- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PLACES IN NEWS 2nd JANUARY 2025
PLACES IN NEWS 2nd JANUARY 2025
02-01-2025

Vembanad Lake
Why in news?
The Alappuzha district administration in Kerala is set to launch a mega plastic cleaning drive as a key initiative under the Vembanad Lake rejuvenation project.
About Vembanad Lake:
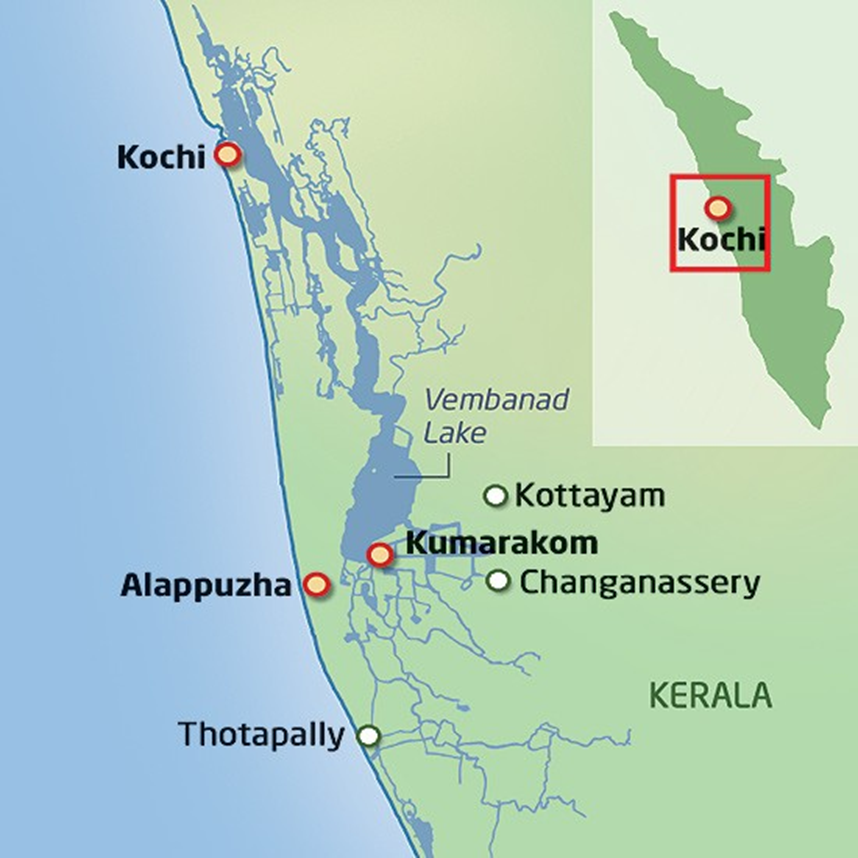
- Geography:
- Vembanad Lake, located in Kerala, is the longest lake in India and the largest in the state. It stretches across several districts, including Alappuzha, Kottayam, and Ernakulam, forming a vital part of Kerala's backwater system.
- The lake is geographically significant as it connects to the Arabian Sea, forming a natural lagoon and serving as a critical link in the region's waterways.
- It is fed by several rivers, including the Pamba, Meenachil, and Achankovil, making it a hub for inland water transport.
- Ecological Importance:
- Recognised as a Ramsar Site, Vembanad Lake holds ecological importance for its unique wetland ecosystem. It supports diverse flora and fauna, including endangered species, and provides a critical habitat for migratory birds. The lake's extensive mangrove forests and associated wetlands play a vital role in carbon sequestration and coastal protection.
- The lake sustains local livelihoods by supporting fisheries and agriculture. It provides water for the nearby rice paddies, famously known as the "Kuttanad region," which is one of the few places in the world where farming is done below sea level.
- Vembanad Lake faces ecological challenges, including pollution and encroachment, which threaten its biodiversity. Conservation initiatives, such as the Ramsar Convention's guidelines, emphasise sustainable practices to protect this fragile ecosystem.
