- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PLACES IN NEWS 29th JANUARY 2025
PLACES IN NEWS 29th JANUARY 2025

Namdapha Tiger Reserve
Why in news?
- After 12 years, a camera trap in Arunachal Pradesh’s Namdapha Tiger Reserve captured an elephant, raising new hopes for conservation.
- The species was thought to have disappeared from the area due to habitat loss and poaching.
- This sighting highlights the reserve’s importance and the need for stronger wildlife protection efforts.
About Namdapha Tiger Reserve:
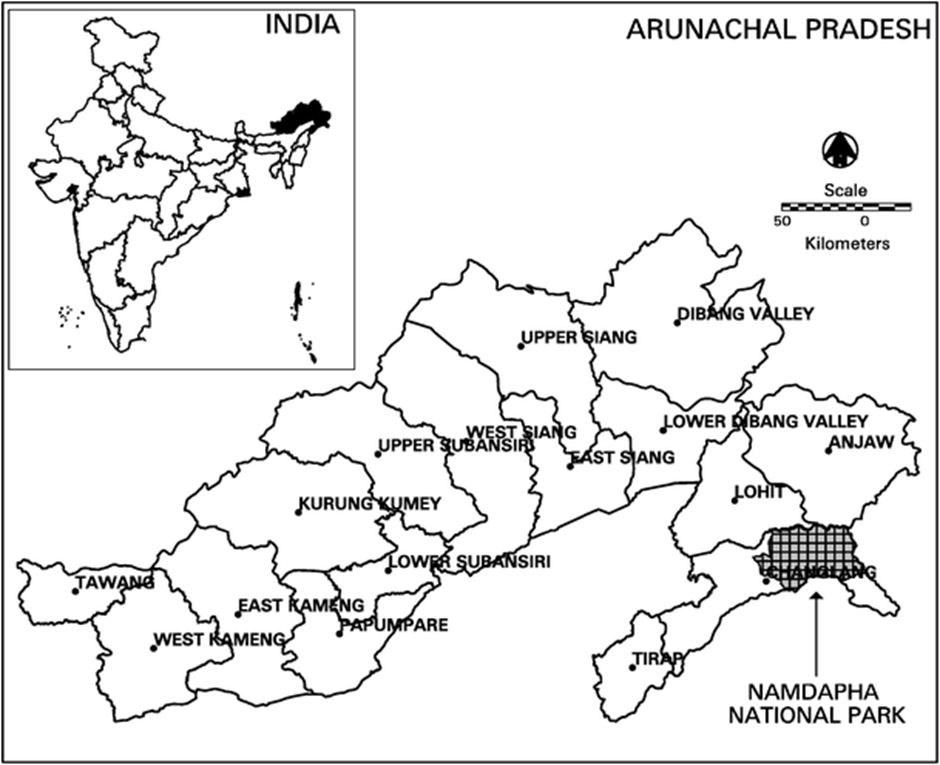
- Location and Geography:
- Namdapha Tiger Reserve is located in Arunachal Pradesh's Changlang district.
- It lies between the Dapha Bum range of the Mishmi Hills and the Patkai range.
- The reserve spans elevations from 200 meters to 4,571 meters above sea level, resulting in a diverse climate.
- Lower elevations experience a tropical climate, while higher regions exhibit temperate conditions, with some areas receiving seasonal snow between December and March.
- Flora and Fauna:
- This altitudinal variation supports a rich array of flora. The park's vegetation transitions from tropical evergreen forests in the lowlands to temperate broadleaf and mixed forests at mid-elevations and alpine vegetation in the highest zones.
- Namdapha is renowned for its diverse fauna. It is the only park in the world to house four large cat species: tiger (Panthera tigris), leopard (Panthera pardus), snow leopard (Panthera uncia), and clouded leopard (Neofelis nebulosa).
- Other significant mammals include the Hoolock gibbon (Hoolock hoolock), India's only ape, and the critically endangered Namdapha flying squirrel (Biswamoyopterus Biswas), which is endemic to the park and was last observed in 1981.
- Reason behind decline in Elephant Population:
- The Indian elephant (Elephas maximus indicus) population in Namdapha has declined due to habitat loss, poaching, and human-wildlife conflicts.
- Encroachment and deforestation have reduced their natural habitat, while illegal hunting for ivory has further threatened their numbers.
- Additionally, competition with humans for land and resources has increased conflicts, adversely affecting elephant populations.
Baltic Sea
Why in news?
- Sweden has seized a ship suspected of damaging a fibre-optic cable under the Baltic Sea, which connects the country to Latvia.
