- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT- First Ladder
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PLACES IN NEWS 4th FEBRUARY 2025
PLACES IN NEWS 4th FEBRUARY 2025

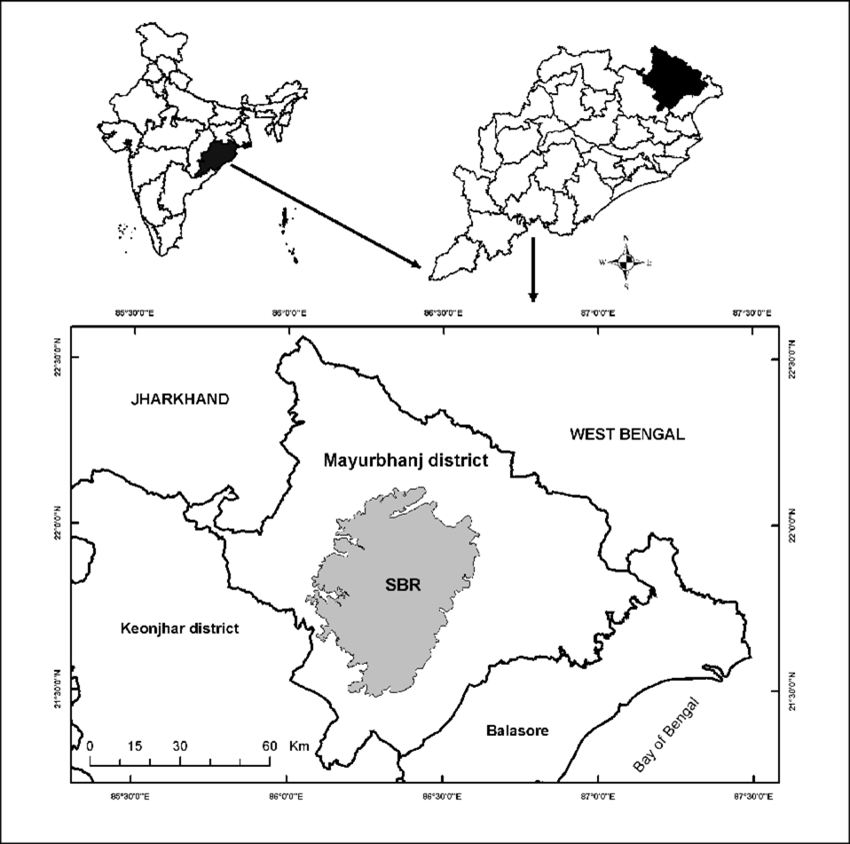
Similipal Biosphere Reserve
Why in news?
A recent study has found that 40.85% of Similipal Biosphere Reserve in Odisha is highly susceptible to forest fires.
About Similipal Biosphere Reserve:
- Location:
- It is situated in the Mayurbhanj district of Odisha and covers an area of 5,569 sq km.
- The reserve is drained by major rivers like Budhabalanga, Khairi, and Salandi, which support the region’s rich biodiversity.
- It is situated in the Mayurbhanj district of Odisha and covers an area of 5,569 sq km.
- Flora and Fauna:
- The reserve is home to moist deciduous and semi-evergreen forests, with dominant tree species including Sal (Shorea robusta), Mahua, Mango, and Jamun.
- Notable fauna include the Royal Bengal Tigers, Indian Elephants, Leopards, Gaur (Indian Bison), and Sambar Deer.
- It is also home to the endangered Forest Owl and rare species like the Flying Squirrel.
- Similipal is also known for its population of melanistic tigers, a rare genetic variant.
- The reserve is home to moist deciduous and semi-evergreen forests, with dominant tree species including Sal (Shorea robusta), Mahua, Mango, and Jamun.
- Protected Areas Covered:
- the biosphere reserve covers, Similipal Tiger Reserve, Hadgarh Wildlife Sanctuary and Kuldiha Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Similipal Tiger Reserve is a part of Project Tiger and is the core area of the biosphere reserve.
