- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Primary Agricultural Credit Societies
Primary Agricultural Credit Societies
07-12-2023
Context
- In December 2023, the Ministry of Cooperation introduced Model Bye-Laws to rejuvenate Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS).
Purpose of Model Bye-Laws
- The Model Bye-Laws are guidelines set by the Ministry of Cooperation to govern PACS operations at the grassroots level.
- Objective: Enhance economic viability and expand the role of PACS in rural areas.
Key Features of Model Bye-Laws
- Enable PACS to diversify over 25 business activities, such as dairy, fishery, floriculture, godown setup, foodgrain procurement, credit services, Fair Price Shops (FPS), community irrigation, and more.
- Provisions for inclusive and broad-based PACS membership, ensuring adequate representation for women and Scheduled Castes/Schedules Tribes.
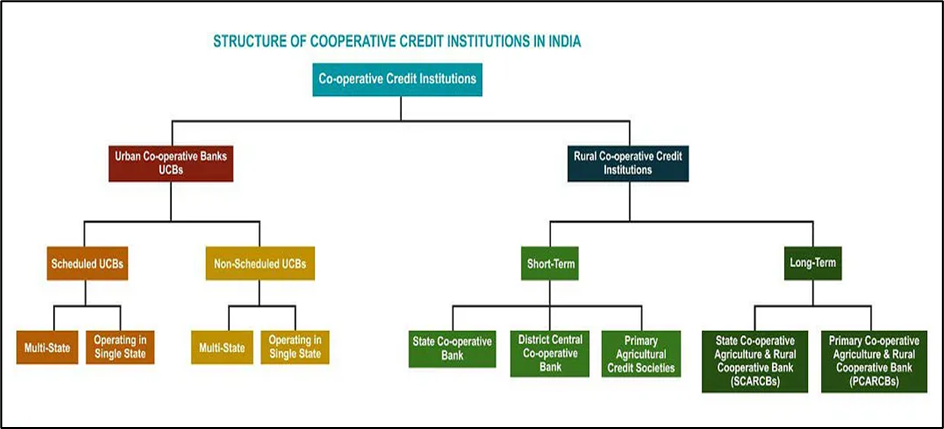
PACS Status and Significance
- As of December 2022, the Reserve Bank of India reported 1.02 lakh PACS in the country, with only 47,297 making a profit by March 2021.
- PACS offer small farmers access to credit for purchasing seeds, fertilizers, and other inputs, contributing to improved production and increased income.
- PACS, primarily located in rural areas, provide convenient access to services for farmers.
- PACS can extend credit with minimal paperwork within a short time, facilitating quick and easy transactions.
Challenges Faced by PACS
- Insufficient Coverage:
- Geographically active PACS cover around 90% of 5.8 Lakh villages, but certain regions, especially in the north-east, exhibit very low coverage.
- Only 50% of all rural households are covered as members, indicating insufficient outreach.
- Insufficient Resources:
- PACS lack resources proportional to the short- and medium-term credit needs of the rural economy.
- Most funds come from higher financing agencies, with limited contributions from owned funds or deposit mobilization by societies.
- Overdues and NPAs
- PACS face significant challenges with large over-dues.
- As per the RBI report, PACS reported lending worth Rs 1,43,044 crore and NPAs of Rs 72,550 crore.
- In Maharashtra, 20,897 PACS, of which 11,326 are in losses, further impacting their financial stability.
- Overdues hinder the circulation of loanable funds, diminish the borrowing and lending capabilities of societies, and tarnish their image.
Way Forward
- Policy Push Needed: These century-old institutions warrant another policy push and can be pivotal in the vision of Atmanirbhar Bharat and Vocal for Local by the Government of India.
- Potential Building Blocks: PACS, with their potential, can be the building blocks of a self-reliant village economy.
- Historical Role: PACS have played a crucial role in the rural financial sector and can have an even more significant impact in the future.
- Enhancing Efficiency: To realize their potential, PACS need to be made more efficient, financially sustainable, and accessible to farmers.
- Strengthen Regulatory Framework: Simultaneously, the regulatory framework must be reinforced to ensure effective governance, enabling PACS to meet the needs of farmers effectively.
Conclusion
In confronting the challenges of insufficient coverage, resource limitations, and financial complexities, PACS stand at a crucial juncture. As vital contributors to rural economies, these institutions require renewed policy attention and comprehensive reforms. Strengthening their efficiency, financial sustainability, and accessibility, while fortifying the regulatory framework, will further empower PACS.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi


