- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PLACES IN NEWS 27th JANUARY 2025
PLACES IN NEWS 27th JANUARY 2025

Bhitarkanika National Park
Why in news?
- The 2025 annual reptile census at Bhitarkanika National Park, Odisha, recorded 1,826 saltwater crocodiles, including 18 rare albino crocodiles.
- Known for its thriving mangrove ecosystem, BNP hosts one of the largest populations of these reptiles in India.
About Bhitarkanika National Park:
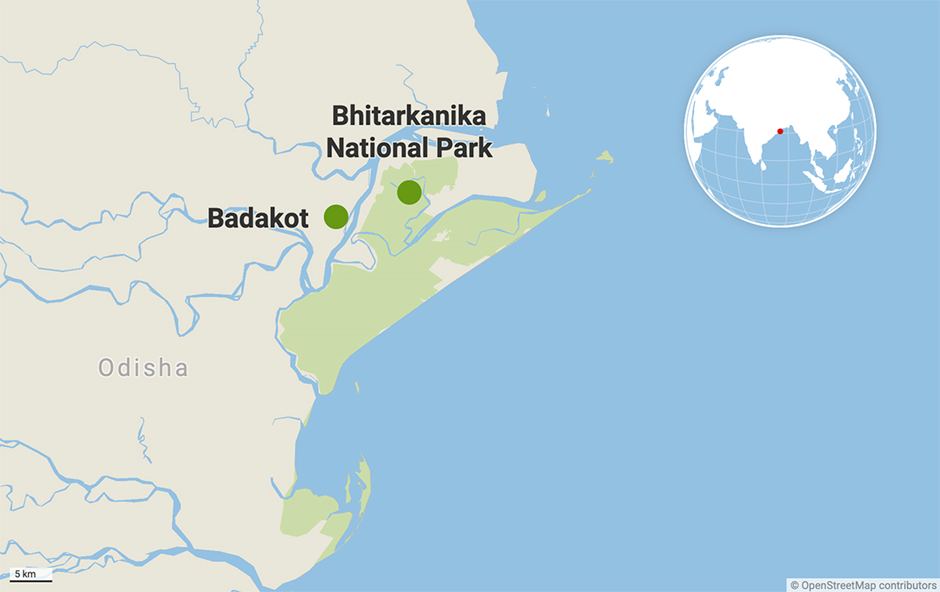
- Location:
- Bhitarkanika National Park is located in the Kendrapara district of Odisha, India, and lies in the estuarial region formed by the Brahmani, Baitarani, Dhamra, and Pathsala rivers.
- These rivers and their tributaries create a dynamic and biodiverse ecosystem. The park covers an area of 145 square kilometres and forms the core of the Bhitarkanika Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Flora and Fauna:
- The park's floral diversity is dominated by lush mangrove forests, comprising 62 species of mangroves, including Sundari, Bani, and Kandelia.
- These mangroves provide vital ecological services, including stabilizing coastlines, mitigating erosion, and serving as a natural barrier against cyclones. The intertidal zones and mudflats further enhance the ecological richness of the park.
- Bhitarkanika is renowned for its thriving faunal diversity, particularly its population of saltwater crocodiles (Crocodylus porosus), which are the largest reptiles in the world.
- It is home to 1,826 saltwater crocodiles, as recorded in the 2025 census, including 18 rare albino crocodiles.
- Additionally, it houses mugger crocodiles (Crocodylus palustris) and the critically endangered gharial (Gavialis gangeticus), highlighting its role as a critical habitat for these species.
- The estuarine ecosystem also supports a wide variety of aquatic species, including fish, crabs, and prawns.
- The park serves as a haven for migratory birds, with species like Asian open-bill storks, black ibis, and egrets flocking to its wetlands.
- It is also home to spotted deer, fishing cats, otters, and various snakes, including the king cobra and Indian python. The endangered olive ridley turtles nest along its coastal areas, adding to its ecological importance.
