- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PLACES IN NEWS 3rd MARCH 2025
PLACES IN NEWS 3rd MARCH 2025
03-03-2025

Gir National Park
Why in news?
- PM Modi will visit Gir Somnath on World Wildlife Day today, highlighting conservation efforts, especially for Asiatic lions.
About Gir National Park:
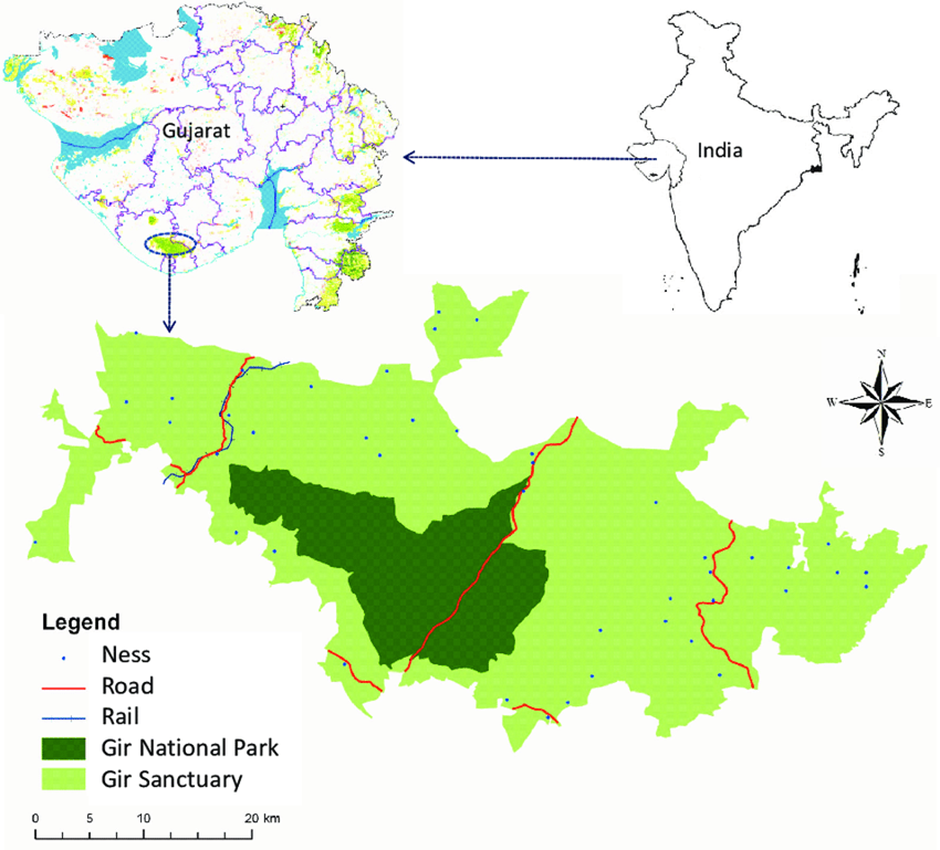
- Location and Geography:
- Gir National Park is located in the Junagadh, Amreli, and Gir Somnath districts of Gujarat, India. It covers 1,412 square kilometres and is part of the Kathiawar-Gir dry deciduous forests.
- The park's terrain includes scrub forests, grasslands, and rocky hills, creating a diverse habitat for numerous species—the region's undulating landscape and open canopy support herbivores and large predators.
- Several rivers, including the Hiran, Shetrunji, Datardi, and Raval, flow through the park, enriching its biodiversity.
- Gir experiences hot summers, moderate monsoons, and mild winters, making it a favourable environment for wildlife conservation.
- Flora and Fauna:
- Gir hosts dry deciduous and thorn forests, with dominant tree species like teak, acacia, jamun, ber, dhak, and flame of the forest.
- The diverse vegetation supports grazing and browsing herbivores, ensuring a stable food chain.
- The park is the last refuge of the Asiatic lion and plays a crucial role in its conservation.
- Other carnivores include leopards, striped hyenas, jungle cats, and golden jackals.
- Herbivores such as chital, sambar, nilgai, four-horned antelope, and wild boar thrive here.
- Gir also supports over 300 bird species, including the crested serpent eagle, Indian eagle-owl, and painted stork.
