- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT Batch
- Polity Module Course
- Geography Module Course
- Economy Module Course
- AMAC Module Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History Module Course
- Environment Module Course
- Governance Module Course
- Science & Tech. Module Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Module Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Module Course
- Essay Module Course
- Current Affairs Module Course
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PLACES IN NEWS 17th JANUARY 2025
PLACES IN NEWS 17th JANUARY 2025

Rwanda
Why in news?
Rwanda has reportedly discovered oil for the first time in Lake Kivu, a resource-rich body of water shared with the Democratic Republic of Congo. Preliminary studies indicate the potential for commercially viable oil reserves beneath the lakebed.
About Rwanda:
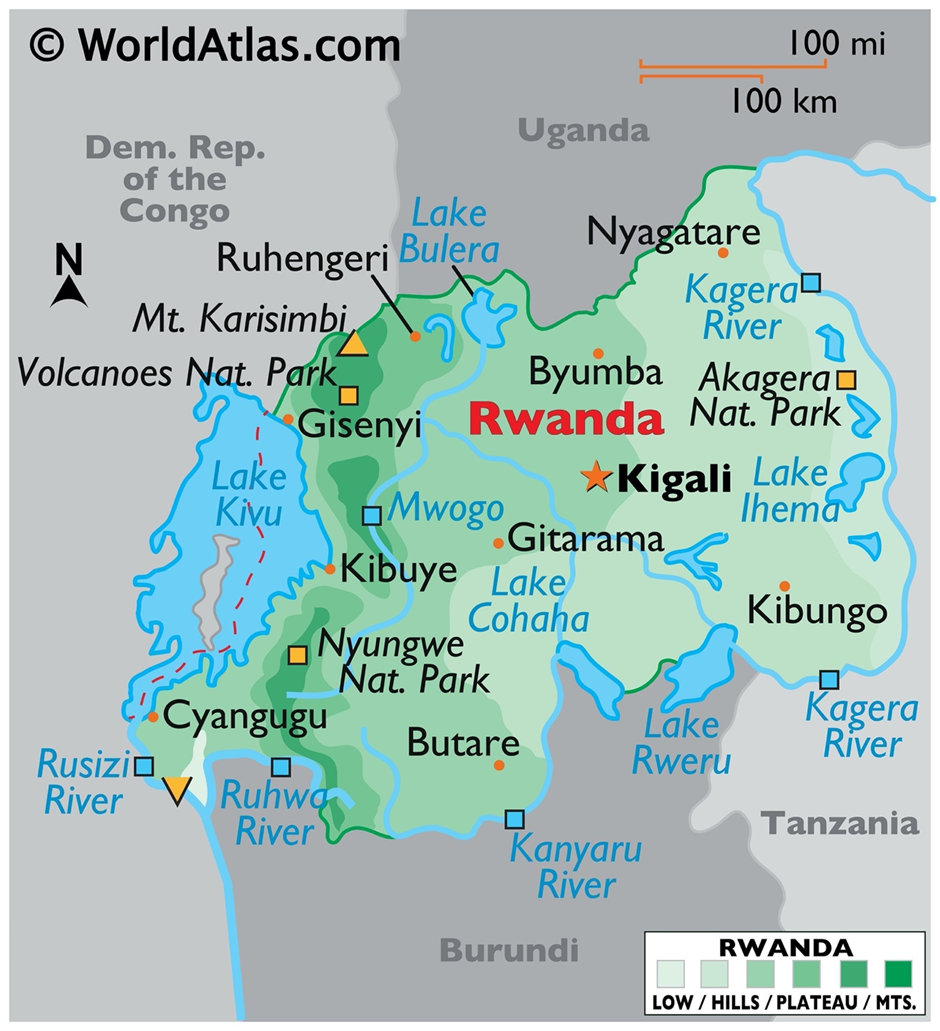
- Location and geography:
- Rwanda, often referred to as the "Land of a Thousand Hills," is a small, landlocked country in East Africa, bordered by Uganda to the north, Tanzania to the east, Burundi to the south, and the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) to the west.
- Its geographic location places it in the heart of the African Great Lakes region, making it a key player in regional dynamics. The country is known for its lush green landscapes, high-altitude terrain, and the volcanic mountains of the Virunga Range, which straddle its northern border.
- Natural resource potential:
- Rwanda has significant natural resource potential, although it remains underexplored compared to its neighbours. It is rich in minerals like cassiterite, wolframite, coltan, and small quantities of gold, which are vital for global electronics manufacturing.
- Recent developments, such as the discovery of oil reserves in Lake Kivu, suggest unexplored energy potential. Rwanda shares Lake Kivu with the DRC, which serves as a crucial source of methane gas for electricity generation. Agriculture, with its fertile soils supporting coffee and tea exports, forms the backbone of the economy.
- Regional conflicts:
- Regional conflicts have shaped Rwanda's modern history. The 1994 genocide left deep scars, but the country has since become a model of recovery and stability in Africa. However, its involvement in the eastern DRC remains contentious.
- Rwanda faces accusations of supporting rebel groups like the M23, exacerbating tensions with the DRC. These conflicts stem from ethnic, political, and resource-related disputes, which also impact the Great Lakes region.
- Certain regions of Rwanda and its neighbours frequently appear in global news. The eastern DRC, bordering Rwanda, remains a hotspot due to ongoing conflicts involving militias and the illegal exploitation of resources.
- The Virunga National Park, spanning Rwanda, Uganda, and the DRC, attracts attention for its endangered mountain gorillas and as a site of conservation efforts amid instability. Domestically, Rwanda’s Kigali garners praise for its transformation into a clean, tech-driven hub in Africa.
Caspian Sea
Why in news?
The Caspian Sea is prone to geological activity due to its tectonic setting. In early 2023, a mud volcano eruption briefly formed a ‘ghost island,’ highlighting the region’s volatile seabed. Such islands, composed of sediment and gases, are temporary and often erode quickly, as seen when this formation disappeared by the end of 2024, reflecting the dynamic nature of the Caspian Sea’s ecosystem.
About Caspian Sea:
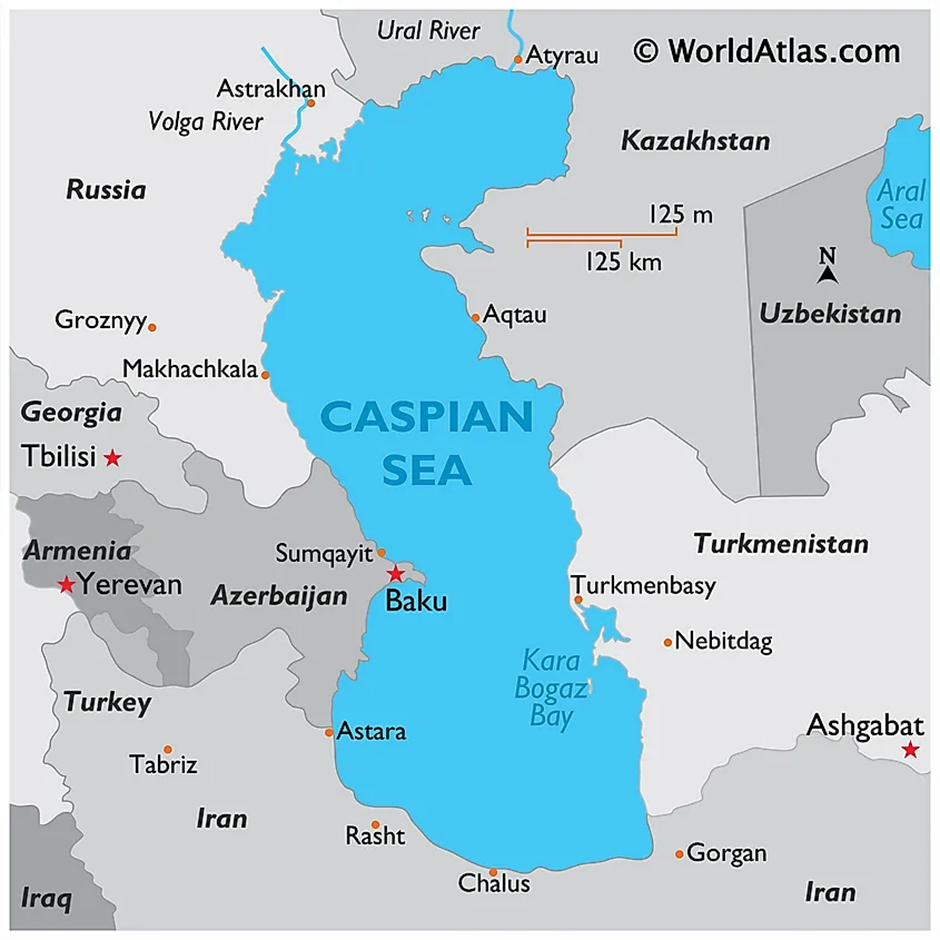
- Location and Geography:
- The Caspian Sea is the world’s largest inland body of water, covering approximately 371,000 square kilometres.
- It is bordered by five countries: Russia, Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan, Iran, and Azerbaijan.
- Major rivers draining into the Caspian Sea include the Volga, Ural, and Terek, with the Volga providing about 80% of the inflow.
- The sea’s salinity averages 12.8 parts per thousand, varying from 1 ppt near the Volga outlet to 200 ppt in areas of high evaporation.
- Potential Natural Resources:
- The Caspian Sea region holds significant natural resources, making it a key economic zone.
- It contains an estimated 48 billion barrels of oil and 8.7 trillion cubic meters of natural gas, accounting for a large share of the world’s energy reserves.
- Major offshore oil and gas fields include Azeri-Chirag-Gunashli in Azerbaijan and Kashagan in Kazakhstan.
- The surrounding area also has large reserves of minerals like salt, gypsum, and limestone.
- The Caspian Sea supports a thriving fishing industry, producing 90% of the world’s sturgeon and the prized Beluga caviar.
- These resources contribute to geopolitical tensions among bordering nations.
- Tectonic activity and Mud Volcanoes:
- The Caspian Sea region experiences significant tectonic activity due to the convergence of the Arabian and Eurasian tectonic plates.
- This tectonic movement leads to the formation of mud volcanoes, especially in Azerbaijan and its Caspian coastline, which are home to nearly 400 mud volcanoes, more than half the total throughout the continents.
- Mud volcanoes occur when underground gas and water pressure force mud, water, and gases like methane to the surface.
- These eruptions can create temporary landforms, such as the ‘ghost island’ observed in early 2023 near Azerbaijan’s coast, which later eroded away.
- Mud volcanoes differ from regular volcanoes as they emit mud and gases instead of lava.
- They can vary in size, with some forming cones several meters high, and may occasionally ignite due to flammable gas emissions, producing flames visible from a distance.
Tripoli, Libya
Why in news?
Tripoli has been in the news recently due to ITA Airways resuming direct flights from Rome after a decade-long break, marking a significant step in reconnecting Libya with Western Europe.