- Ecological significance:
- Bhitarkanika plays a crucial role in preserving the fragile coastal ecosystem of eastern India. Its mangroves act as carbon sinks, reducing greenhouse gas concentrations, while its rich biodiversity sustains livelihoods for local communities through fishing and ecotourism.
- The park’s conservation efforts have successfully protected endangered species, making it a cornerstone of India’s wildlife heritage.
- Bhitarkanika’s unique blend of rivers, mangroves, and diverse fauna underscores its significance as a biodiversity hotspot and a critical area for ecological balance.
Nahargarh Wildlife Sanctuary
Why in news?
The Rajasthan Forest Department plans to revise the boundary of Nahargarh Wildlife Sanctuary to improve habitat management and conservation efforts.
About Nahargarh Wildlife Sanctuary:
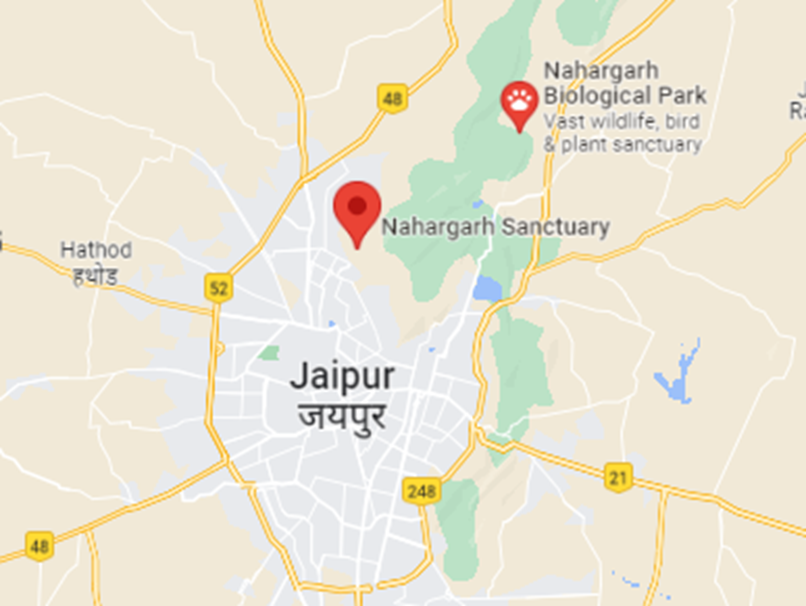
- Location:
- Nahargarh Wildlife Sanctuary is located in the Aravalli hills near Jaipur, Rajasthan. It covers an area of approximately 52 square kilometres.
- It is situated around the historic Nahargarh Fort, blending natural beauty with cultural heritage. The sanctuary's terrain features rocky hills, dense forests, and open grasslands, creating a unique ecological zone.
- Flora and Fauna:
- The sanctuary’s floral diversity includes dry deciduous and tropical forests, with species such as dhok (Anogeissus pendula), babool, and ber.
- These trees, along with shrubs and grasses, support the sanctuary’s ecosystem and provide a sustainable habitat for various wildlife species.
- Nahargarh Wildlife Sanctuary is home to various faunal species, including predators such as leopards, hyenas, jackals, and jungle cats.
- It also shelters herbivores like nilgai, sambar, and chinkara, along with smaller mammals such as hares and porcupines.
- The sanctuary is an important birding site, with species like peafowls, partridges, woodpeckers, and migratory birds adding to its avian diversity. Reptiles, including monitor lizards and snakes, also thrive in its environment.
- Ecological significance:
- The sanctuary plays a significant role in preserving the biodiversity of the Aravalli hills, which act as a green lung for the region.
- Its proximity to Jaipur enhances its ecological significance, offering a natural refuge amidst urban expansion.
- Conservation efforts focus on protecting wildlife, mitigating human-wildlife conflict, and promoting ecotourism to raise awareness about its ecological importance.
Strait of Hormuz
Why in news?
- The UK has raised concerns over Iran's alleged efforts to redirect ships into its waters during IRGC naval drills near the Strait of Hormuz, a vital global oil transit route.