- Cultural Significance:
- The lake holds cultural significance as it is deeply woven into the traditions of Kerala. It serves as the venue for the annual Nehru Trophy Boat Race, a globally renowned event that showcases the region’s rich heritage and vibrant community spirit.
- Houseboats and traditional canoe rides on the lake attract thousands of tourists every year, contributing significantly to the state's economy while offering a glimpse into the tranquil backwaters and rural life of Kerala.
Pangong Tso
Why in news?
A statue of Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj was recently inaugurated on the banks of Pangong Tso, situated at an altitude of 14,300 feet in Ladakh.
About Pangong Tso:
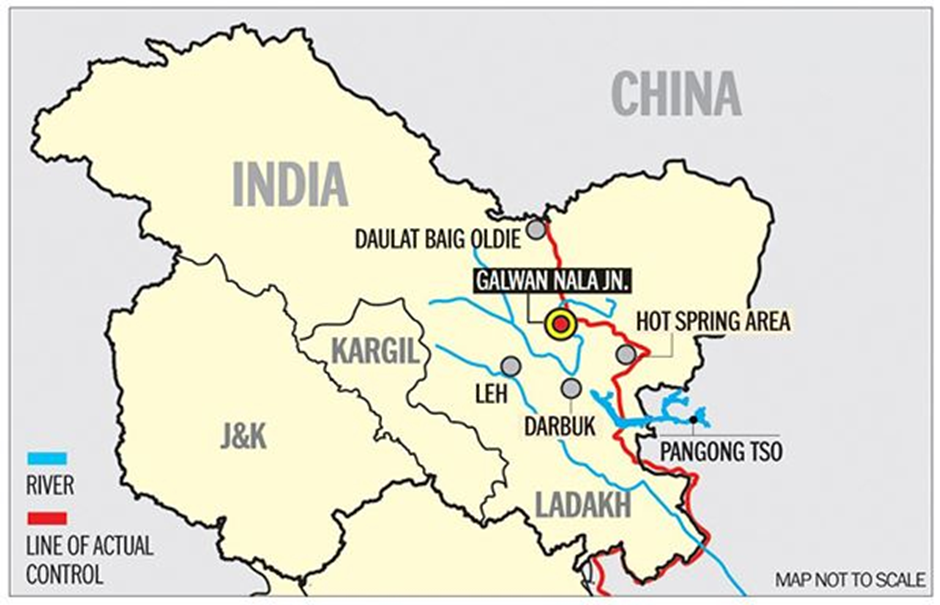
- Geographical Importance:
- Pangong Tso, a high-altitude lake located in the Himalayas, lies at an elevation of about 14,270 feet.
- It stretches across eastern Ladakh in India and extends into Tibet, China, covering a length of approximately 134 kilometres.
- The lake's geography is unique, as it is a saline water body in a cold desert environment.
- Despite its saltwater nature, the lake freezes completely during winter due to extreme temperatures, showcasing its distinct climatic conditions.
- The lake's ecosystem supports a limited but unique range of flora and fauna. Migratory birds, such as bar-headed geese and Brahminy ducks, frequent the region, adding to its ecological significance.
- Strategic Importance:
- Strategically, Pangong Tso holds immense importance due to its proximity to the Line of Actual Control (LAC) between India and China. The lake spans both nations, with a significant portion under Chinese control. This has made it a focal point during border tensions and military standoffs.
- The area around Pangong Tso serves as a critical zone for India's defence and surveillance efforts. Its location highlights the need for robust infrastructure, including roads and communication networks, to ensure swift military mobility in this remote region.
- The lake has been at the centre of recent geopolitical events, reflecting the complex dynamics between India and China. Its strategic value underscores the necessity of maintaining a strong military presence while seeking peaceful resolutions to disputes.
- Pangong Tso is also a symbol of India's sovereignty and resilience in maintaining control over its border regions. Efforts to boost tourism in the area, such as improved facilities and cultural events, aim to showcase its natural beauty while emphasising its national significance.