About Libya:
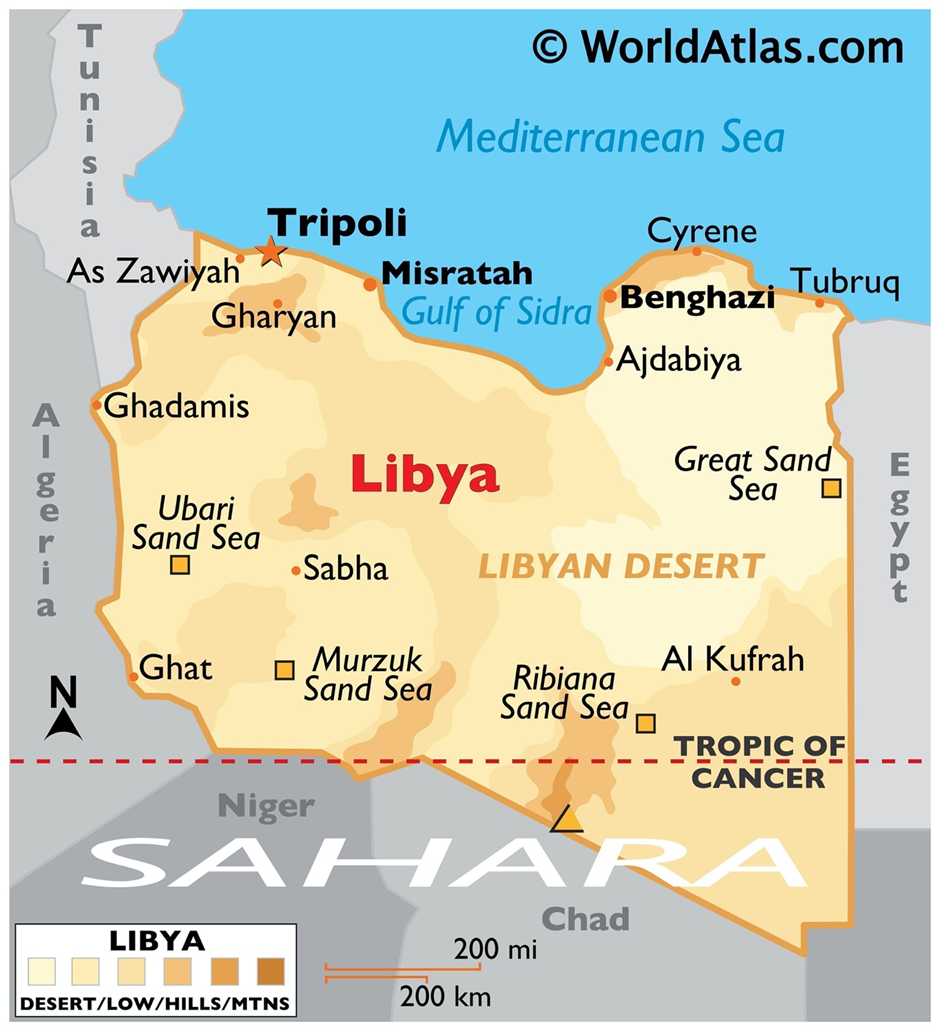
- Geography and Location
- Libya, located in North Africa, is the fourth-largest country on the continent and the 16th largest globally.
- It shares borders with Egypt to the east, Sudan to the southeast, Chad and Niger to the south, Algeria to the west, and Tunisia to the northwest.
- The Mediterranean Sea lies to its north, giving Libya a 1,770 km coastline, the longest in Africa. The majority of the country lies in the Sahara Desert, with arid landscapes dominating most of its geography.
- Key regions include Tripolitania, Cyrenaica, and Fezzan, which have historical and administrative significance.
- Its capital, Tripoli, is a major urban centre situated on the Mediterranean coast.
- Regional Conflicts and Multidimensional Impact
- Libya has been mired in conflict since the 2011 NATO-backed uprising that led to the ousting and death of long-time ruler Muammar Gaddafi.
- The power vacuum resulted in a civil war, dividing the country into factions.
- The Government of National Unity (GNU) in Tripoli and the Libyan National Army (LNA) led by General Khalifa Haftar in the east are the main rival authorities.
- The conflict has had profound impacts:
- Political Instability: Frequent clashes have hindered the formation of a unified government.
- Economic Disruption: Libya, with Africa's largest proven oil reserves, has suffered from declining oil production due to blockades and infrastructure damage.
- Humanitarian Crisis: Displacement, loss of livelihoods, and a lack of basic services have affected millions.
- Migration and Human Trafficking: Libya’s position as a gateway to Europe has made it a hub for irregular migration and trafficking networks.
- Other relevant Key Facts:
- Libya is a member of the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC).
