- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PLACES IN NEWS 30 NOVEMBER 2024
PLACES IN NEWS 30 NOVEMBER 2024
30-11-2024
Karbi Anglong
Why in news?
- In Assam's Karbi Anglong, Kuki leaders have agreed to surveys in their villages to address claims that around 1,000 Kukis from violence-hit Manipur have settled there, allegations they deny.
- The surveys, initiated by Karbi Anglong Autonomous Council (KAAC) Chief Executive Member Tuliram Ronghang, aim to clarify concerns about illegal settlements.
- A task force comprising local leaders, revenue officials, and student organizations was formed to identify and deport illegal immigrants if found.
- The KAAC governs Karbi Anglong and West Karbi Anglong under the Sixth Schedule of the Constitution, ensuring tribal rights and administrative autonomy in the region.
About Karbi Anglong:
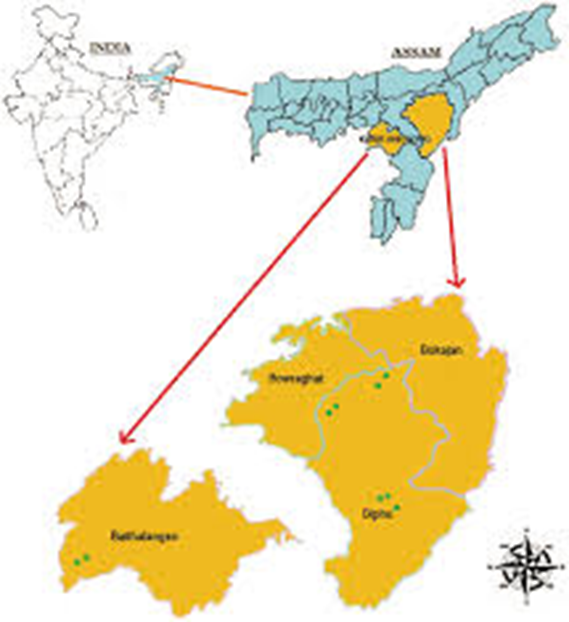
- Karbi Anglong is the largest district in Assam, covering both Karbi Anglong and West Karbi Anglong.
- It is part of Meghalaya plateau, which is an extension of Indian Deccan plate and features a rugged topography with steep slopes and valleys.
- It is interspersed with plains and river valleys, including the Dhansiri River, which provides vital water resources.
- The district experiences a tropical monsoon climate with significant rainfall, fostering rich biodiversity and dense forest cover.
- Its forests are home to diverse flora and fauna, including species like elephants, tigers, and hornbills, making it ecologically significant.
- The region is rich in mineral resources such as coal, limestone, feldspar, and clay, which support local industries.
- The fertile soil and favourable climate contribute to agriculture, with crops like ginger, rubber, and tea cultivated extensively.
- Karbi Anglong is inhabited by diverse communities, with the Karbis being the predominant tribe, followed by other ethnic groups contributing to its cultural vibrancy.
Notre Dame Cathedral
Why in news?
- French President Emmanuel Macron visited Notre Dame Cathedral ahead of its reopening on December 7, five years after a fire devastated its roof and spire.
- Built in 1163, the Gothic masterpiece, famed for its rib vaulting, flying buttresses, and stained-glass windows, suffered extensive damage in 2019.
- Though the cause of the fire remains uncertain, possibilities include an electrical fault or a burning cigarette.
- Restoration efforts, funded by over $882 million in global donations, have rebuilt the spire and roof, cleaned stonework and paintings, and restored or replaced furniture. The reopening ceremony will include a blessing, organ performance, and a service.