- The incident, raising security concerns, occurred in October 2023.
- Authorities are investigating potential foreign involvement, as similar infrastructure disruptions have heightened regional tensions in recent years.
About Baltic Sea:
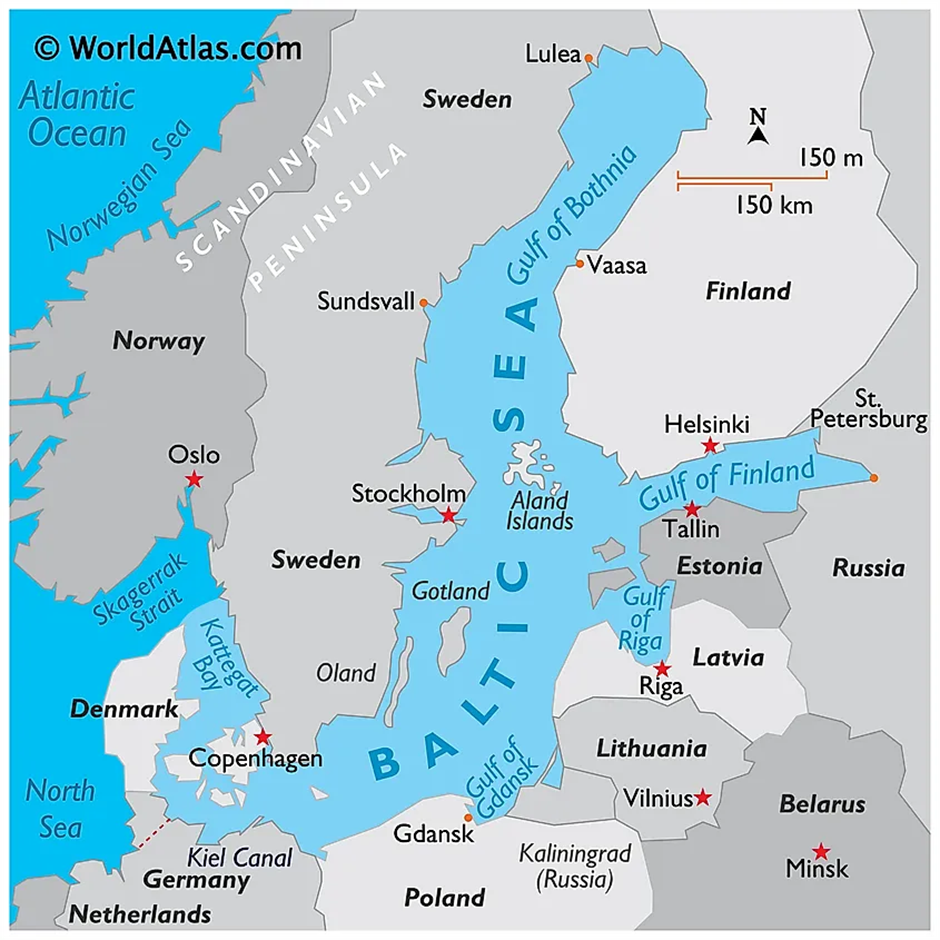
- Location and Geography:
- The Baltic Sea, a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, is bordered by several Northern and Central European countries, including Sweden, Finland, Russia, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Germany, and Denmark.
- It connects to the North Sea through the Danish Straits, serving as a crucial conduit for maritime trade and cultural exchange in the region.
- Geographically, the Baltic Sea is characterised by its relatively shallow waters and low salinity, resulting from limited exchange with the North Sea and substantial freshwater inflow from surrounding rivers.
- The sea's basin was formed by glacial erosion during the last Ice Age, leading to its current structure of numerous bays, gulfs, and archipelagos.
- The climate around the Baltic Sea varies from oceanic in the west to continental in the east and north, influencing its ecological dynamics.
- Infrastructural growth:
- In recent years, the Baltic Sea region has witnessed significant infrastructure developments, particularly in the energy and communication sectors.
- Projects like the Nord Stream pipelines, designed to transport natural gas from Russia to Germany, exemplify the area's strategic importance. However, these developments have not been without controversy.
- For instance, the Nord Stream pipelines have faced environmental concerns and geopolitical tensions, especially following the unexplained explosions in 2022 that damaged sections of the pipelines.
- Denmark's recent permission for preservation work on the damaged Nord Stream 2 pipeline underscores ongoing challenges in maintaining such infrastructure.
- Security concerns around the region:
- The Baltic Sea has also become a focal point for security concerns due to repeated incidents of damage to undersea cables and pipelines.
- Over a 15-month period, at least 11 such infrastructures were damaged, prompting NATO to initiate Operation Baltic Sentry to enhance surveillance and protection measures.
- These incidents have raised suspicions of deliberate sabotage, potentially linked to hybrid warfare tactics aimed at destabilising the region. The complexity of attributing responsibility for these damages adds to the geopolitical tensions in the area.
Surajpur Wetland
Why in news?
The Greater Noida Authority has launched a project to protect and conserve the Surajpur Wetland, a vital ecosystem in Uttar Pradesh.
About Surajpur Wetland:
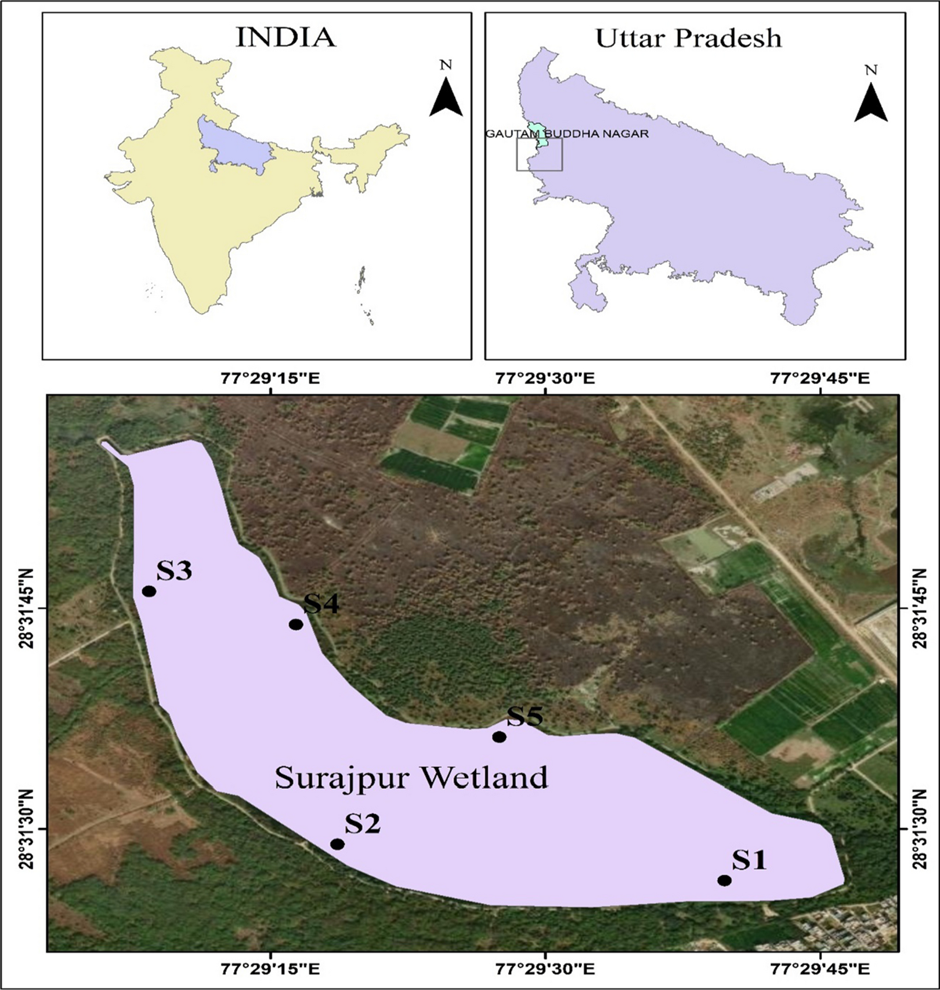
- The Surajpur Wetland, located near Surajpur Village in Dadri Tehsil, falls under the Greater Noida Industrial Development Authority in Uttar Pradesh.
- It serves as a prime example of an urban wetland within the Yamuna River basin, playing a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance.
- Spanning 308 hectares of catchment area, with 60 hectares covered by water, it acts as a green lung for Greater Noida, helping regulate local climate and groundwater recharge.
- Recognized as an Important Bird Area (IBA) by BirdLife International, the wetland provides a vital breeding ground for waterfowl such as the Spot-billed Duck, Lesser-whistling Duck, Cotton Pygmy Goose, and Comb Duck.
- It also supports wintering migratory birds, including the Red-crested Pochard, Ferruginous Pochard, Bar-headed Goose, Greylag Goose, Common Teal, Northern Shoveler, and Gadwall.
- Besides its rich avian diversity, six species of mammals, including the Nilgai, Indian Grey Mongoose, Indian Hare, Golden Jackal, and Five-striped Squirrel, inhabit the wetland.
