- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PLACES IN NEWS 31st JANUARY 2025
PLACES IN NEWS 31st JANUARY 2025

Kara Sea
Why in news?
The Kara Sea is witnessing increased Russian maritime activity.
About Kara Sea:
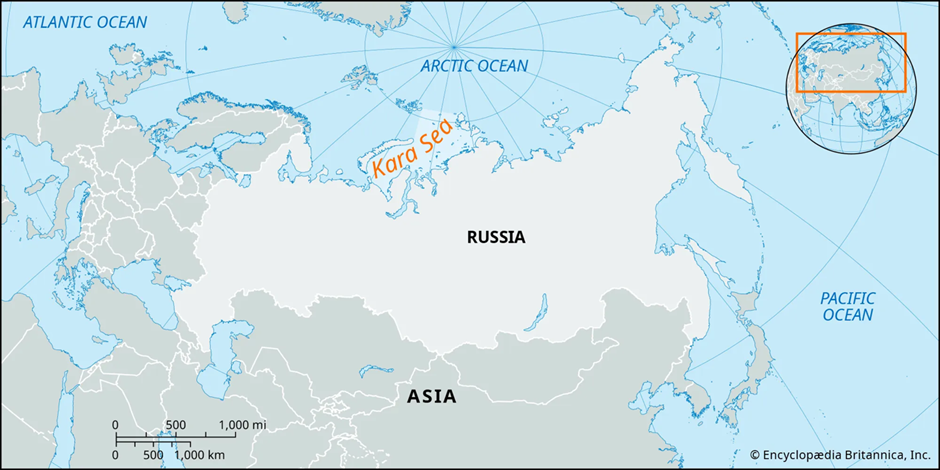
- Location:
- The Kara Sea is a marginal sea in the Arctic Ocean. It lies north of Siberia, Russia, and is bounded by Novaya Zemlya to the west and the Severnaya Zemlya archipelago to the east.
- It covers approximately 880,000 square kilometres and connects to the Arctic Basin in the north, the Barents Sea in the west, and the Laptev Sea in the east.
- Strategic Importance:
- The Kara Sea's position is becoming increasingly pivotal. As Arctic ice diminishes due to climate change, new shipping routes are emerging, notably the Northern Sea Route (NSR), which passes through the Kara Sea.
- This route offers a shorter passage between Europe and Asia than traditional routes like the Suez Canal.
- This growing accessibility has led to increased commercial interest, particularly from Russia, China, and other nations looking to capitalise on shorter shipping times and resource transportation.
- Challenges in the region:
- Despite its potential, Arctic shipping faces major challenges. Extreme weather conditions, unpredictable ice movement, and inadequate infrastructure pose significant risks to navigation.
- The lack of developed search and rescue capabilities, ports, and refuelling stations complicates emergency response efforts.
- Additionally, the fragile Arctic ecosystem is highly vulnerable to pollution, with oil spills and increased human activity threatening marine life and indigenous communities.
- Regulatory compliance is crucial for sustainable Arctic operations. The Polar Code, implemented by the International Maritime Organisation (IMO), establishes mandatory safety and environmental standards.
- While many Arctic nations have integrated these regulations into their policies, enforcement remains a concern, especially as commercial activities increase.
- Balancing commercial interests with environmental protection and international cooperation is essential for the long-term viability of Arctic shipping.
Ghaggar River
Why in news?
A joint committee formed by the National Green Tribunal (NGT) has determined that the Ghaggar River's water contains biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) levels two to three times higher than the prescribed limit, rendering it unsuitable for outdoor bathing.
About Ghaggar River:
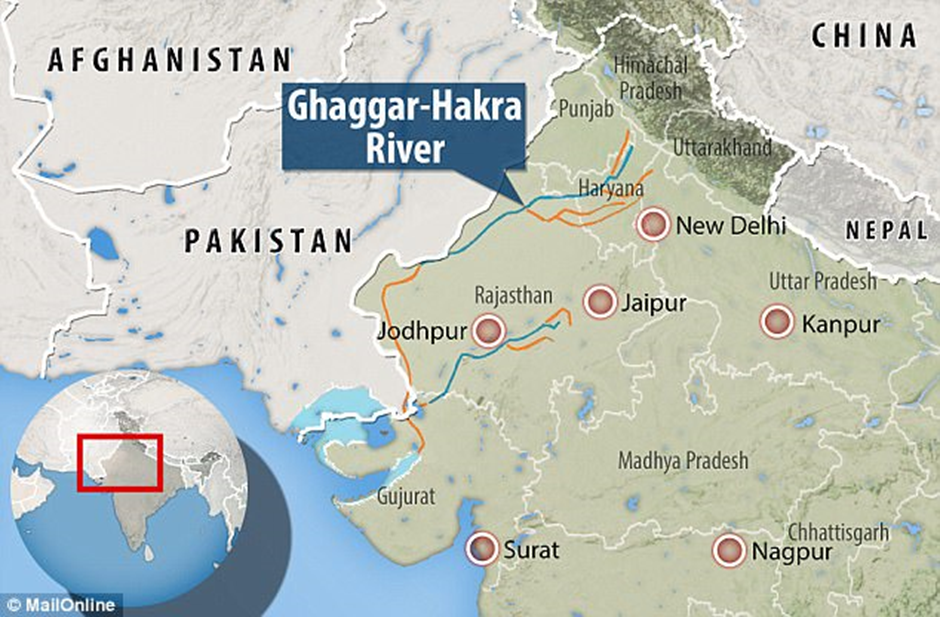
- Origin:
- The Ghaggar River originates in the Shivalik Hills of Himachal Pradesh, India, near the town of Kalka.
- It flows through the states of Punjab, Haryana, and Rajasthan before eventually dissipating into the Thar Desert.
- It is an intermittent river, meaning its flow is seasonal, primarily during the monsoon.
- Historically, the Ghaggar is believed to be the remnant of the ancient Saraswati River, holding significant cultural and historical importance.
- Ecological Importance:
- Ecologically, the Ghaggar River supports diverse flora and fauna, providing water for agriculture and sustaining local communities.
- Its seasonal flow, primarily during the monsoon, replenishes groundwater levels and supports various ecosystems along its course.
- Rise in Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD):
- In recent years, the river has experienced a significant increase in Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) levels, indicating a rise in organic pollution.
- This escalation is primarily due to the discharge of untreated or inadequately treated industrial effluents and sewage into the river.
- Industries along the riverbanks release pollutants directly into the water, while municipal waste management systems often fail to treat sewage effectively before disposal. Additionally, poor waste management practices contribute to the degradation of water quality.
- Elevated BOD levels deplete the river's dissolved oxygen, adversely affecting aquatic life by creating hypoxic conditions unsuitable for survival.
- This deterioration disrupts the ecological balance, leading to a decline in biodiversity. For local communities relying on the Ghaggar for daily needs, polluted water poses serious health risks, including waterborne diseases.
- The pollution also impacts agriculture, as farmers using contaminated river water for irrigation may experience reduced crop yields and soil degradation.
- Furthermore, the pollution of the Ghaggar River affects groundwater quality, exacerbating health issues for communities dependent on these water sources.
- Addressing these challenges requires comprehensive strategies, including the enforcement of environmental regulations, the establishment of effective waste treatment facilities, and public awareness campaigns to promote sustainable practices.
- Collaborative efforts between government agencies, industries, and local communities are essential to restore the Ghaggar River's health and ensure its continued ecological and economic benefits.
Kanha Tiger Reserve
Why in news?
A 2-year-old tigress was recently discovered dead in Kanha Tiger Reserve, located in Mandla district, Madhya Pradesh.
About Kanha Tiger Reserve:
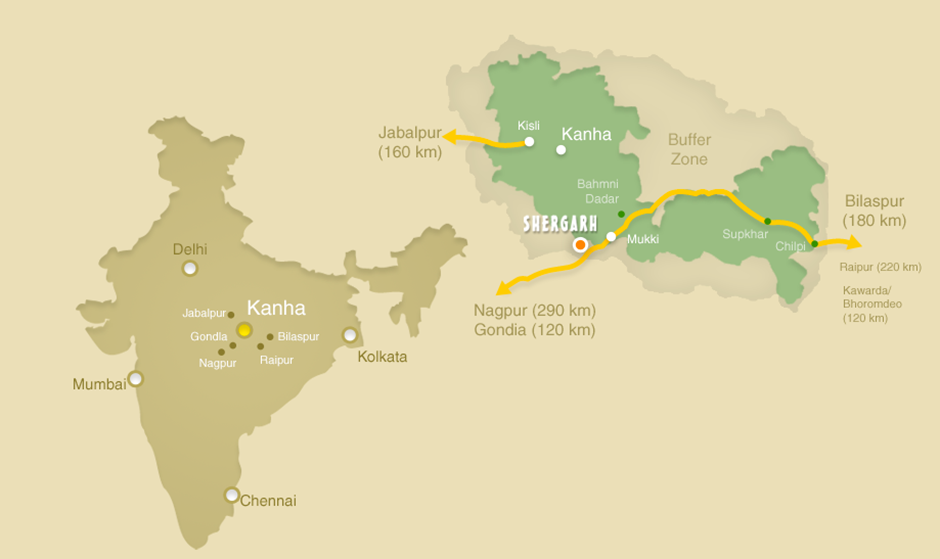
- Location:
- Kanha Tiger Reserve is situated in the Mandla and Balaghat districts of Madhya Pradesh, India. It lies at the heart of the Satpura Hills, with the Banjar and Kolar rivers flowing through the reserve.
- Kanha covers an area of around 940 square kilometres, making it one of the largest and most important tiger reserves in India.
- Flora and Fauna:
- Kanha's flora is diverse, with dense sal forests, grasslands, and bamboo thickets. The reserve is home to several species of trees and plants, such as Sal (Shorea robusta), teak, bamboo, and tendu.
- The reserve is renowned for its fauna, particularly its population of Barasingha (Swamp Deer), a species once critically endangered but now thriving due to intensive conservation efforts. Kanha is home to over 500 Barasingha, a significant success in wildlife conservation.
- Kanha is also famous for its population of tigers, leopards, wild dogs (dhole), and various species of deer, including spotted deer and sambar.
- The reserve also supports bears, jackals, and numerous smaller mammals. It has a rich diversity of birds, including Indian rollers, eagles, and vultures, as well as reptiles such as pythons and crocodiles.
Kurdistan region
Why in news?
India recently sent humanitarian aid to the Kurdistan region of Iraq to assist those affected by natural disasters and ongoing conflicts.
About Kurdistan region:
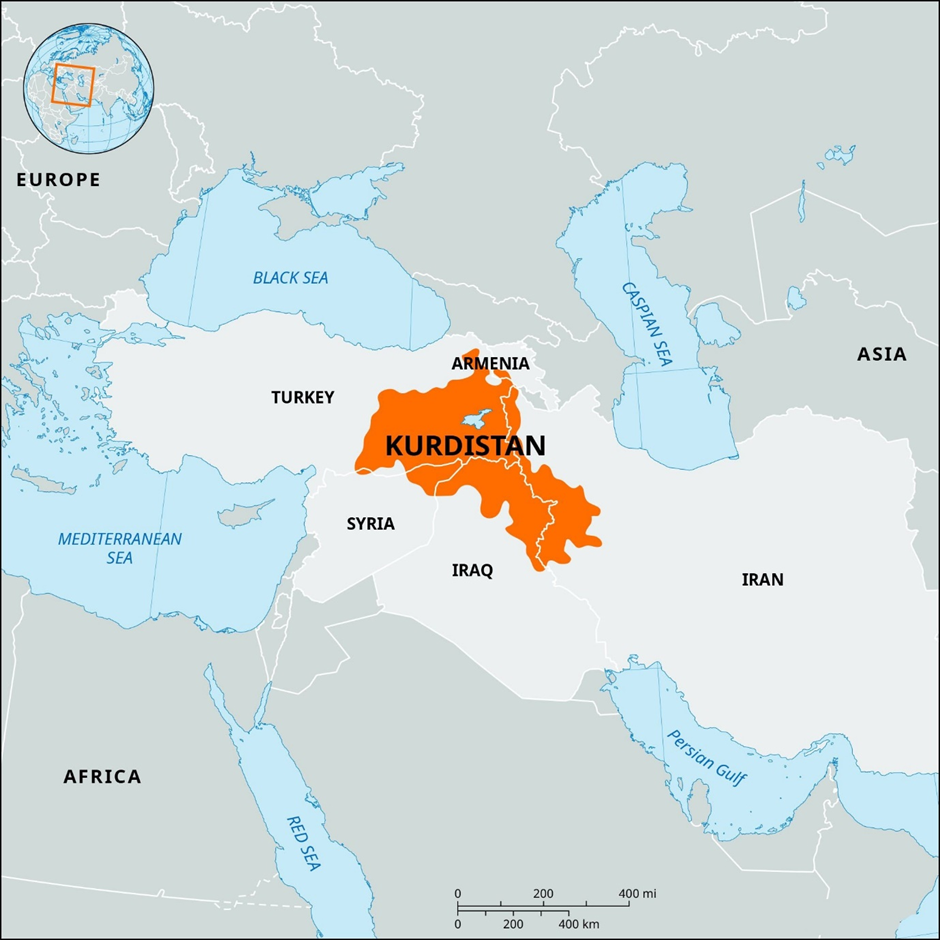
- Location and Demography:
- The Kurdistan Region is an autonomous region in northern Iraq, bordered by Turkey to the north, Iran to the east, and Syria to the west.
- The region encompasses diverse landscapes, including mountainous terrains, plateaus, and fertile plains. Major rivers such as the Tigris and Euphrates flow through parts of the region, contributing to its agricultural productivity.
- The population is ethnically diverse, predominantly Kurdish, with significant communities of Arabs, Turkmen, Assyrians, Armenians, and others. Religiously, the majority are Sunni Muslims, with minorities practicing Christianity, Yazidism, and other faiths.
