- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PLACES IN NEWS 3rd FEBRUARY 2025
PLACES IN NEWS 3rd FEBRUARY 2025
03-02-2025

New Ramsar sites from India
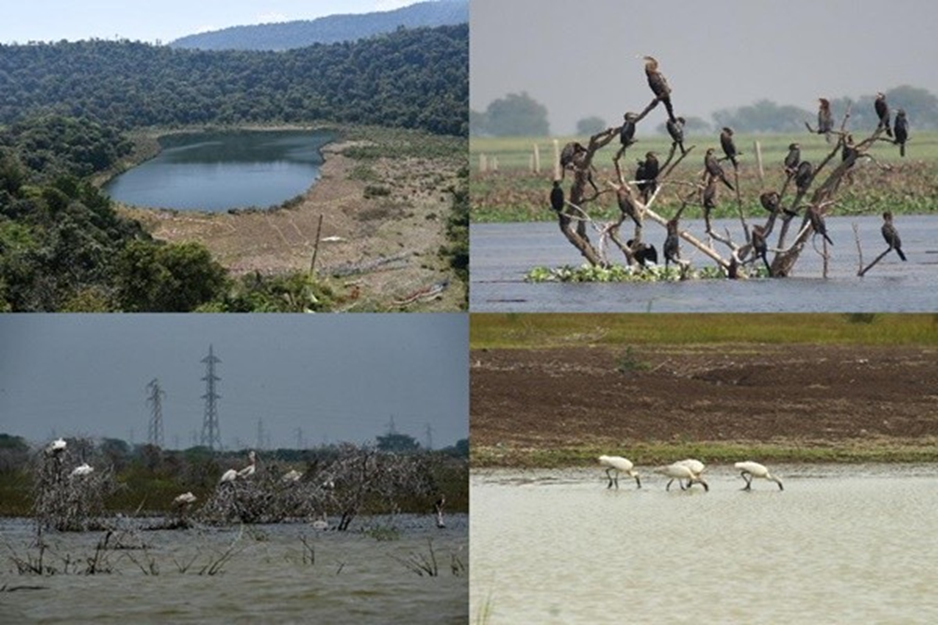

- Recently, four wetlands from India have been added to the list of Ramsar sites, highlighting their global ecological importance.
- The newly designated Ramsar sites include Sakkarakottai Bird Sanctuary and Therthangal Bird Sanctuary in Tamil Nadu, Khecheopalri Wetland in Sikkim, and Udhwa Lake in Jharkhand.
-
Sakkarakottai Bird Sanctuary:
- Sakkarakottai Bird Sanctuary is located in Tamil Nadu’s Ramanathapuram district. It is a crucial wetland that supports diverse resident and migratory birds.
- It serves as a breeding and wintering ground for species like herons, egrets, and storks.
- As part of the Point Calimere Wildlife and Bird Sanctuary network, it plays a vital role in avian conservation. The sanctuary also supports local agriculture by acting as a freshwater source and a natural flood buffer.
- However, habitat degradation and pollution threaten its ecological balance, making its Ramsar designation essential for improved conservation efforts.
-
Therthangal Bird Sanctuary:
- Therthangal Bird Sanctuary, in the Sivaganga district of Tamil Nadu, is a small yet significant wetland that provides habitat to over 50 bird species.
- It supports migratory birds along the Central Asian Flyway and aids groundwater recharge.
- With its diverse aquatic vegetation, the sanctuary plays a key role in biodiversity conservation.
- Despite its ecological significance, threats like unregulated fishing and land encroachment persist, making the Ramsar recognition crucial for enhanced protection.
-
Khecheopalri Wetland:
- Khecheopalri Wetland is a sacred high-altitude glacial lake in Sikkim that lies within the Khangchendzonga Biosphere Reserve.
- The pristine freshwater lake supports rare and endemic species while acting as a carbon sink.
- It plays a crucial role in local hydrology and serves as a habitat for migratory birds. Cultural and religious beliefs have long influenced conservation practices here.
- However, tourism pressure and invasive species pose challenges, making the Ramsar designation a step toward sustainable management.
-
Udhwa Lake:
- Udhwa Lake is the only Ramsar site in Jharkhand and consists of two interconnected lakes in the Sahibganj district.
- It is a vital habitat for migratory birds like bar-headed geese and supports local fisheries.
- The wetland also plays a key role in flood control, groundwater recharge, and water purification. Surrounded by fertile alluvial soil, it sustains nearby agriculture.
- However, encroachment and siltation threaten its ecological health. The Ramsar recognition strengthens conservation efforts and opens avenues for eco-tourism development, benefiting both the environment and local communities.
Guneri village
Why in news?
The Gujarat government has designated the inland mangrove ecosystem in Guneri village, Kutch district, as the state's first Biodiversity Heritage Site.
About Guneri village Mangrove Ecosystem:
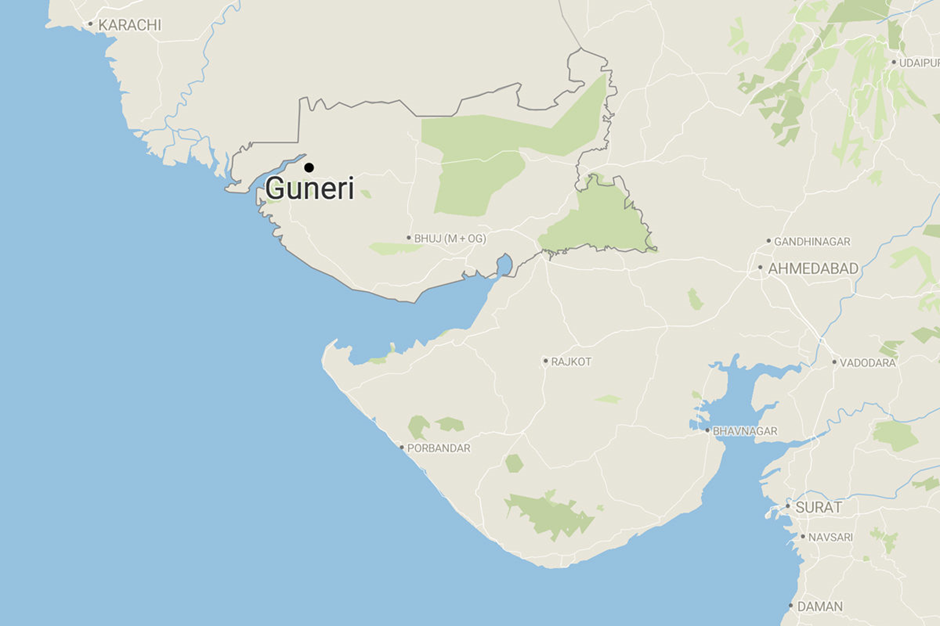
- The Guneri village mangrove ecosystem, located in Kutch district, Gujarat, is an inland mangrove forest, making it ecologically unique.
- Unlike coastal mangroves, these mangroves thrive in saline, arid conditions, demonstrating exceptional adaptability.
- This site has been designated as Gujarat’s first Biodiversity Heritage Site (BHS) due to its ecological and conservation significance under the Biological Diversity Act of 2002. The recognition ensures legal protection and promotes sustainable management practices.
- Mangroves act as a natural barrier against environmental challenges such as desertification, salinity intrusion, and soil erosion. In the arid landscape of Kutch, they play a crucial role in stabilising fragile ecosystems.
- These mangroves support rich biodiversity, including various species of birds, fish, and invertebrates. They provide breeding and nesting grounds for several species, contributing to regional ecological balance.
- The site is an important carbon sink, absorbing atmospheric carbon dioxide and mitigating the impact of climate change. Inland mangroves, despite their smaller coverage, contribute significantly to carbon sequestration.
- Local communities, including pastoralists and fishermen, depend on this ecosystem for their livelihoods. Mangroves provide fodder, fuelwood, and non-timber forest products, ensuring economic benefits while promoting sustainable use.
- The adaptation of mangroves to high salinity levels in an inland setting presents a unique research opportunity in climate resilience, soil salinity management, and ecological restoration.
- Threats such as deforestation, overgrazing, and habitat destruction pose challenges to the survival of this rare mangrove ecosystem. The Biodiversity Heritage Site status aims to curb these threats through community participation and conservation initiatives.
- The Guneri mangrove ecosystem exemplifies the role of inland wetlands in biodiversity conservation, reinforcing the need for holistic wetland management policies in India.
