-reliance on foreign technology, especially from countries with strained relations like China, can pose a security risk to India.
- Self-reliance is a process that minimizes the risks associated with relying on external technology.

-
Technological Independence:
- Self-reliance necessitates the development of secure and reliable hardware, software, and networking components.
- India's self-reliance on technology reduces potential risks by gaining greater control over the entire supply chain, rather than relying on foreign technology.
Challenges Related to Cybersecurity in India
-
Profit-Friendly Infrastructure Mindset:
- The private sector's significant investments in IT, electricity, and telecom post-liberisation raise concerns about their insufficient focus on cyber-attack preparedness and recovery in regulatory frameworks.
-
Absence of Separate Procedural Code:
- There is no distinct procedural code for investigating cyber or computer-related offenses.
-
Trans-National Nature of Cyber Attacks:
- Cyber crimes are primarily transnational, making it challenging and often delayed to collect evidence from foreign territories.
-
Expanding Digital Ecosystem:
- India has successfully digitalized its economic factors in recent years, establishing a unique niche in the process.
- The advancement of advanced technologies like 5G and IoT is expected to enhance the coverage of the internet-connected ecosystem.
- Digitalization in India has led to the storage of crucial consumer and citizen data in digital format, making it a breeding ground for potential hackers and cyber-criminals.
-
Limited Expertise and Authority:
- Crypto-currency offenses are under-reported due to limited capacity to solve such crimes.
- State cyber labs, while capable of analyzing hard disks and mobile phones, are not yet recognized as 'Examiners of Electronic Evidence' by the Central Government.
Domestic Achievements in the field
-
Domestic Supply Chain Partners:
- India is actively diversifying its supply chain partners, particularly in the technology sector, to counter the dominance of Chinese players in the manufacturing ecosystem.
- The government is working on establishing more secure and trustworthy supply chains to mitigate the risk of malware and cyber threats.
-
5G and Mobile Broadband:
- The government has awarded 100 5G Use Case labs to educational institutions nationwide, demonstrating its commitment to enhancing 5G infrastructure.
- India has transitioned from the 5G rollout stage to the 5G reach-out stage, resulting in a threefold increase in median mobile broadband speed in just one year.
-
Broadband Speed:
- India's broadband speed has risen from 118th to 43rd globally, indicating a significant increase in high-speed internet access in the country.
-
Startup Ecosystem:
- India's startup ecosystem is experiencing a significant growth, with a rapid rise in the number of startups.
- The number of startups has significantly increased from 100 startups in 2014 to around 100,000 today.
Initiatives taken
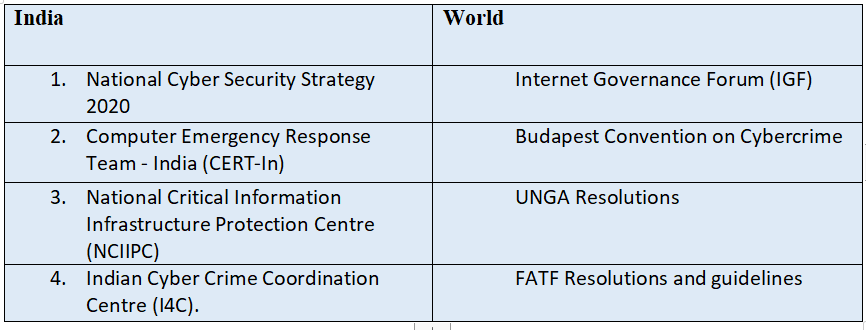
Way Forward
-
Gulshan Rai Committee recommendations:
- Develop an advanced Social Media Analytics application to monitor activities related to Ministries of Home, External Affairs, Defence, and other government organizations on social media platforms.
- The government aims to decrease its reliance on foreign servers and establish a single, secure gateway for all government communication.
- Enhance cyber forensic awareness among states through the establishment of cyber forensic laboratories, workshops, and international cooperation.
- Aim should be to foster cybersecurity research and development through collaborations between government agencies, academic institutions, and private sector companies.
- Support cybersecurity startups and SMEs by providing funding, incentives, and support to develop innovative cybersecurity solutions, thereby fostering the creation of homegrown technologies.
Conclusion
Need is to implement Gulshan Rai committee recommendations in mission mode. This would pave a long-term road for Atmanirbhar Bharat in cybersecurity too.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi