- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT- First Ladder
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
SC refuses to permit euthanasia
SC refuses to permit euthanasia
The Supreme Court on Tuesday refused to grant an aged couple’s plea to allow “passive euthanasia” for their 30-year-old son, who has been lying comatose at home for 11 years after a fall from the fourth floor of a building.
- This decision has reignited discussions on the legal and ethical aspects of euthanasia in India.
Background of the Case
- Supreme Court Decision: The Court denied the petition, ruling that since the patient was not on life support but was receiving nutrition through a feeding tube, allowing him to die would be considered active euthanasia, which remains illegal in India.
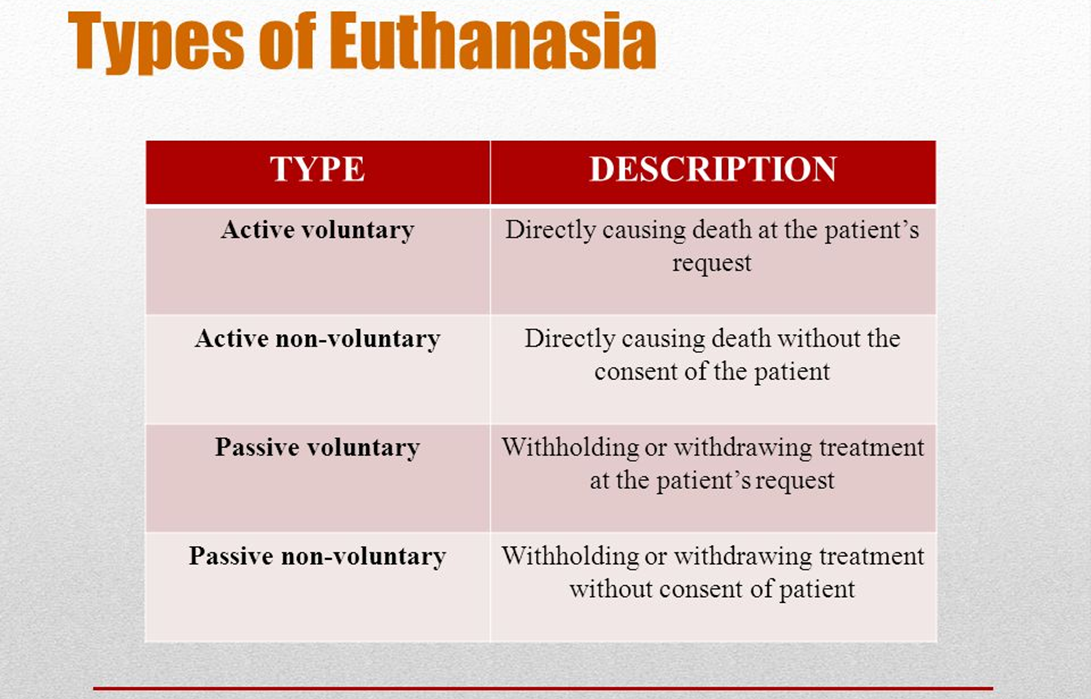
What is Passive Euthanasia?
- Definition: Passive euthanasia involves stopping or withdrawing medical treatment, like life support, to let a person die naturally. It is different from active euthanasia, which involves directly causing death, such as administering a lethal injection.
- Active Euthanasia: This involves taking direct action to cause death.
Euthanasia in India
- Legal Milestones:
- 2011 - Aruna Shanbaug Case: The Supreme Court first recognized passive euthanasia in this case involving a nurse in a permanent vegetative state.
- 2018 - Common Cause vs Union of India: The Court confirmed the right to die with dignity under Article 21, allowed passive euthanasia, and accepted living wills for terminally ill patients.
- Article 21: This fundamental right ensures the right to life and personal freedom. The Supreme Court has included the right to a dignified death within this.