Manjeera River
Why in news?
- Two individuals from Hyderabad drowned in the Manjeera River in Medak, Telangana.
About Manjeera River:

- The Manjeera (Manjira) River is a major tributary of the Godavari River. It originates from the Balaghat range at an altitude of 823 meters in the Ahmednagar district of Maharashtra.
- The river flows through the states of Maharashtra, Karnataka, and Telangana, covering a catchment area of 30,844 square kilometres.
- It moves through Osmanabad, Latur, and Bidar before entering Telangana.
- The final stretch forms the border between Maharashtra and Telangana before merging with the Godavari River.
- The major tributaries of the Manjeera River are Terna, Manyad, Lendi, Gharni, Tawarja, and Teru, along with the Haridra River, which merges with Manjeera before it joins the Godavari River.
Lankamalleswara Wildlife Sanctuary
Why in news?
- The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) has discovered ancient rock art and inscriptions in Lankamalleswara Wildlife Sanctuary, Andhra Pradesh, shedding light on early human habitation, cultural practices, and historical significance of the region.
About Lankamalleswara Wildlife Sanctuary:
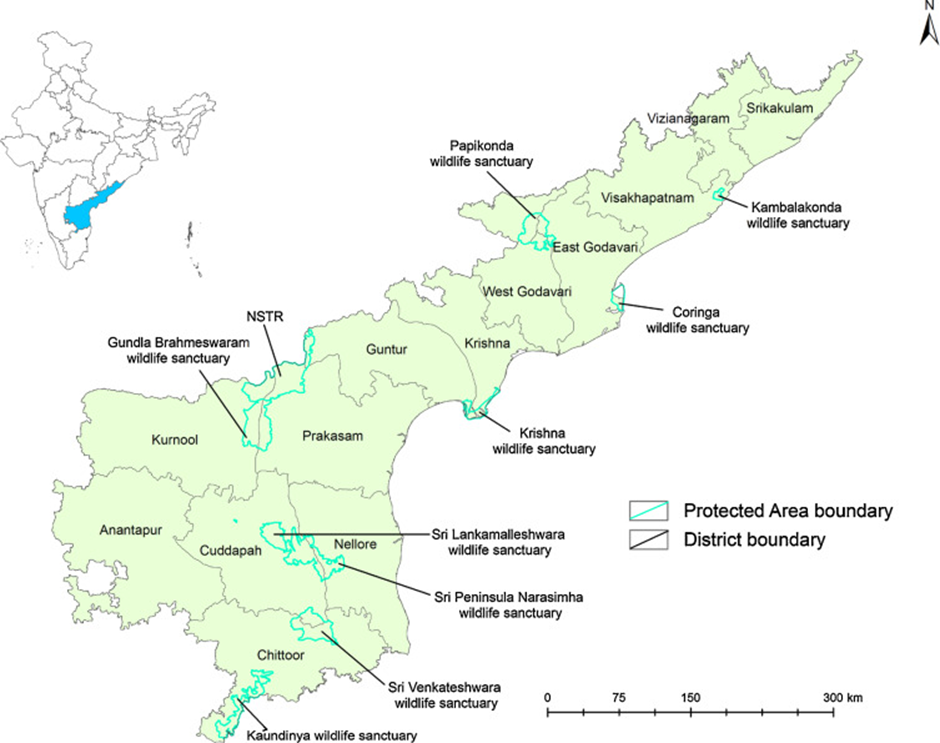
- Location:
- Lankamalleswara Wildlife Sanctuary is located in the Kadapa district of Andhra Pradesh.
- It serves as a catchment area for the Pennar River, also known as Uttara Pinakini.
- The Telugu Ganga Canal flows through its eastern flank, draining into the Pennar River.
- Flora and Fauna:
- The sanctuary features southern tropical dry deciduous forests, scrub forests, tropical thorn forests, and tropical dry evergreen forests.
- It is home to rare and endangered plant species such as red sanders and sandalwood.
- The riparian vegetation includes Arjun trees, Jamun, wild mangoes, Axlewood, date palms, bamboo, and Anjan trees.
- The sanctuary supports diverse wildlife, including species like the common toad, bullfrog, common Indian skink, and green vine snake.