About Notre Dame Cathedral:
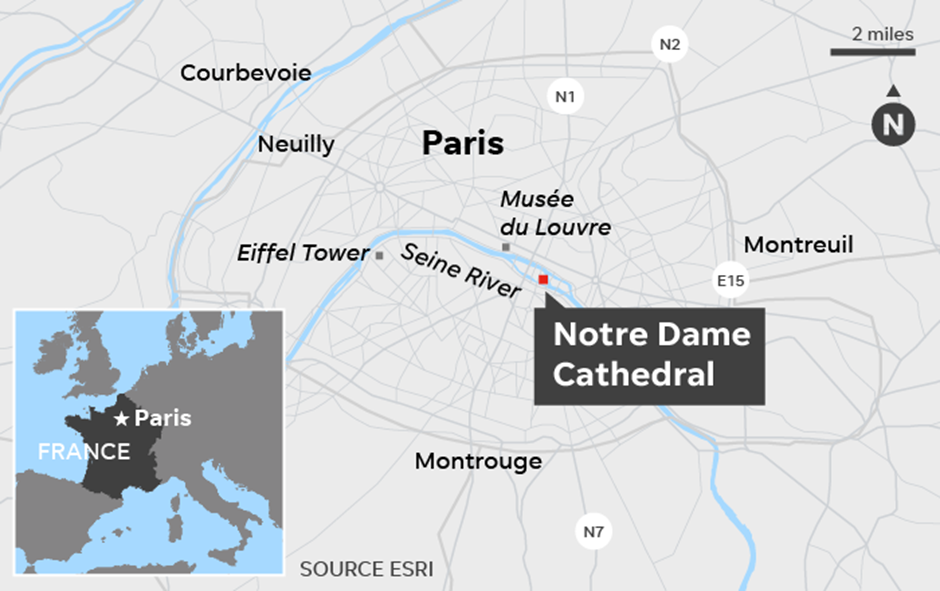
- Notre-Dame de Paris is a Gothic cathedral located on Île de la Cité (a natural island in Seine in eastern Paris), renowned for its size, antiquity, and architectural significance.
- Built on the ruins of earlier churches and a Gallo-Roman temple to Jupiter, its construction was initiated by Bishop Maurice de Sully in 1160.
- The foundation stone was laid in 1163 by Pope Alexander III, with the high altar consecrated in 1189. The choir, western façade, and nave were completed by 1250, followed by additional embellishments over the next century.
- The cathedral is celebrated for its architectural features, including rib vaulting, flying buttresses, and intricately carved stone gargoyles.
- Its stunning stained-glass windows, particularly the iconic rose windows, are considered masterpieces of medieval art.
- The cathedral houses numerous religious artifacts, including the Crown of Thorns, believed to have been worn by Jesus during the crucifixion.
- Notre-Dame was rescued from deterioration after the French Revolution and hosted Napoleon’s coronation as emperor in 1804.
- A fire in April 2019 destroyed the roof, Viollet-le-Duc’s spire, and parts of the rib vaulting.
- President Macron pledged reconstruction within five years, and Notre-Dame is set to reopen on December 7, 2024, with restoration costs estimated at $850 million.
Chad
Why in news?
- Chad announced the termination of its key defence cooperation agreement with France, signalling a shift toward asserting its sovereignty.
- This decision follows Chad's earlier expulsion of U.S. troops before its May presidential elections, marking a broader distancing from traditional Western allies.
- Chad, a critical player in combating Islamist militants in the Sahel, hosts 1,000 French troops providing logistical support.
- Despite ending the agreement, Chadian authorities emphasized maintaining ties with France in non-military domains, describing the nation as an "essential partner."
- The move aligns with a broader trend in the region, as Mali, Niger, and Burkina Faso have also severed French security ties, often favouring Russian alliances.
About Chad:

- Chad is a large landlocked country in north-central Africa, covering 1,284,000 square kilometres, making it the 20th largest country globally.
- It is bordered by Libya to the north, Sudan to the east, Niger, Nigeria, and Cameroon to the west, and the Central African Republic to the south.
- The capital, N’Djamena, is 1,060 kilometres from the nearest seaport in Douala, Cameroon.
- The country’s landscape consists of a basin surrounded by the Ennedi Plateau and Tibesti Mountains, including Emi Koussi, Africa's highest volcano.
- Lake Chad, which gives its name to the country was previously enormous but is now only 17,806 square kilometres in extent.
- Chari and Logone are the main rivers draining into Lake Chad.
- The climate varies: the Sahara in the north receives less than 50 mm of rain annually, while the central Sahel region gets 300-600 mm, and the southern Sudanian zone receives over 900 mm.
Sahel region
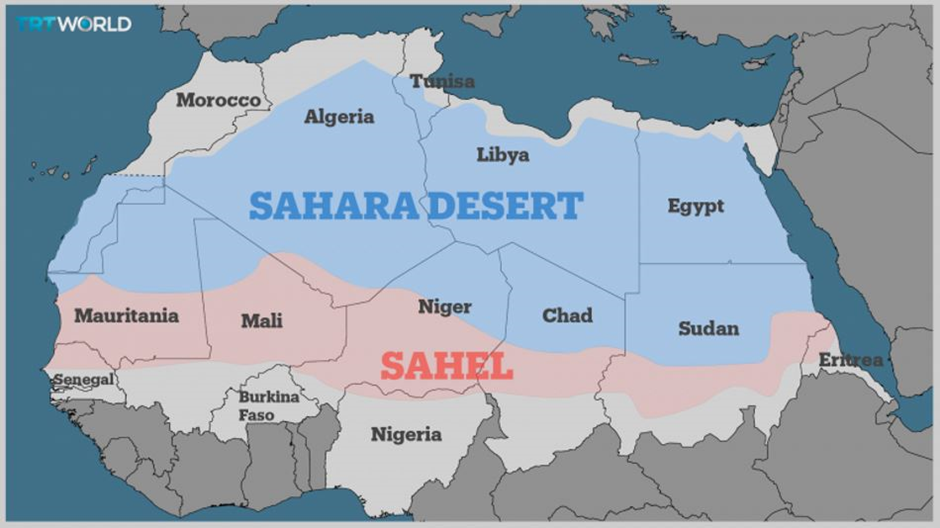
- Geography:
- The Sahel is a semi-arid belt across Africa, stretching from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Red Sea in the east.
- It spans approximately 5,400 km, acting as a transitional zone between the Sahara Desert to the north and the savannahs to the south.
- The region includes parts of several countries: Senegal, Gambia, Mauritania, Guinea, Mali, Burkina Faso, Niger, Chad, Cameroon, Eritrea and Nigeria.
- The landscape is characterized by a mix of sandy plains, rocky plateaus, and scattered hills, with very limited vegetation in some areas.
2. Climate:
- The Sahel has a hot, dry climate, with temperatures often exceeding 40°C (104°F) during the day.
- It has a short rainy season from May to October, with rainfall ranging from less than 200 mm in the north to over 600 mm in the southern parts.
- The rainy season is irregular and highly unpredictable, contributing to periodic droughts that severely affect agriculture and livelihoods.
- The region experiences significant fluctuations in temperature, with cold nights and very hot days during the dry season.
3. Desertification:
- Desertification is a significant environmental issue in the Sahel due to both natural and human-induced factors.
- Overgrazing by livestock, deforestation, and unsustainable farming practices contribute to soil degradation and erosion.
- Climate change exacerbates desertification, with decreasing rainfall and higher temperatures, leading to more severe droughts and the expansion of the Sahara Desert.
- The loss of vegetation and arable land further reduces the region's agricultural capacity, threatening food security for millions of people.
- International efforts, such as the Great Green Wall initiative, are focused on combating desertification by replanting trees and promoting sustainable land management practices.
Lothal
Why in news?
- A tragic incident occurred on November 27, 2024, when 23-year-old Surabhi Verma, a PhD scholar from IIT Delhi, died after a trench at the Lothal Harappan archaeological site collapsed on her.
- The research team, which was studying paleoclimatology, had dug the pit in a prohibited area without proper permissions from authorities.
- The Gujarat police and district administration have sought explanations from IIT Delhi, IIT Gandhinagar, and the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) regarding safety protocols and permissions.
- Lothal, a protected site since 1999, falls under strict regulations, with a 100-meter prohibited area surrounding the monument.
About Lothal:

Lothal is one of the most significant Harappan sites, located in the present-day state of Gujarat, India. It is situated on the banks of the Gulf of Khambhat, near the Saurashtra region, and was an important urban centre of the Indus Valley Civilization (IVC).
-
- Town Planning:
- The town was meticulously planned with a grid pattern, akin to other Harappan sites.
- It had well-organized streets, drainage systems, and public baths, demonstrating advanced urban planning and engineering.
- Religion:
- People of Lothal worshipped a fire god, possibly the horned deity on seals.
- Fire-altars suggest religious ceremonies involving fire worship.
- A sea goddess may have been worshipped, linked to the ancient port and modern local traditions.
- Cremation practices and post-cremation burials were also observed.
- Architecture:
- Lothal's architecture was constructed from mud-bricks, with buildings primarily consisting of residential and public structures.
- The most notable architectural feature is the dockyard, which highlights Lothal's significance as a port city.
- Metallurgy and Jewellery:
- Lothal was an important centre for bead-making and metallurgy. Archaeological findings include semi-precious stones like carnelian, agate, and turquoise, suggesting skilled craftsmanship in jewellery making.
- The city also saw the production of copper and bronze tools, with a focus on metallurgy.
- Cultivation and Diet:
- The region's economy was primarily based on agriculture, with evidence of wheat, barley, and cotton cultivation.
- The diet likely included fish, as Lothal was a coastal city, and other agricultural products like cereals and legumes.
- Trade
- Lothal had trade routes linking it to Dholavira and Sutkagan Dor on the Makran coast.
- It maintained trade relations with the Sumerian civilization as evident from archaeological findings.
- Trade facilitated cultural and material exchanges between these regions