Ivory Coast
Why in news?
- Ivory Coast has officially requested the departure of French forces stationed in the country, signalling a shift in its foreign and security policies.
- The government emphasized the need to assert sovereignty and reduce dependence on external military support.
- This decision aligns with a growing trend in West Africa, where several nations are re-evaluating their relationships with former colonial powers.
About Ivory Coast:
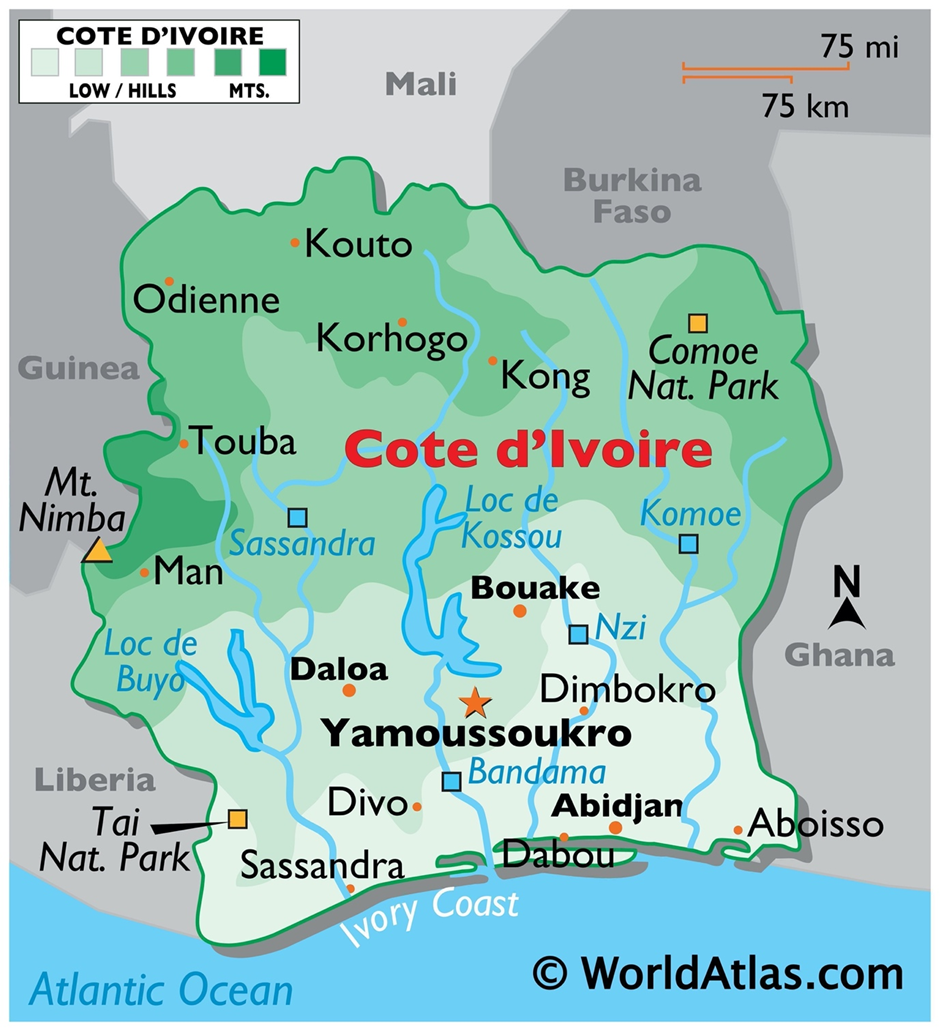
- Geography and resources:
- Ivory Coast, also known as Côte d'Ivoire, is located in West Africa, bordered by Liberia and Guinea to the west, Mali and Burkina Faso to the north, Ghana to the east, and the Gulf of Guinea to the south.
- The country is rich in natural resources, including cocoa, coffee, palm oil, gold, diamonds, and petroleum. Ivory Coast is the world's leading producer of cocoa, contributing significantly to its economy. Fertile lands and favourable climatic conditions make it an agricultural powerhouse in Africa.
- Regional Security Realignment:
- French troops have been stationed in Ivory Coast since 2002, following a civil war that divided the country into a rebel-controlled north and a government-controlled south. Their primary role was to stabilise the region, enforce peace agreements, and support United Nations missions in addressing the country's political and security challenges.
- Over time, the presence of French forces became a contentious issue. Critics argue that the troops symbolise Ivory Coast's lingering ties to colonial influence, undermining its sovereignty. Recent public sentiment has leaned toward reducing reliance on foreign military support and building domestic defence capabilities.
- This decision by Ivory Coast aligns with a broader trend in West Africa, where countries like Mali and Burkina Faso have also asked French forces to leave. In Mali, tensions escalated due to disagreements over anti-terrorism strategies, leading to the withdrawal of French troops in 2022. Burkina Faso followed suit in 2023, reflecting growing dissatisfaction with the perceived inefficacy of foreign military interventions in curbing extremist violence.
- These nations aim to reassert their sovereignty while exploring alternative security partnerships, including increased collaboration with regional alliances and other international actors. This shift also highlights the emergence of nationalist sentiments and a demand for greater autonomy in handling domestic affairs.
- The move also resonates with a wider reassessment of Africa's post-colonial relationships with former European powers. Many countries are striving for a more balanced and equal partnership that respects their sovereignty and promotes mutual development.
- While the departure of French troops presents opportunities for enhanced sovereignty and unity, it also brings challenges, including the immediate need to bolster national security forces and foster effective regional cooperation to maintain stability. Ivory Coast’s evolving stance symbolises a turning point in the geopolitics of West Africa.
Kenya
Why in news?
- Kenya's Maasai Olympics, a unique initiative blending tradition and conservation, witnessed women running to challenge gender norms and bridge the gender gap.
- Traditionally focused on male athleticism, the event now includes women competing in activities like running, showcasing their strength and determination.
About Kenya:
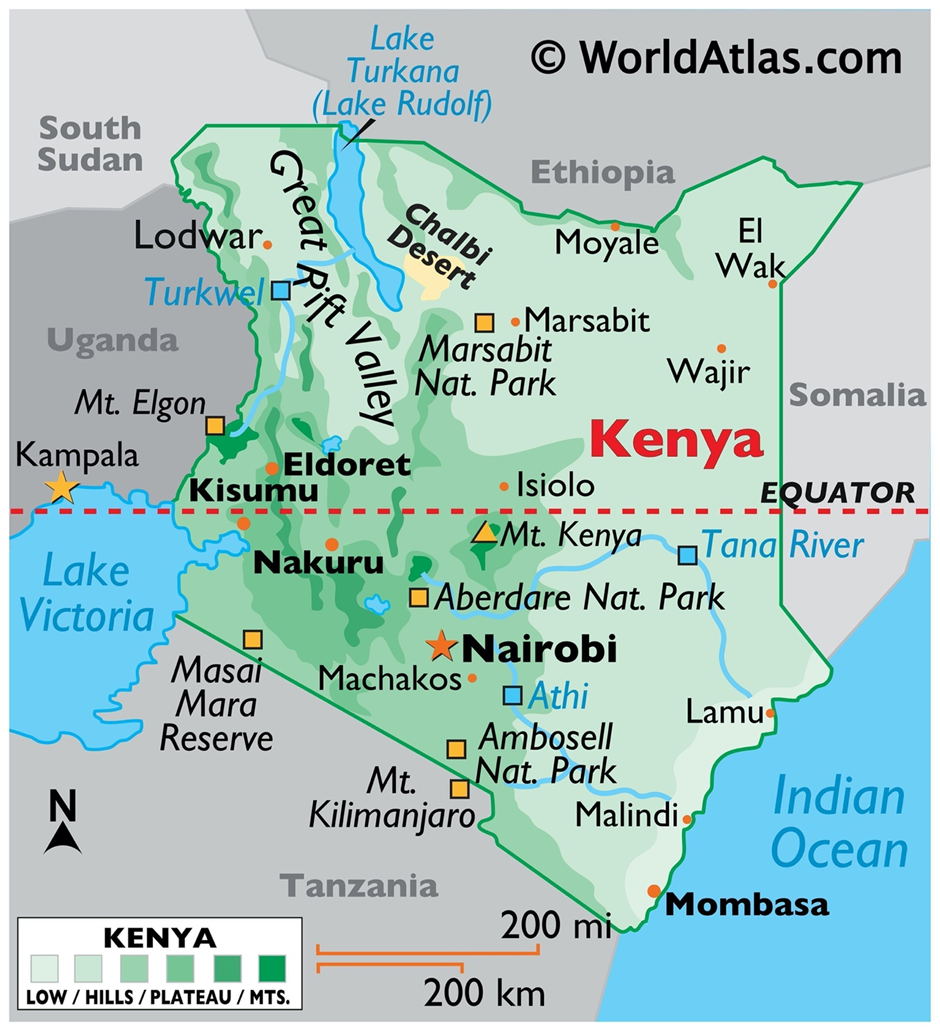
- Geography:
- Kenya is located in East Africa, bordered by Somalia to the east, Tanzania to the south, Uganda to the west, South Sudan to the northwest, Ethiopia to the north, and the Indian Ocean to the southeast.
- The country is known for its diverse landscapes, ranging from the Great Rift Valley and savannas to mountain highlands and coastal beaches.
- Kenya is rich in natural resources, including fertile agricultural land, wildlife, and minerals like limestone, soda ash, and rare earth metals. The country's abundant biodiversity, particularly in parks like Masai Mara and Amboseli, makes it a global hub for wildlife tourism.
- Colonial History:
- Kenya was colonised by Britain in the late 19th century, becoming a British protectorate in 1895 and later a colony in 1920.
- During colonial rule, the country experienced land alienation, forced labour, and suppression of local communities, leading to the Mau Mau rebellion in the 1950s.
- Kenya gained independence in 1963, under the leadership of Jomo Kenyatta.
- Existing challenges:
- Despite economic growth, Kenya faces challenges such as corruption, poverty, ethnic tensions, and environmental degradation.
- Climate change has led to prolonged droughts, impacting agriculture and wildlife conservation. Regions like Turkana and Mandera often face food insecurity due to arid conditions.
- The Nairobi area frequently appears in the news as the economic hub of East Africa, while Lamu and Mombasa are highlighted for their strategic locations along the Indian Ocean, essential for trade and tourism.
- Conservation challenges in regions like Masai Mara underscore Kenya's struggle to balance development and environmental preservation.
- About Masaai Tribe:
- The Maasai are an indigenous community primarily inhabiting the southern Kenya and northern Tanzania regions. They are known for their rich culture, distinctive clothing, and deep connection to their lands. Their traditional way of life revolves around cattle herding, which they consider a symbol of wealth and sustenance.
- Maasai culture is marked by elaborate ceremonies, including rites of passage like Enkipaata and Eunoto, as well as a strong oral tradition. They practice semi-nomadic lifestyles, moving in search of pasture for their cattle.
- The Maasai Olympics, initiated in 2012, is a cultural shift from lion hunting to athletic competition to promote wildlife conservation. The event features traditional Maasai games like spear-throwing and modern sports like running. Recent editions have included women, allowing them to participate in running events, promoting gender equality and empowerment within the community.
- The Maasai Mara, often associated with these tribes, provides a backdrop for the Olympics, merging Maasai cultural values with a modern conservation ethos. The event celebrates the tribe's heritage while addressing pressing social and ecological issues.
|
UPSC CSE PYQs Q. Which of the following countries are well known as the two largest cocoa producers in the world? (2024)
Answer: Option C |
|
Also Read |
|