South Georgia Island
Why in news?
The world's largest iceberg, A23a, which broke off from Antarctica's Filchner Ice Shelf, is now drifting toward South Georgia Island, a crucial wildlife habitat.
About South Georgia Island:
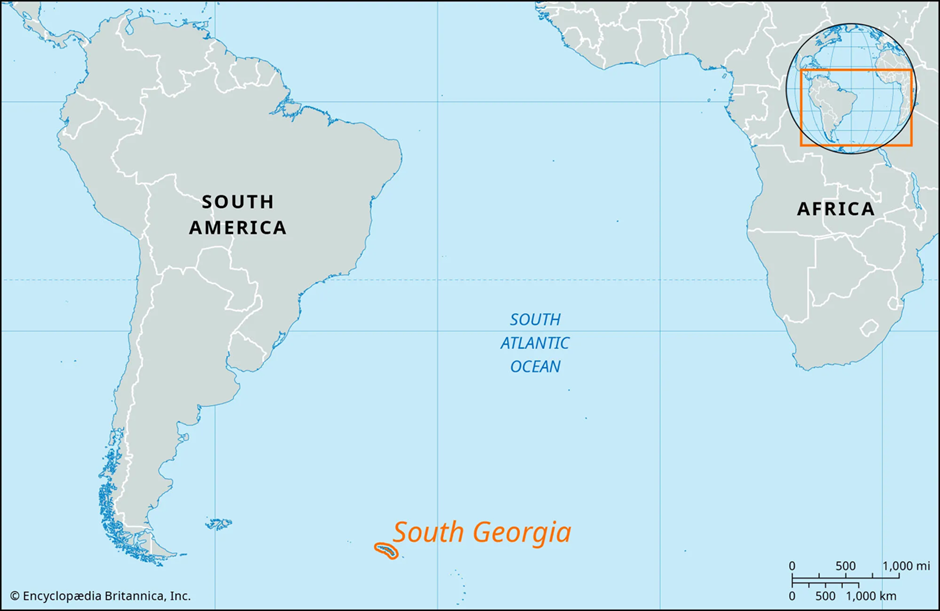
- South Georgia Island is a remote, rugged island located in the southern Atlantic Ocean, about 1,390 kilometres east of the Falkland Islands.
- It is part of the British Overseas Territory of South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands.
- The island spans approximately 3,755 square kilometres and is surrounded by icy waters and dramatic, mountainous landscapes. Its location makes it an important destination for scientific research and ecological conservation.
- South Georgia is known for its rich biodiversity and ecological significance. It serves as a crucial breeding and feeding ground for many marine species, including the iconic King penguin, which is one of the island's most recognised residents.
- The island is home to over 30 million breeding seabirds, including species like the Antarctic petrel, albatrosses, and skuas, making it one of the world’s most important seabird habitats.
- South Georgia is also a vital sanctuary for seals, with large populations of fur seals and elephant seals that haul out on its beaches.
- The surrounding waters are rich in krill, which serve as the primary food source for many of these species.
- The island’s marine ecosystem is equally vital, as it supports a variety of fish species and marine mammals, including whales.
- South Georgia Island is also an important site for scientific research, particularly in the fields of climate change, marine biology, and conservation ecology.
- The island's status as a protected area ensures that its unique wildlife and ecosystems remain safeguarded against human exploitation, although challenges such as climate change and the potential threat posed by icebergs like A23a remain significant.
Araku Valley
Why in news?
The three-day Araku Utsav, known as ‘Chali’, has begun in the picturesque Araku Valley, Andhra Pradesh. The festival features a marathon, cultural performances, and food stalls, celebrating the region’s rich heritage.