- The country follows a Mediterranean climate in its coastal regions, while the rest experiences desert conditions.
- Great Man-Made River Project: Libya developed one of the world’s largest irrigation systems, sourcing water from underground aquifers.
Sariska Tiger Reserve
Why in news?
The National Green Tribunal (NGT), following the Supreme Court's directives, has intensified action against illegal activities in Rajasthan's Sariska Tiger Reserve, aiming to protect its ecological balance.
About Sariska Tiger Reserve:
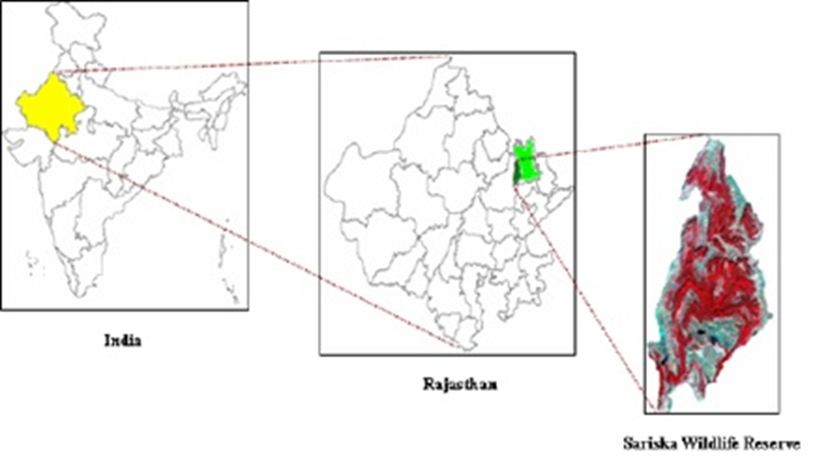
- Location:
- Sariska Tiger Reserve, located in the Alwar district of Rajasthan, lies in the Aravalli Hills, covering an area of approximately 881 square kilometres.
- It is well-connected to nearby cities, being around 107 km from Jaipur and 200 km from Delhi, making it a popular destination for wildlife enthusiasts and tourists.
- The terrain is a mix of dry deciduous forests, rocky hills, grasslands, and scrub-thorn landscapes, characteristic of the semi-arid regions of India.
- Flora and Fauna:
- The reserve supports a rich variety of flora. Dominant tree species include Dhak (Butea monosperma), Khair (Acacia catechu), Dhok (Anogeissus pendula), and Ber (Ziziphus mauritiana).
- These provide critical habitat for the fauna, especially during the dry months. Seasonal water bodies and man-made structures like Siliserh Lake and ancient water reservoirs sustain the ecosystem.
- Fauna in Sariska is diverse and includes Bengal tigers, leopards, striped hyenas, golden jackals, and jungle cats.
- The reserve also hosts a variety of herbivores, such as chital, sambhar, nilgai, wild boar, and langurs. Bird species like the Indian peafowl, parakeets, and hornbills are frequently spotted, alongside reptiles like monitor lizards and various snakes.
- Conservation efforts:
- Sariska is vital for tiger conservation in India. After the alarming loss of its tiger population in 2004 due to poaching, it became the first reserve in the country where tigers were successfully reintroduced under Project Tiger.
- The initiative was a significant step in wildlife conservation, involving the relocation of tigers from Ranthambore National Park. The growing tiger population in Sariska symbolises hope for balancing conservation and coexistence.
- The reserve holds ecological, cultural, and historical importance. Ancient structures, including the Pandupol Temple and Kankwari Fort, add to its appeal.
- However, challenges like encroachment, mining, and tourism pressures threaten its fragile ecosystem. Efforts by authorities, backed by judicial intervention, aim to address these issues, ensuring Sariska remains a haven for wildlife while contributing to India’s broader tiger conservation goals. Its role in maintaining biodiversity and supporting ecological stability underscores its national and global significance.
|
Also Read |
|
UPSC Foundation Course |
|
| CSAT Foundation Course | |