- Such actions heighten regional tensions, impacting maritime security and raising fears over disruptions to the flow of energy supplies.
About Strait of Hormuz:
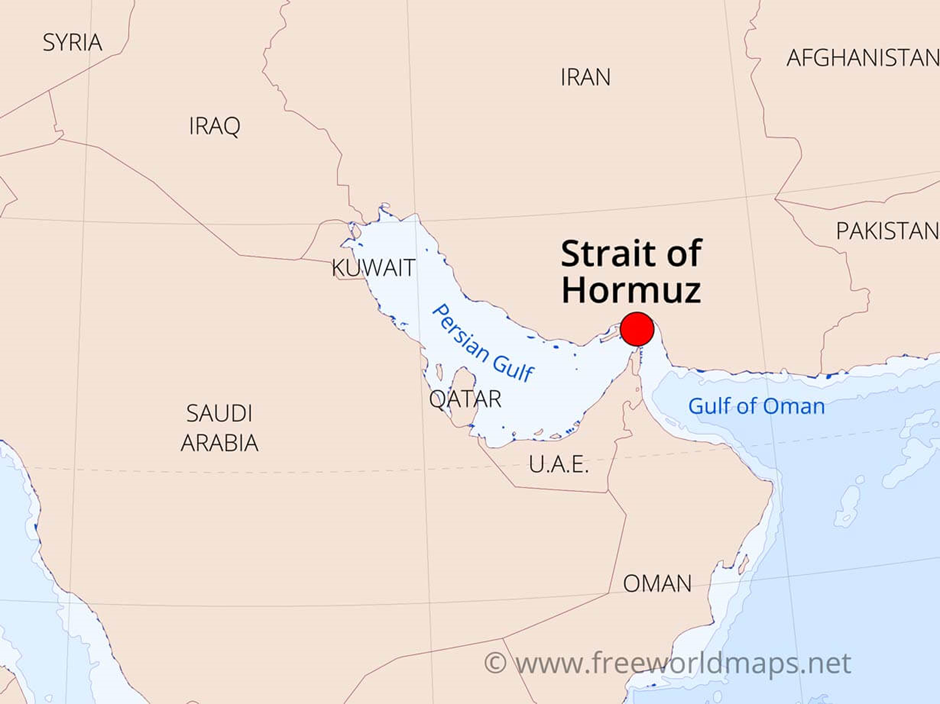
- Location:
- The Strait of Hormuz is a strategically significant waterway located between the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman, connecting the Middle East with the Arabian Sea and the Indian Ocean.
- It is bordered by Iran to the north and Oman and the United Arab Emirates to the south, making it a critical chokepoint for maritime trade and energy transportation.
- The strait is only 39 kilometres wide at its narrowest point, with a navigable channel of just three kilometres in each direction for shipping.
- Despite its limited size, it facilitates the passage of approximately 20% of the world’s crude oil and one-third of global liquefied natural gas (LNG), making it a crucial lifeline for energy-importing nations.
- Multidimensional Geopolitical significance:
- The strait's geopolitical importance extends beyond energy transportation. It serves as a focal point for regional rivalries, particularly between Iran and Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) states, and is frequently impacted by tensions involving major powers like the United States, China, and Russia.
- Iran has repeatedly used the threat of blocking the strait as leverage during political or military conflicts, including disputes over sanctions and nuclear programs.
- Additionally, the strait’s proximity to key military bases of global powers underscores its strategic value in maintaining regional stability.
- Impact of disruption on India:
- Disruption in the Strait of Hormuz has far-reaching consequences, particularly for energy security. India, as the world’s third-largest oil importer, relies heavily on the Middle East for crude oil and LNG, with a significant portion of its imports transiting through this waterway.
- Any disruption in the strait, whether due to geopolitical tensions, naval conflicts, or piracy, directly impacts India’s energy supply, causing price volatility and increased import costs.
- This, in turn, affects India’s domestic fuel prices and economic stability, given the country’s dependence on imported energy to sustain industrial and transportation needs.
