- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT- First Ladder
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Railways plans to go nuclear as part of its green drive
Railways plans to go nuclear as part of its green drive

Indian Railways is exploring the use of nuclear power as part of its efforts to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and increase the use of renewable energy. In addition to nuclear power, the Railways is also setting up solar and wind power plants.
What are Nuclear Powered Trains?
- About
- Nuclear-powered trains use heat from nuclear reactions to create high-pressure steam. This steam drives turbines: one turbine powers the train, and the other generates electricity for onboard equipment such as air conditioners and lights.
- History
- The idea of nuclear-powered trains was seriously considered in the 1950s when it became an official goal of the USSR's Ministry of Transport.
- Functioning
- The proposed design involves a portable nuclear reactor that heats a fluid to produce steam. This steam drives electric turbines, generating power for the train.
- Safety Considerations
- Thorium reactors are being considered because they have lower radiation risks compared to other nuclear materials. The reactor design includes safety features to minimize risks and prevent misuse.
- Potential Benefits
- Reduced Carbon Emissions: Nuclear power can lower CO2 emissions compared to fossil fuels, supporting efforts to combat climate change.
- Energy Efficiency: Nuclear reactors provide a lot of energy with minimal fuel, which could lower operational costs and reduce environmental impact for long-distance rail transport.
- Low Infrastructure Requirements: Nuclear-powered trains could run without overhead electric lines, cutting infrastructure costs and increasing operational flexibility.
- Extended Range: These trains could travel long distances without needing frequent refueling, benefiting both freight and passenger services.
- High Efficiency: Continuous power from nuclear reactors could enhance rail transport performance.
- Challenges
- Radiation Risks: Ensuring safety against radiation and preventing leaks are major concerns. Adequate shielding and safety measures are needed to protect passengers and crew.
- High Costs: Developing and implementing nuclear-powered trains involves high costs, including creating small, safe reactors and integrating them into locomotives.
- Technical Complexity: Designing and maintaining nuclear reactors for trains is complex and presents engineering challenges.
How Indian Railways Plans to Reduce its Reliance on Fossil Fuels
- Nuclear Power Exploration
- Indian Railways is discussing with the Nuclear Power Corporation of India (NPCIL) about using nuclear power. They are considering setting up their own power plants, small reactors, and other power-generating units.
- Net Zero Carbon Emission Target
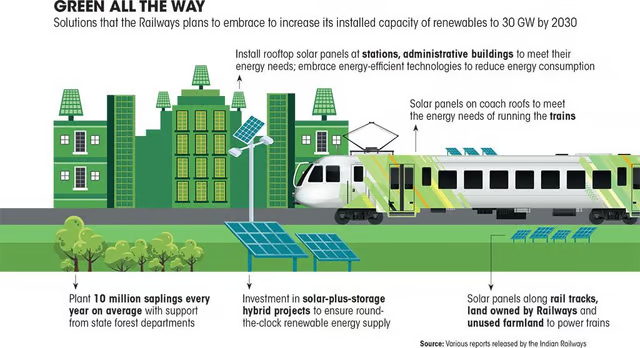
- The Railways aims to achieve net zero carbon emissions by 2030. To reach this goal, they will need 30,000 MW of renewable energy capacity by 2029-30.
- Current Renewable Energy Efforts
- Indian Railways is partnering with Solar Energy Corporation of India (SECI), NTPC, and the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) to boost renewable energy use.
- In 2023, they commissioned around 147 MW of solar power and 103 MW of wind power.
- They have electrified nearly 63,500 kilometers of their broad-gauge network (over 96% of the total).
- 2,637 stations and service buildings now have solar rooftop plants with a total capacity of 177 MW.
Why Indian Railways Need Alternative Sources of Energy
- High Energy Consumption
- Indian Railways uses over 20 billion kWh of electricity annually, which is about 2% of the country’s total power consumption. This high usage calls for more sustainable energy solutions.
- Increasing Power Demand
- Power needs are expected to rise from 4,000 MW in 2012 to about 15,000 MW by 2032 due to ongoing electrification efforts. This growth highlights the need for diverse energy sources.
- Electrification Targets
- Indian Railways plans to electrify 100% of its broad-gauge network by 2030, significantly increasing electricity demand and necessitating alternative energy sources.
- Environmental Impact
- Reliance on diesel and electricity results in high CO2 emissions. Indian Railways aims to cut emissions intensity by 33% below 2005 levels by 2030.
- Diminishing Revenue Surplus
- Revenue earnings are not keeping pace with expenditure. Between 2013-14 and 2023-24, revenue expenditure is expected to grow faster than revenue receipts. Indian Railways seeks to generate its own energy to reduce expenditure on external sources.
- Cost Optimization
- As the largest consumer of electricity, Indian Railways spends about Rs 20,000 crore annually. The organization is looking to cut costs through renewable energy and more affordable power generation models.
|
National Rail Plan (NRP) for India – 2030 Indian Railways have prepared a National Rail Plan (NRP) for India – 2030. The Plan is to create a ‘future ready’ Railway system by 2030. The NRP is aimed to formulate strategies based on both operational capacities and commercial policy initiatives to increase modal share of the Railways in freight to 45%. The objective of the Plan is to create capacity ahead of demand, which in turn would also cater to future growth in demand right up to 2050 and also increase the modal share of Railways to 45% in freight traffic and to continue to sustain it. The key objectives of the National Rail Plan are:-
58 Super critical Projects of a total length of 3750 kms costing ₹39,663 Crore and 68 Critical Projects of a total length of 6913 kms costing ₹75,736 Crore, have been identified for completion by 2024. |
Conclusion
Indian Railways' move towards alternative energy sources is driven by high energy consumption, increasing power needs due to electrification, environmental concerns, and the need for cost management. Nuclear-powered trains could offer benefits such as reduced carbon emissions and greater efficiency, but they come with significant challenges related to safety, cost, and technical complexity. As technology advances and research continues, nuclear power might play a role in the future of rail transport, contributing to a more sustainable and efficient railway system.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi
UPSC Prelims Result 2024 Out: Expected Cut Off & Other Details, UPSC Prelims 2024 Answer with Explanation, Daily Prelims Quiz, Daily Current Affairs, MONTHLY CURRENT AFFAIRS TOTAL (CAT) MAGAZINE, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Karol Bagh, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Delhi, Daily Mains Question Answer Practice, ENSURE IAS UPSC Toppers, UPSC Toppers Marksheet, Previous Year Interview Questions, UPSC Syllabus