- Recent Causes of Natural Disasters:
- Wildfires: The Kurdistan Region has experienced a concerning rise in wildfires in recent years. These fires are primarily caused by a combination of natural and human-made factors, including hot and dry weather conditions, accidents, and military activities such as fighting between the Turkish Armed Forces and the Kurdistan Workers Party (PKK) insurgent group.
- Floods: In March 2024, heavy rains led to flash floods in the Dohuk governorate, causing water inundation across the city, transportation disruptions, and raising concerns about potential flooding.
- Droughts and Heatwaves: The region has faced increasing droughts and rising temperatures, leading to water scarcity and agricultural challenges. Iraq's President Abdul Latif Rashid has warned of escalating natural disasters, citing frequent droughts, floods, and rising temperatures impacting all parts of the country due to climate change.
- Dust Storms: The region has observed more frequent and intense dust storms (shamal and haboob) due to low soil moisture caused by urbanisation, agriculture, and climate change.
Teesta River
Why in news?
The Environment Ministry of India has approved the reconstruction of the Teesta Dam along Teesta River in Sikkim despite safety concerns raised by experts and the fact that certain pending approvals have not been granted.
About Teesta River:
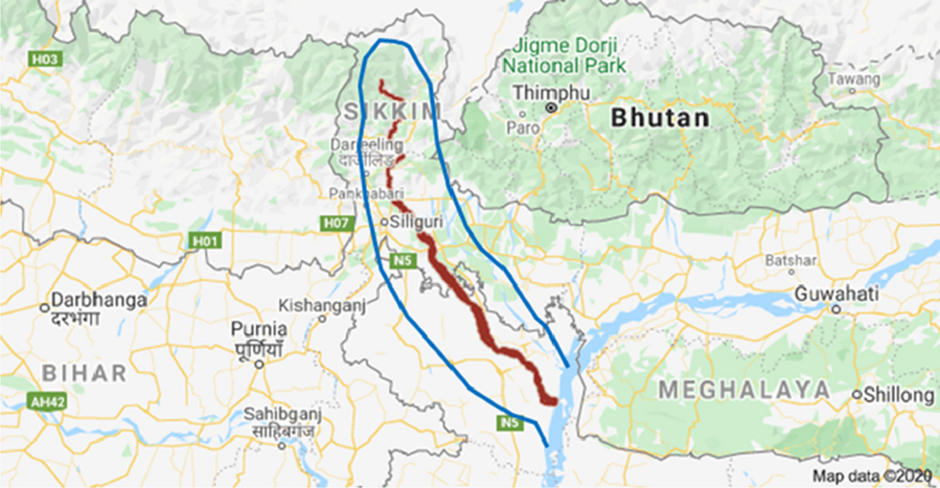
- Origin:
- The Teesta River originates from the Teesta Khangtse Glacier in the Sikkim Himalayas at over 5,400 meters.
- It is fed by streams from Tso Lhamo Lake, Gurudongmar Lake, and valleys like Thangu and Yumthang.
- Flowing through towns such as Chungthang, Singhik, and Singtam, it is joined by tributaries like the Kanaka River and Ranikhola. The river reaches Rangpo, where it merges with the Rangpo River, forming the boundary between Sikkim and West Bengal. Before the Teesta Bridge, it is joined by its largest tributary, the Rangeet River.
- After crossing India, it joins the Jamuna River at Phulchhari Upazila in Bangladesh.
- Dam Construction and Associated Issues:
- The construction of dams along the Teesta River, such as the Teesta Dam and Teesta-VI Dam, is primarily driven by the need for hydroelectric power generation.
- The region is rich in water resources, and the dams help harness the river's flow for electricity production, benefiting both local economies and national power grids.
- The dams are also seen as a means of flood control and irrigation for the agricultural regions downstream, ensuring water supply during dry periods.
- Its major issues include environmental concerns that have emerged due to the alteration of natural water flow, disruption of ecosystems, and the submergence of forested areas.
- There are safety concerns about the structural integrity of dams in a seismically active region like Sikkim, raising the risk of disasters like landslides and dam breaches.
- Local communities have also expressed concerns about displacement and loss of livelihoods, as the construction could affect agricultural land and the river's natural habitat.
|
UPSC CSE PYQs Q1. Which one of the following statements best describes the ‘Polar Code’? (2022)
Answer: Option A Q2. Which one of the following protected areas is well-known for the conservation of a subspecies of the Indian swamp deer (Barasingha) that thrives well on hard ground and is exclusively graminivorous? (2020)
Answer: Option A Q3. With reference to river Teesta, consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (2017)
Answer: Option B Q4. Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) is a standard criterion for: (2017)
Answer: Option C Q5. Consider the following pairs :
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched? (2016)
Answer: Option C |
|
Also Read |
|
UPSC Foundation Course |
|
| CSAT Foundation Course | |