- Notably, it is the only known habitat of the endangered bird, Jerdon’s Courser.
- Recent Archaeological Findings:
- A team from the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) discovered three ancient rock shelters and 30 inscriptions in the sanctuary.
- One rock shelter contained prehistoric paintings of animals, human figures, and geometric designs, dated to the Megalithic (Iron Age) and Early Historic Period (2500 BCE–2nd Century CE).
- The inscriptions, spanning the 4th to 10th centuries CE, provide insights into the region's historical and cultural significance.
Korkai
Why in news?
- Korkai, an ancient port city of the Pandyan Empire in Tamil Nadu, is set for major excavations, aiming to uncover insights into its maritime trade, cultural heritage, and historical significance.
About Korkai:
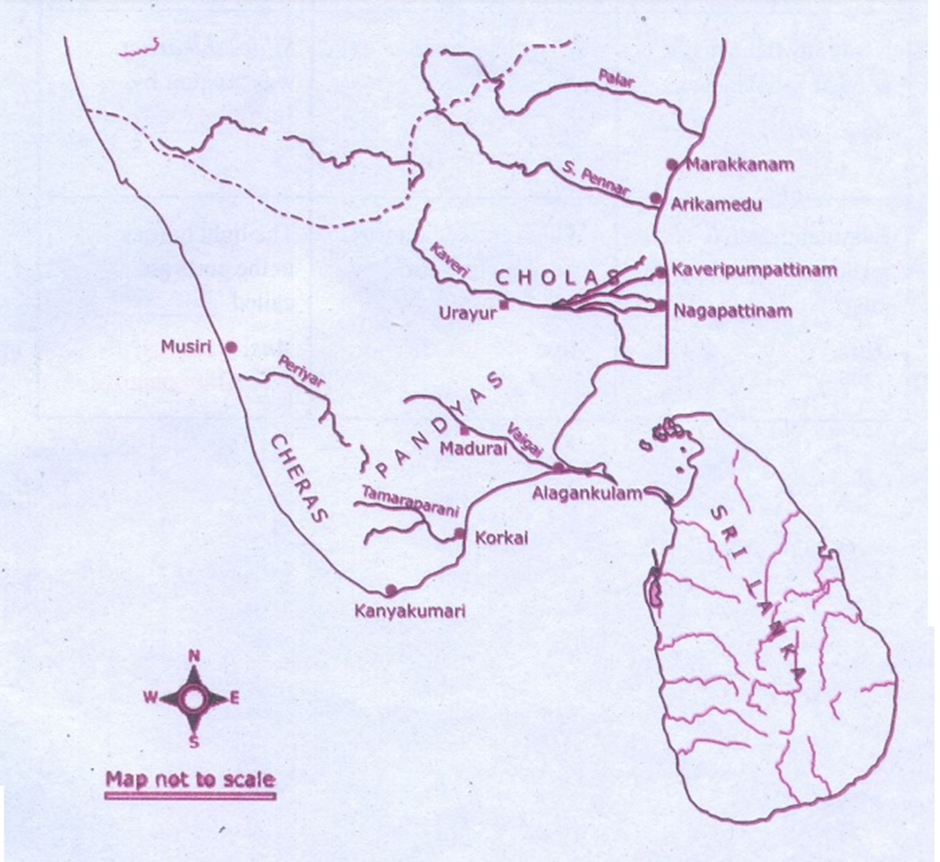
- Location:
- Korkai is a small village in the Srivaikuntam taluk of Thoothukudi district, Tamil Nadu.
- It lies about 3 km north of the Thamirabarani River and 6 km inland from the Bay of Bengal, though it was historically a coastal port.
- Over the past 2,000 years, sedimentation has caused the sea to recede, shifting Korkai away from the coastline.
- Historical Significance:
- Korkai was the capital and major trade hub of the Early Pandyan Kingdom. It finds mention in Sangam literature, which describes its strategic role in the Pandyan administration. The town was also referred to as Pandya-Kavada in ancient texts.
- Korkai was a thriving centre for pearl fishing, with its fisheries renowned in both Indian and foreign accounts.