- Despite its ecological significance, the wetland faces threats from polluted wastewater discharge, which degrades its water quality and disrupts wildlife habitats.
- Conservation initiatives, such as those by the Greater Noida Authority, are crucial for protecting and restoring this valuable ecosystem.
Lake Tanganyika
Why in news?
Fishers on Lake Tanganyika, one of Africa's largest freshwater lakes, are grappling with declining fish stocks due to overfishing, pollution, and climate change.
About Lake Tanganyika:
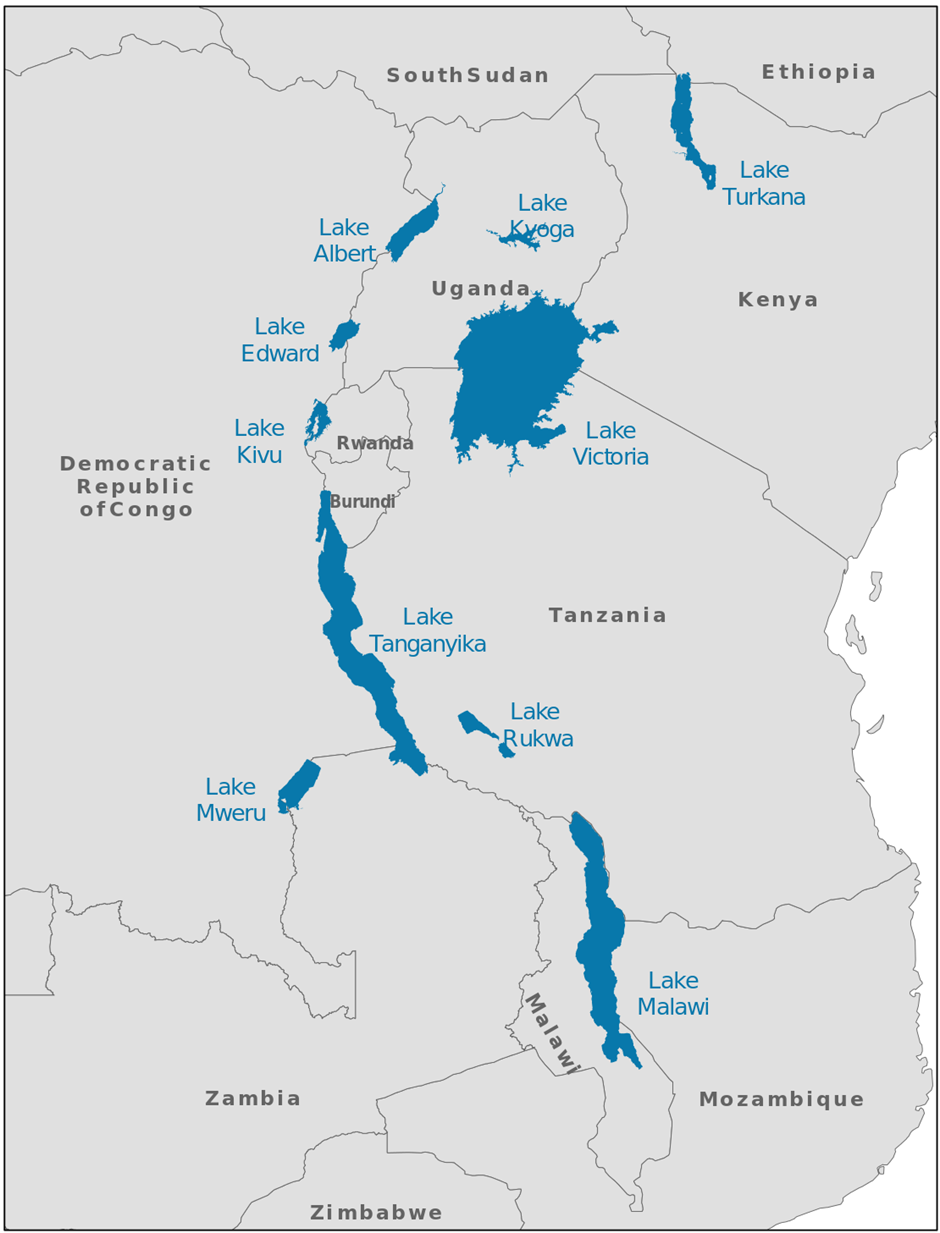
- Geography and Location:
- Lake Tanganyika is located in East Africa, bordered by four countries: Tanzania, Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), Burundi, and Rwanda.
- It covers an area of approximately 32,900 square kilometers and is the second-deepest lake in the world, with a depth of 1,470 meters.
- It serves as a vital resource for fisheries, transportation, and agriculture.
- Economic Significance:
- The lake supports millions of people through fishing, with species such as Nile perch and tropical fish being commercially valuable.
- Agriculture around the lake is supported by its water, including crops like cassava, rice, and maize.
- Shipping routes across the lake are vital for trade and connecting remote regions, especially between the DRC and Tanzania.
- Ecological Importance:
- Lake Tanganyika is rich in biodiversity, with over 200 species of fish, many of which are endemic.
- The lake's mangrove forests and shoreline ecosystems provide critical habitats for aquatic species and migratory birds.
- The lake is part of the East African Rift System, a geologically active region, contributing to its unique ecosystems.
- Concerns about Lake Tanganyika:
- Pollution from industrial waste and agricultural runoff is deteriorating the lake's water quality and harming aquatic life.
- Overfishing is depleting fish stocks and affecting local communities' food security.
- Invasive species like the water hyacinth and Nile perch threaten the lake’s biodiversity and disrupt the ecosystem.
Z-Morh Tunnel
Why in news?
In January 2025, the Z-Morh Tunnel in Jammu and Kashmir was inaugurated in a ceremony attended by Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
About Z-Morh Tunnel:
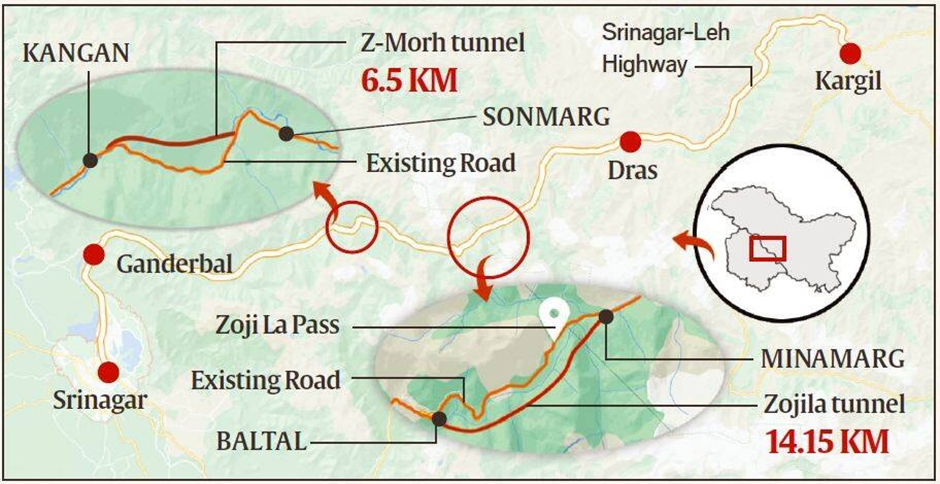
- Geographical importance:
- The Z-Morh Tunnel is situated in the Z-Morh Pass, connecting Sonamarg in Jammu and Kashmir to Ladakh. This strategic location is part of the Srinagar-Leh Highway, a vital route for both civilian and military purposes.
- The tunnel's construction through the Z-Morh Pass addresses the challenges posed by heavy snowfall and avalanches, which previously limited access to the region during winter months.
- By providing an all-weather passage, the tunnel significantly
enhances connectivity between Kashmir and Ladakh, facilitating smoother travel and communication. - This development is particularly crucial for the Indian Armed Forces, as it ensures the uninterrupted movement of personnel and supplies to the strategically sensitive Ladakh region.
- Economic Impact:
- Economically, the Z-Morh Tunnel is poised to significantly boost the region's development. By ensuring all-weather connectivity, the tunnel facilitates the movement of goods and services, thereby promoting trade between Kashmir and Ladakh.
- This improved access is expected to stimulate local economies, create employment opportunities, and enhance the overall economic integration of the region.
- Moreover, the tunnel is anticipated to bolster the tourism industry by providing easier access to Sonamarg, a popular tourist destination known for its scenic beauty.
- The development of infrastructure around the tunnel is likely to attract more visitors, leading to increased revenue and economic growth.
- Additionally, the tunnel's construction has generated employment opportunities during its development phase, contributing to the local economy.
|
UPSC CSE PYQs Q1. Which one of the following National Parks has a climate that varies from tropical to subtropical, temperate and arctic? (2015) (a) Khangchendzonga National Park Answer: Option D Q2. Consider the following pairs: (2013)
Which of the above pairs is/are correctly matched? (a) 1 only Answer: Option A
|
|
Also Read |
|
| NCERT Books For UPSC | |
| Best IAS Coaching in Delhi | |