- Courses
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
REGULATING ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
REGULATING ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE


Latest Context
A new draught of the Artificial Intelligence Act, which would regulate programmes like OpenAI's ChatGPT, has received preliminary approval from the European Parliament. The legislation was drafted in 2021 with the intention of introducing responsibility, transparency, and trust to Al as well as developing a framework to reduce dangers to the EU's values of democracy, safety, and health.
Facts about EU’s Artificial Intelligence Act (AIA)
-
AIA was proposed by the European Commission on April, 2021.
-
Aim: To create a legal framework for the development and deployment of artificial intelligence systems in the European Union.
-
Focus: It focuses on artificial intelligence systems that could harm people's health, safety, or fundamental rights. Included in these are the applications of AI in healthcare, education, employment, law enforcement, and access to basic services.
-
Objective: To ensure that AI is developed and used in a way that is safe and respects fundamental rights.
-
The AI law seeks to "strengthen Europe's position as a global hub of excellence in AI from the lab to the market" and ensure that AI in Europe complies with the 27-nation bloc's values and rules, similar to how the EU's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) of 2018 made it an industry leader in the world's data protection regime.
Need for Regulating Artificial Intelligence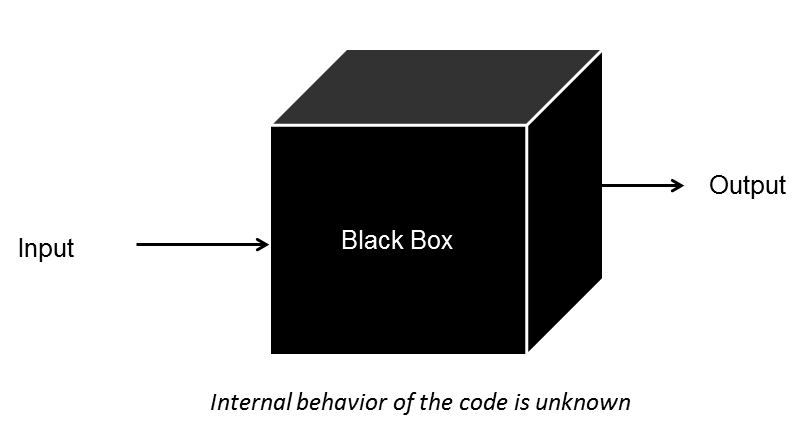
-
Safety: There is a risk that it could cause harm to people, either intentionally or unintentionally. For example, an autonomous vehicle that is not properly regulated could cause a serious accident.
-
Black Box: Certain AI tools are so complex that they resemble a "black box." This implies that even those who build them are unable to fully comprehend how they operate or how particular solutions or judgements are reached.
-
It's similar to a secret box that produces an output but whose precise workings are unknown.
-
Inaccuracy and Biases: Artificial intelligence (AI) tools have already resulted in issues like unfair treatment due to biases built into AI systems, mistaken arrests due to facial recognition software, and more recently, chatbots based on large language models like GPT-3 and 4 creating content that may be inaccurate or using copyrighted material without permission.
-
While these chatbots have the ability to produce high-quality content that is hard to distinguish from human-written content, their work may not always be accurate or allowed by law.
-
Trust: Regulating AI can help build trust by ensuring that it is developed and used in a way that is transparent, ethical, and aligned with societal values

Way Forward
- To regulate artificial intelligence, a straightforward regulatory framework must be developed that outlines the capabilities of AI and identifies those that are more prone to abuse.
- The government should prioritize data privacy, integrity, and security while ensuring businesses have access to data.
- To reduce the use of "black boxes," mandatory explainability should be implemented. This will promote transparency and assist businesses comprehend the thinking behind each decision they make.
- To formulate effective regulations, policymakers must try to strike a balance between the scope of the regulation and the vocabulary used, and they should seek input from a variety of stakeholders, including industry experts and businesses.