- Furthermore, India’s strategic investments in the region, such as the development of the Chabahar Port in Iran, rely on the stability of shipping lanes through the strait. Disruptions also hamper bilateral trade with Gulf nations, which are among India’s largest trading partners and sources of remittances from the Indian diaspora.
- The Strait of Hormuz, therefore, remains a vital artery for global energy and trade, with its stability integral to maintaining India’s energy security, economic growth, and regional influence in the Indian Ocean and Middle East.
Amur River
Why in news?
- In January 2025, the Amur River witnessed severe flooding, affecting communities along the Russia-China border.
- The flooding, driven by heavy rainfall and melting snow, caused significant displacement and infrastructure damage.
- Both nations coordinated disaster management efforts, highlighting the importance of cross-border collaboration in addressing environmental challenges and mitigating humanitarian crises.
About Amur River:
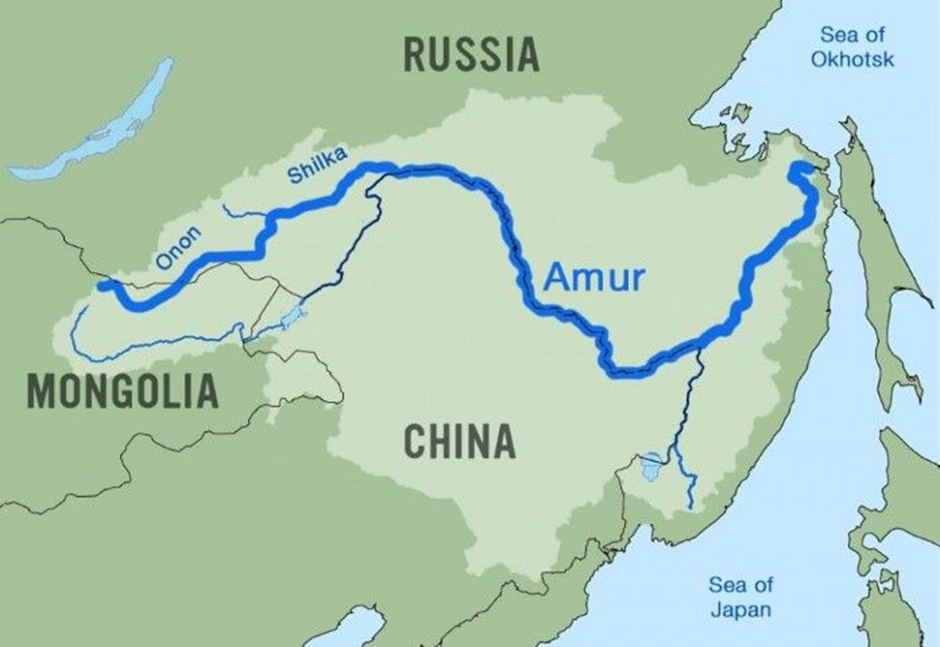
-
- Origin and path:
- Origin and path:
- The Amur River, known as Heilong Jiang in Chinese, originates at the confluence of the Shilka and Argun rivers, approximately 303 meters above sea level.
- It flows eastward, forming much of the border between China's Heilongjiang province and Russia's southeastern Siberia, before turning north-eastward at Khabarovsk and emptying into the Sea of Okhotsk via the Strait of Tartary.
- The river spans about 2,824 kilometres, draining a basin of approximately 1.855 million square kilometres.
- Flooding and its impact:
- Flooding and its impact:
- In January 2025, the Amur River experienced significant flooding, particularly near Komsomolsk-on-Amur.
- Water levels rose by 17-20 centimetres daily, with forecasts predicting a peak between 930 and 980 centimetres by mid-September. This unprecedented rise threatened approximately 600 houses, affecting around 50,000 residents.
- Authorities issued emergency warnings and initiated evacuations in vulnerable areas, including the settlement of Mendeleyev. Over 11,000 specialists, in collaboration with military and emergency services, worked tirelessly to reinforce dams and restore infrastructure.