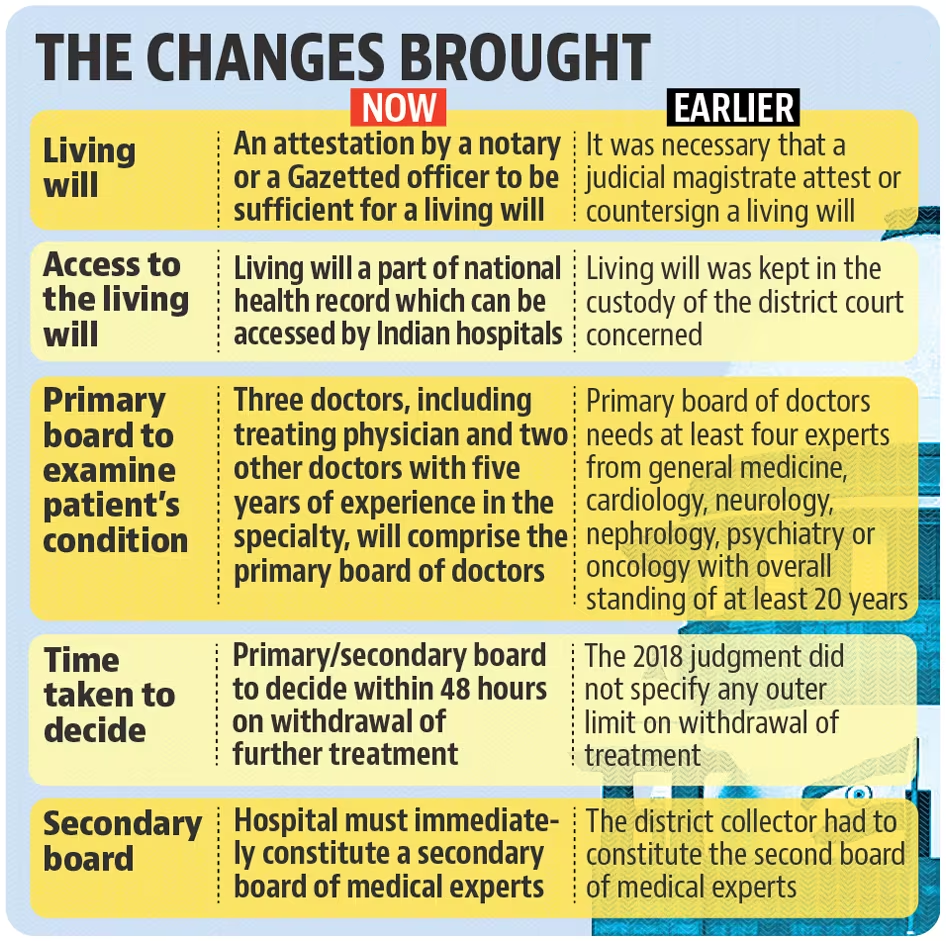
Recent Changes in Guidelines (2023)
- Attestation of Living Will: The need for a judicial magistrate’s attestation was removed. Now, a living will can be attested by a notary or a gazetted officer.
- Integration with National Health Digital Record: Living wills must be part of the National Health Digital Record, making them easily accessible for hospitals and doctors.
- Appeal Process: If a medical board denies euthanasia, the patient's family can appeal to the High Court, which will form a new medical board to reassess the case.
Different Countries with Euthanasia
- Netherlands, Luxembourg, Belgium: Allow both euthanasia and assisted suicide for people with unbearable suffering with no hope of improvement. The Netherlands has a detailed legal framework for this.
- Switzerland: Euthanasia is banned, but assisted suicide is permitted under strict conditions, focusing on personal choice and mental capacity.
- Australia: Euthanasia is legal in some states for adults with terminal illnesses and a prognosis of death within six or twelve months. Laws vary by state.
Ethical Considerations of Euthanasia
- Autonomy and Informed Consent: Euthanasia respects the right of individuals to make decisions about their own lives, especially to end suffering if mentally competent. Informed consent ensures decisions are made voluntarily and with full understanding.
- Quality of Life vs. Sanctity of Life: The debate often centers on whether improving quality of life (ending suffering and maintaining dignity) is more important than the belief in the sanctity of life (life’s inherent value), which varies by personal beliefs.
- Legal and Social Implications: Laws on euthanasia differ by country, reflecting diverse cultural attitudes. Socially, it involves the roles of medical professionals, societal responsibilities, and ensuring equitable access to palliative care and support.
Conclusion
As India grapples with the complex issues surrounding euthanasia, it is essential to strike a balance between respecting individual autonomy and upholding social values. The recent changes in the guidelines are a step towards a more accessible and streamlined process for passive euthanasia. Moving forward, the focus should be on enhancing palliative care and support systems to provide alternatives to euthanasia. Additionally, ongoing conversations and legal adjustments will be crucial in addressing the emerging needs and ethical concerns of end-of-life care.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi
UPSC Prelims Result 2024 Out: Expected Cut Off & Other Details, UPSC Prelims 2024 Answer with Explanation, Daily Prelims Quiz, Daily Current Affairs, MONTHLY CURRENT AFFAIRS TOTAL (CAT) MAGAZINE, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Karol Bagh, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Delhi, Daily Mains Question Answer Practice, ENSURE IAS UPSC Toppers, UPSC Toppers Marksheet, Previous Year Interview Questions, UPSC Syllabus