About Araku Valley:
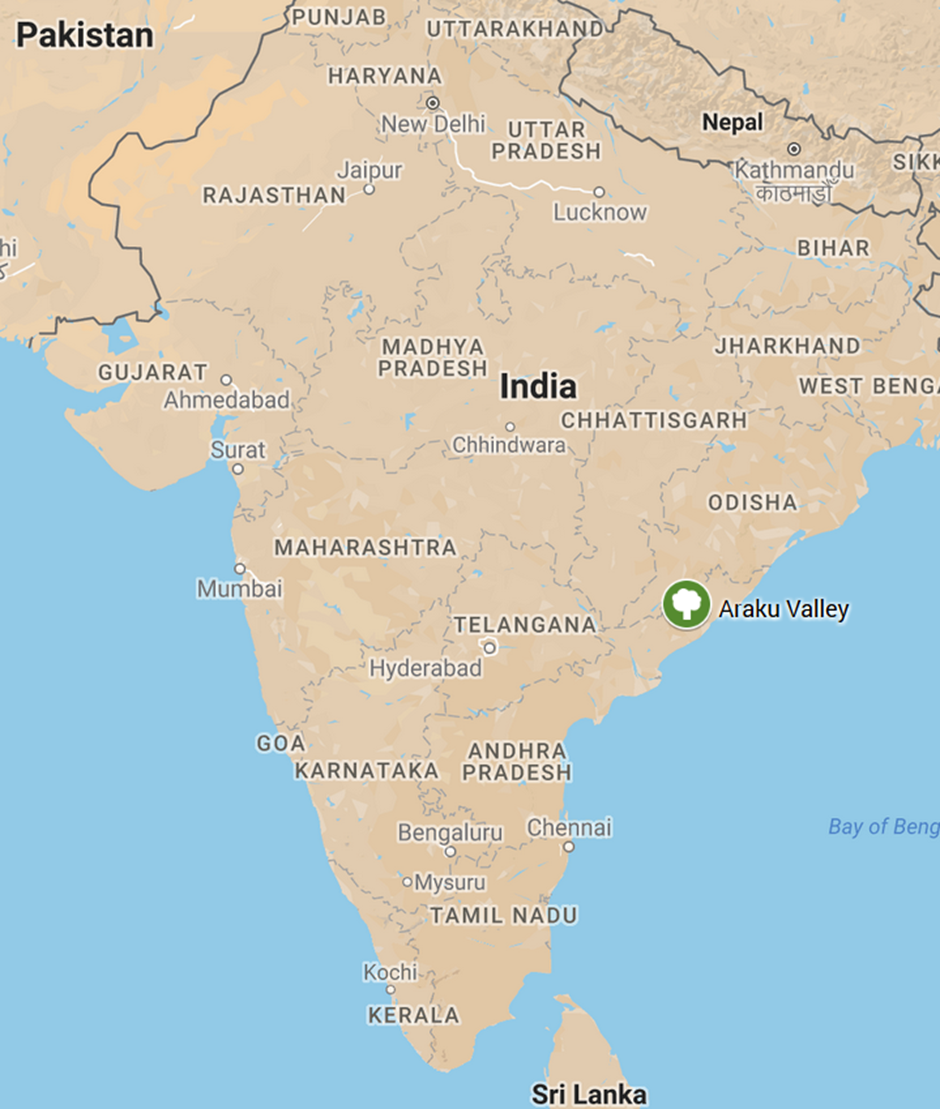
- Location and Geography:
- Araku Valley is located in the Eastern Ghats of Andhra Pradesh, India, about 120 kilometres north of Visakhapatnam.
- It is nestled in a breathtaking mountainous region, known for its lush greenery, coffee plantations, and rich tribal culture. The valley lies at an altitude of 900 to 1,000 meters, providing a temperate climate ideal for coffee cultivation.
- The topography of Araku Valley is marked by rolling hills, deep ravines, and dense forests, which are part of the Eastern Ghats' foothills.
- The valley is traversed by several rivers and streams, contributing to the area’s fertile soil and lush vegetation. The region's hilly terrain makes it a challenging yet scenic location for both agricultural and ecological research.
- Geographically, Araku Valley experiences a moderate climate, with temperatures ranging from 20°C to 30°C and a significant amount of rainfall, making it perfect for the cultivation of coffee and other crops.
- Coffee Production:
- Coffee production in Araku Valley is notable, as the region is one of India’s premium coffee-producing areas.
- The Arabica coffee grown here is known for its unique flavour profile, which is attributed to the high altitude, rich soil, and favourable climate conditions.
- In recent years, Araku Valley has become a popular destination for organic coffee farming.
- Statistics show that Araku Valley produces nearly 3,500 tonnes of coffee annually, with a significant portion being exported.
- The valley has gained recognition for producing some of the best organic coffee in India, with increasing global demand.
|
Also Read |
|
| FREE NIOS Books | |