- The flooding caused extensive damage to homes, infrastructure, and agricultural lands, leading to significant economic losses and displacement of communities.
- The event underscored the vulnerability of the Amur River basin to extreme weather events, highlighting the need for enhanced flood management and preparedness strategies to mitigate future risks.
Azores Archipelago
Why in news?
- In January 2025, the Azores Archipelago, situated in the North Atlantic Ocean, experienced heightened seismic activity, triggering concerns over possible volcanic eruptions.
- The region, known for its volcanic origins, is monitored closely for signs of increased activity, with experts assessing risks to local populations and infrastructure.
About Azores Archipelago:
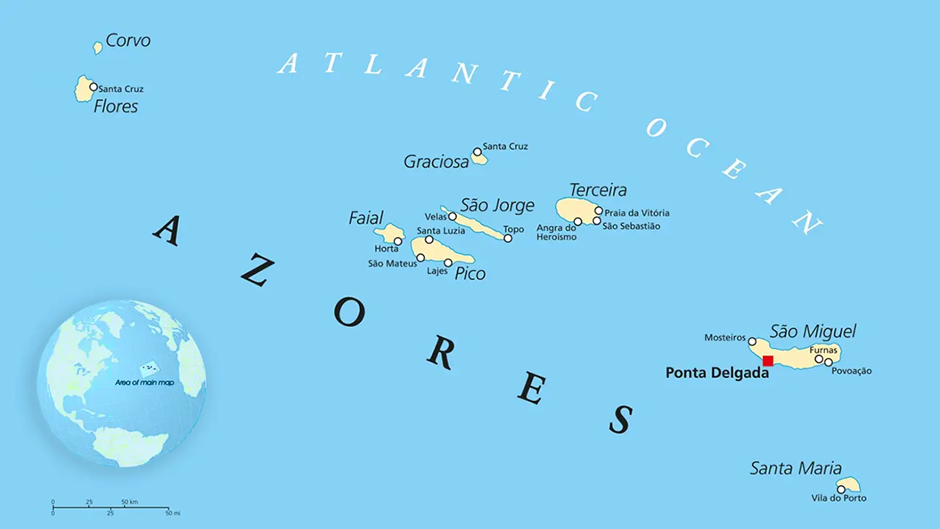
-
- Location:
- Location:
- The Azores Archipelago, located in the North Atlantic Ocean, is a group of nine volcanic islands situated approximately 1,500 kilometres west of mainland Portugal.
- The islands lie at the intersection of three tectonic plates: the Eurasian Plate, the North American Plate, and the African Plate.
- This unique positioning makes the Azores region geologically active, with volcanic eruptions and seismic events occurring periodically.
- Recent tectonic activity:
- Recent tectonic activity:
- The recent increase in volcanic activity in January 2025 is primarily attributed to the tectonic interactions in the region.
- The North American Plate and Eurasian Plate are moving away from each other along the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, creating a divergent boundary that allows magma to rise from the Earth's mantle, forming volcanoes.
- Additionally, the African Plate is converging with the Eurasian Plate, leading to complex seismic and volcanic interactions, including the subduction of oceanic crust beneath the continental plates.
- As magma rises from these geological processes, it leads to increased volcanic pressure and the potential for eruptions.
- In recent months, seismic activity has intensified, indicating that magma is accumulating beneath the surface, which can cause shifts in the Earth's crust and lead to eruptions or earthquakes.
- Experts are closely monitoring the situation to assess the risk of significant volcanic events and their potential impact on local populations and infrastructure.
|
UPSC CSE PYQs
Q. Consider the following pairs:
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched? (2010)
Answer: Option B Q2. Two important rivers- one with its source in Jharkhand (and known by a different name in Odisha) and another, with its source in Odisha merge at a place only a short distance from the coast of bay of Bengal before flowing into the sea. This is an important site of wildlife and biodiversity and a protected area. Which one of the following could be this? (2011)
Answer: Option A |
|
Also Read |
|
| FREE NIOS Books | |