- the biosphere reserve covers, Similipal Tiger Reserve, Hadgarh Wildlife Sanctuary and Kuldiha Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Reason Behind Rise in Forest Fires:
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures and prolonged dry spells create conditions conducive to wildfires.
- Anthropogenic Activities: Slash-and-burn agriculture, collection of Mahua flowers, and illegal logging often lead to accidental fires.
- Natural Causes: Lightning strikes and dry vegetation during peak summer months contribute to the spread of fires.
- Wind Patterns: Strong winds in the dry season accelerate the spread of flames across vast forested areas.
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures and prolonged dry spells create conditions conducive to wildfires.
- NDMA and Forest Fire Management:
- The National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) has issued forest fire prevention and control guidelines, emphasizing early detection and mitigation strategies.
- The Forest Fire Alert System, along with satellite-based monitoring, plays a crucial role in identifying fire-prone areas and responding swiftly to outbreaks.
- Additionally, community involvement and awareness programs are essential in curbing human-induced fires, promoting sustainable practices, and ensuring the preservation of Similipal’s fragile ecosystem.
- The National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) has issued forest fire prevention and control guidelines, emphasizing early detection and mitigation strategies.
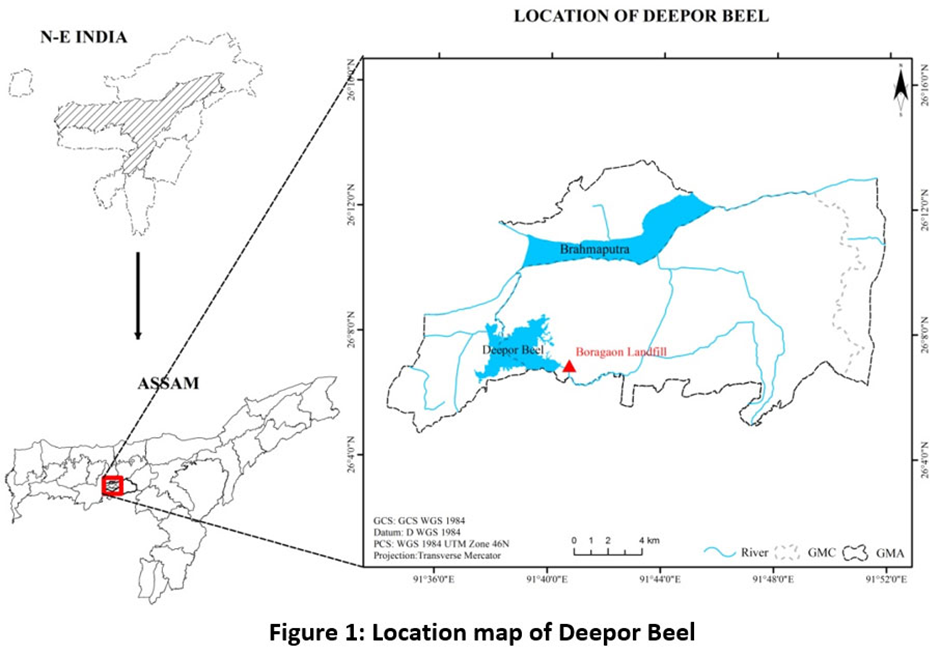
Deepor Beel
Why in news?
The recent Bird Festival at Deepor Beel in Assam recorded an increase in both migratory and resident bird populations. The rise in avian diversity highlights the wetland’s ecological significance and the success of conservation efforts in protecting this vital habitat.
About Deepor Beel:
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Location and Geography:
- Location and Geography:
-
-
-
-
- Deepor Beel is a perennial freshwater lake situated on the outskirts of Guwahati, Assam.
- It occupies a former channel of the Brahmaputra River, covering an area of approximately 4.1 sq km.
- The lake serves as Guwahati’s primary stormwater storage basin, preventing urban flooding.
- Its outflow, the Khandajan rivulet, drains into the Brahmaputra, maintaining the region’s hydrological balance.
-
-
-
-
- Ecological Conservation:
- Ecological Conservation:
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Deepor Beel was recognised as a Ramsar Site in 2002. It is the only Ramsar site in Assam, highlighting its global environmental importance.
- In 2004, it was designated an Important Bird and Biodiversity Area (IBA) by BirdLife International.
- The wetland supports a rich biodiversity, including over 50 species of fish, which sustain around 1,200 households from 12 surrounding villages through fishing-based livelihoods.
- The Rani and Garbhanga hills, located to the south of Deepor Beel, form a crucial corridor for Asiatic elephants, linking them to larger forested landscapes.
-
-
-
-
- Significance for Avian Species:
- Significance for Avian Species:
-
-
-
-
- Deepor Beel was recognised as a Ramsar Site in 2002. It is the only Ramsar site in Assam, highlighting its global environmental importance.
-
- Deepor Beel serves as a staging site on migratory flyways, attracting large concentrations of aquatic birds, especially during winter.
- The wetland provides refuge to several globally threatened species, including Spot-billed Pelican (Near Threatened), Lesser and Greater Adjutant Storks (Endangered), and Baer’s Pochard (Critically Endangered).
- The lake’s shallow waters, marshy areas, and rich aquatic vegetation create an ideal habitat for both migratory and resident birds.
- Deepor Beel serves as a staging site on migratory flyways, attracting large concentrations of aquatic birds, especially during winter.
Mathikettan Shola National Park
Why in news?
After an extensive gap, the golden-headed cisticola, a small passerine bird, was recently recorded for the first time in Mathikettan Shola National Park, Idukki.
About Mathikettan Shola National Park:
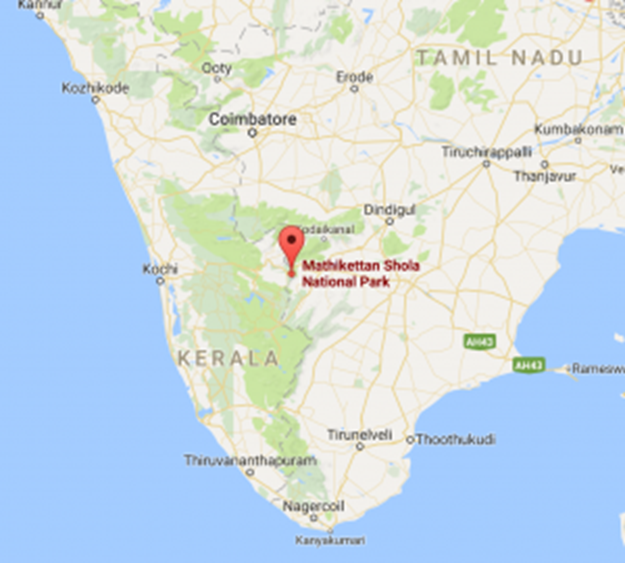
- Location:
- Mathikettan Shola National Park is situated in the Idukki district of Kerala and spans an area of 12.82 sq km.
- It forms part of the southern Western Ghats, a UNESCO World Heritage Site known for its exceptional biodiversity.
- The park is located between Eravikulam National Park and Periyar Tiger Reserve, acting as a vital corridor for wildlife movement.
- Mathikettan Shola National Park is situated in the Idukki district of Kerala and spans an area of 12.82 sq km.
- Flora and Fauna:
- The park is dominated by tropical evergreen forests and shola grasslands, which thrive in the misty, high-altitude climate of the Western Ghats.
- It is home to rare and endemic plant species, many of which have medicinal value.
- Mathikettan Shola supports a diverse range of fauna, including:
- Mammals: Indian Elephant, Nilgiri Tahr, Leopard, Sambar Deer, and Malabar Civet.
- Birds: Black-and-orange Flycatcher, White-bellied Blue Robin, and now the newly recorded Golden-headed Cisticola.
- Reptiles and Amphibians: Several endemic species, including Malabar Pit Viper and Purple Frog.
- The park is dominated by tropical evergreen forests and shola grasslands, which thrive in the misty, high-altitude climate of the Western Ghats.
- Ecological Importance:
- The national park plays a crucial role in conserving the biodiversity of the Western Ghats, a global biodiversity hotspot.
- It serves as an elephant corridor, ensuring the free movement of large mammals.
- The dense vegetation regulates local climate patterns and maintains watershed stability, benefiting nearby agricultural communities.
- The national park plays a crucial role in conserving the biodiversity of the Western Ghats, a global biodiversity hotspot.
Aral Sea
Why in news?
The Aral Sea, once one of the world’s largest inland water bodies, is facing an environmental catastrophe as rapid desertification continues. The lake’s shrinking has led to severe ecological and socio-economic consequences for Central Asia.
About Aral Sea:
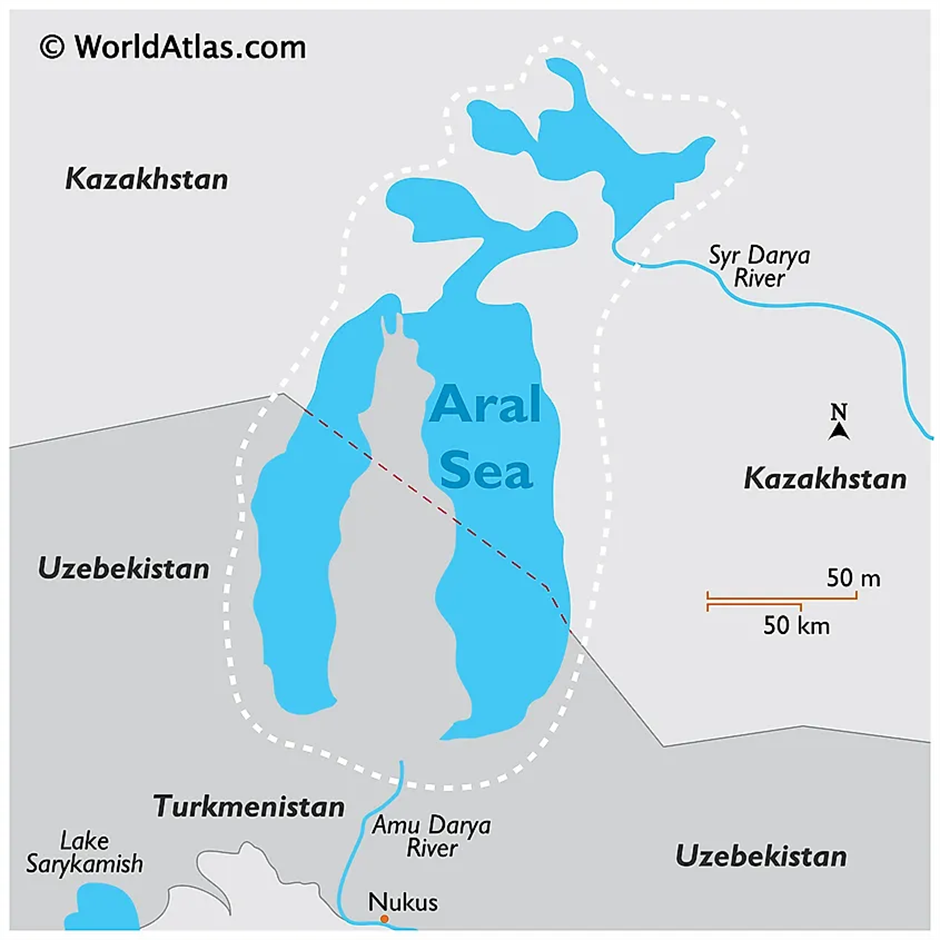
- Location and Geography:
- The Aral Sea is an endorheic (closed-basin) lake located between Kazakhstan to the north and Uzbekistan to the south in Central Asia.
- Historically, it was the Third-largest lake in the world, covering approximately 68,000 sq km in the 1960s.
- The Amu Darya and Syr Darya rivers, originating from the Pamir and Tien Shan mountains, were their primary sources of freshwater.
- The Aral Sea is an endorheic (closed-basin) lake located between Kazakhstan to the north and Uzbekistan to the south in Central Asia.
- Reason Behind Drying Up:
- Soviet Irrigation Projects (1960s): The large-scale diversion of the Amu Darya and Syr Darya rivers for cotton farming under Soviet policies drastically reduced the inflow of water into the Aral Sea.
- Unsustainable Agriculture: The excessive use of river water for irrigation canals left minimal supply to replenish the sea, accelerating its shrinkage.
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures and decreased precipitation further worsened evaporation rates, leading to the formation of the Aralkum Desert in the former seabed.
- Salinity Increase: As the water level dropped, the concentration of salt in the remaining water rose sharply, making it uninhabitable for aquatic life.
- Economic and Health Crisis: The collapse of the fishing industry, dust storms carrying toxic salt and pesticides, and severe respiratory diseases among local populations have turned the crisis into a humanitarian disaster.
- Soviet Irrigation Projects (1960s): The large-scale diversion of the Amu Darya and Syr Darya rivers for cotton farming under Soviet policies drastically reduced the inflow of water into the Aral Sea.
- Conservation Efforts:
- Efforts such as the North Aral Sea restoration project by Kazakhstan have shown limited success, but the South Aral Sea continues to shrink.
- The Aral Sea remains one of the world’s worst human-made environmental disasters, serving as a stark warning about the consequences of unsustainable water management.
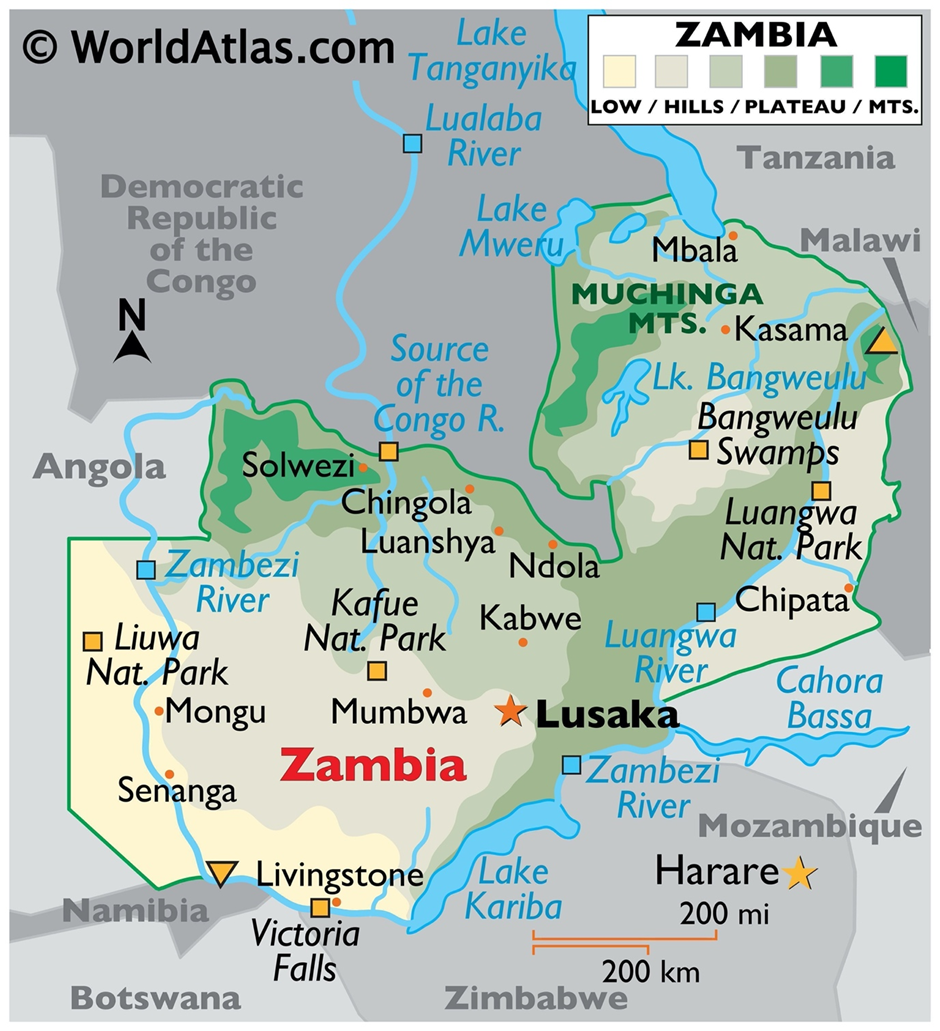
Zambia
Why in news?
- Zambia has secured $184 million in fresh funding from the IMF to stabilise its struggling economy.
- The capital, Lusaka, a key financial and political centre in Southern Africa, remains at the forefront of Zambia’s economic recovery efforts amid mounting debt and inflationary pressures.
About Zambia:
-
Location and Geography:
- Zambia is a landlocked country in Southern Africa, bordered by Angola, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Tanzania, Malawi, Mozambique, Zimbabwe, Botswana, and Namibia.
- The country is located on a high plateau, with an average elevation of 1,000 to 1,500 meters above sea level, making its climate predominantly tropical savanna.
- Zambia is home to some of Africa’s most significant water bodies, playing a crucial role in its ecosystem and economy. Lake Tanganyika, the world’s second-deepest freshwater lake, and Lake Bangweulu are located in the north, supporting rich biodiversity and local livelihoods.
- Lake Kariba, one of the largest artificial lakes, is shared with Zimbabwe and serves as a major source of hydroelectric power, contributing to Zambia’s energy sector.
- The Zambezi River, after which the country is named, flows through Zambia and drains into the Indian Ocean. It is renowned for Victoria Falls, which is one of the largest and most famous waterfalls in the world.
- Other major rivers, such as the Kafue and Luangwa, further enrich Zambia’s landscape, supporting biodiversity, agriculture, and local communities through irrigation and fisheries.
- Zambia is a landlocked country in Southern Africa, bordered by Angola, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Tanzania, Malawi, Mozambique, Zimbabwe, Botswana, and Namibia.
- Economic Crisis in Zambia:
- Zambia has been grappling with a severe economic crisis, primarily due to high debt, inflation, and currency devaluation.
- The debt crisis has been a major concern, with Zambia becoming the first African country to default on sovereign debt in 2020.
- The crisis stems from:
- Excessive Borrowing: Heavy reliance on foreign loans, particularly from China, to finance large-scale infrastructure projects.
- Depreciation of the Kwacha: The Zambian Kwacha has lost value significantly, making debt repayments in foreign currency more expensive.
- Falling Copper Prices: Zambia, one of the world’s largest copper producers, is highly dependent on mineral exports. Declining copper prices and reduced demand have weakened the economy.
- Inflation and Food Shortages: Inflation rates have soared, leading to higher prices for essentials such as food, fuel, and transportation.
- Power Crisis: Droughts have reduced water levels in Lake Kariba, impacting Zambia’s hydroelectric power generation, and causing frequent electricity shortages that affect industries and households.
- Excessive Borrowing: Heavy reliance on foreign loans, particularly from China, to finance large-scale infrastructure projects.
- Zambia has been grappling with a severe economic crisis, primarily due to high debt, inflation, and currency devaluation.
|
UPSC CSE PYQs Q1. Consider the following pairs:
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
Answer: Option C
Q2. Which of the following has/have shrunk immensely/dried up the recent past due to human activities?
Select the correct answer using the code given below: (2018)
Answer: Option A |
|
Also Read |
|
| FREE NIOS Books | |