- The Periplus of the Erythraean Sea and Ptolemy's writings mention Korkai as an important emporium of trade.
- Archaeological evidence, including Roman rouletted ware and megalithic burial urns, indicates long-distance trade with Rome and Southeast Asia.
- Excavations have revealed Tamil-Brahmi inscriptions, graffiti, black-and-red pottery, and a 2,000-year-old Vanni tree.
- These findings highlight Korkai’s rich cultural heritage, tracing its origins to 785 BCE.
- Interpretation of satellite imagery suggests the Tamiraparani River once flowed differently, making Korkai a prominent harbour in its time.
Khajuraho
Why in news?
- The Khajuraho Dance Festival 2025 captivated audiences with classical performances and set a Guinness World Record for the largest dance gathering, celebrating India's rich cultural heritage at the UNESCO-listed Khajuraho Temples.
About Khajuraho:
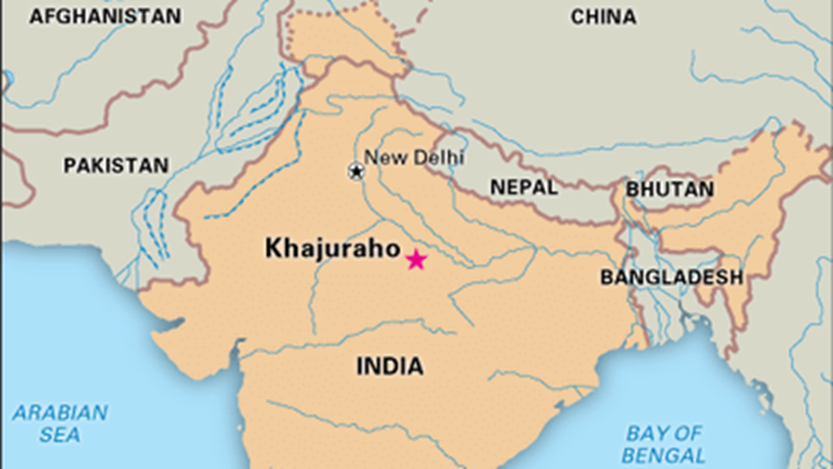
- Location:
- Khajuraho is a small town in the Chhatarpur district of Madhya Pradesh, India.
- It lies near the Ken River, approximately 175 km southeast of Jhansi and 620 km from Delhi.
- Khajuraho is part of the Bundelkhand region, known for its historical and architectural significance.
- Cultural and Religious Significance:
- Khajuraho is world-renowned for its UNESCO-listed Khajuraho Group of Monuments, reflecting India's rich heritage.
- The temples, built between 950 and 1050 CE by the Chandela dynasty, exemplify the Nagara-style architecture with intricate carvings.
- The temples are dedicated to Hindu deities like Shiva, Vishnu, and Devi, along with Jain Tirthankaras, showcasing religious inclusivity.
- The annual Khajuraho Dance Festival celebrates Indian classical dances like Bharatanatyam, Kathak, Odissi, Kuchipudi, Mohiniyattam, and Manipuri, promoting cultural tourism.
- Khajuraho Temples:
- The Khajuraho temple complex originally had 85 temples, but only 25 remain today, spread across the Western, Eastern, and Southern groups.
- The Kandariya Mahadeva Temple, dedicated to Lord Shiva, is the largest and most intricately designed temple in Khajuraho.
- The Lakshmana Temple is another significant structure, known for its Vaikuntha Vishnu idol and highly detailed sculptures.
The Parshvanatha and Adinatha Temples represent the Jain heritage of Khajuraho. - The Shaivite Chausath Yogini Temple, the oldest surviving temple in Khajuraho, is dedicated to the 64 Yoginis, female tantric deities. It follows a circular architectural layout, unlike other temples in the complex.
- The sensual sculptures of Khajuraho, often associated with Tantric traditions, symbolise the fusion of spiritual and worldly pursuits.
|
UPSC CSE PYQs Q. With reference to ancient South India, Korkai, Poompuhar and Muchiri were well known as (2023)
Answer: Option B Q. With reference to Chausath Yogini Temple situated near Morena, consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above are correct? (2021)
Answer: Option CQ. Consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (2019)
Answer: Option A |



