- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Polling Stations Constructed in Sonai Rupai Wildlife Sanctuary
Polling Stations Constructed in Sonai Rupai Wildlife Sanctuary
14-05-2024

The National Green Tribunal (NGT) has taken a significant step by seeking detailed information from Assam's Chief Secretary regarding the construction of polling stations, schools, and other structures within the Sonai Rupai Wildlife Sanctuary and a reserve forest.
- This action highlights the violation of the Forest (Conservation) Act, 1980.
About Sonai Rupai Wildlife Sanctuary:
- Located in the northwestern region of the Sonitpur district of Assam, the Sonai Rupai Wildlife Sanctuary includes approximately 200 square kilometres of protected area.
- Situated along the foothills of the majestic Great Himalayan Range, the sanctuary has a rich and diverse ecosystem.
- The sanctuary was officially declared a protected area in 1998, recognizing its ecological importance.
- The climate within the sanctuary is characterized as subtropical, with hot and humid summers and heavy summer rains, which often lead to flooding and river overflows.
- Burhi Dihing River passes through this sanctuary in the region.
- The Namchang River, originating from the state of Arunachal Pradesh, enters the sanctuary and merges with the Burhidihing River, further enriching the aquatic ecosystem.
- The sanctuary predominantly consists of evergreen forests, providing a habitat for numerous plant and animal species. However, grasslands are also prevalent within the region, contributing to its diverse vegetation.
- The sanctuary is famous for its remarkable fauna, with elephants and Indian bison being the main attractions. Other notable animal species found in the sanctuary include deer, one-horned rhinoceros, leopard, tiger and some rare species of cats.
What is the Great Himalayan Range?
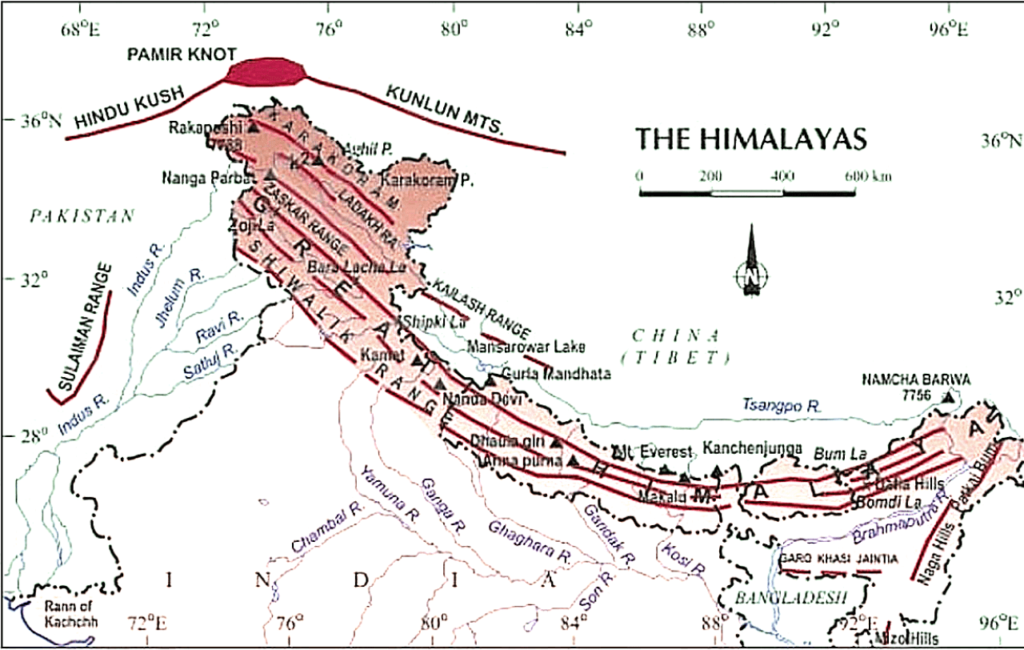
- The Great Himalayas constitute the highest and northernmost section of the Himalayan mountain ranges.
- Extending southeastward across northern Pakistan, northern India, and Nepal, the range then trends eastward through Sikkim state (India) and Bhutan before turning northeastward across northern Arunachal Pradesh state (India).
- Almost throughout its entire length, the Great Himalayas border the southern Tibet Autonomous Region of China to the north.
- With an average elevation of more than 20,000 feet (6,100 meters), this majestic mountain range spans approximately 1,400 miles (2,300 km).
- The Great Himalayas are home to many of the world's tallest peaks, including, from west to east, Nanga Parbat, Annapurna, Mount Everest, and Kanchenjunga.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi



