- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PLACES IN NEWS 17 NOVEMBER 2024
PLACES IN NEWS 17 NOVEMBER 2024
17-11-2024
Barak River
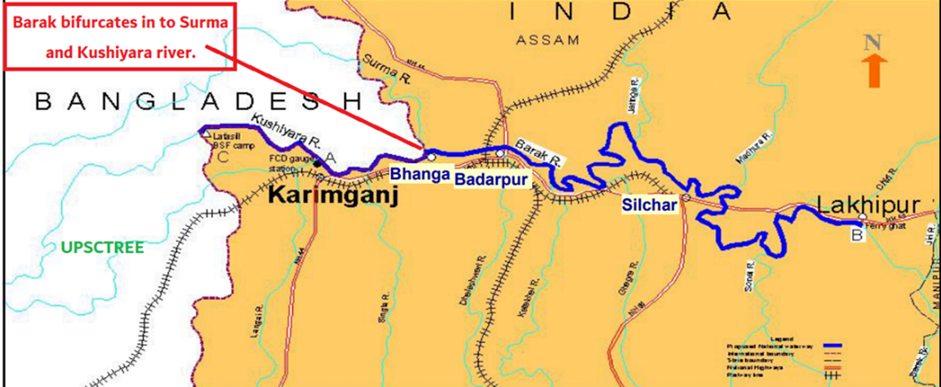
In November 2024, 3 bodies recently discovered in Manipur's Barak River are feared to be linked to the disappearance of six people from a displacement camp.
Geographic Details:
- Region: 2nd largest river in Northeast India, after the Brahmaputra.
- States & Countries: Flows through India (Manipur, Nagaland, Mizoram, Assam) and Bangladesh.
Course of the River:
- Origin:
- Rises from the Manipur Hills in Senapati district of Manipur, at an elevation of 2,331 meters.
- Path:
- Flows through the Nagaland-Manipur border, then enters Assam.
- After Assam, it enters Bangladesh, where it is known as the Surma River and Kushiyara River.
- Further downstream, it becomes the Meghna River before joining the Ganga and Brahmaputra in the Bay of Bengal.
Length & Geography:
- Total Length: Around 900 km, with 564 km within India.
- Geographical Boundaries:
- North: Barail Range (separating it from the Brahmaputra basin).
- East: Naga and Lushai hills.
- South & West: Bangladesh.
- Forest Coverage: 72.58% of the basin is covered by forests.
- Water Bodies: Only 1.92% of the basin area is covered by water bodies.
Tributaries:
- Main Tributaries:
- Jiri, Dhaleswari, Singla, Longai, Sonai, and Katakhal.
Basin Information:
- The river is part of the composite Ganga-Brahmaputra-Meghna basin, covering about one-third of the land area of India.
Which are the main tributaries of the Brahmaputra River?
- Right Bank Tributaries: Lohit, Dibang, Subansiri, Jiabharali, Dhansiri, Manas, Torsa, Sankosh, Teesta.
- Left Bank Tributaries: Burhidihing, Desang, Dikhow, Dhansiri, Kopili.
Avian Botulism: Sambhar Lake

- High temperatures and reduced salinity in Sambhar lake may have created conditions conducive to avian botulism, resulting in the mass deaths of migratory birds in Rajasthan.
- At least 600 migratory bird deaths were reported by the Centre for Avian Research Institute earlier.
- According to reports, the deaths began on October 26, 2024 and continued for approximately two weeks.
- Avian Botulism is a disease caused by the ingestion of a toxin produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum.
- It leads to paralysis and can be fatal for birds.
Causes:
- The toxin is produced by Clostridium botulinum, which is found in wetland sediments.
- These bacterial spores are present in most wetland habitats, affecting invertebrates like insects, mollusks, crustaceans, and vertebrates, including healthy birds.
- Wild birds are particularly affected by type C and type E botulism toxins.
Environmental Conditions:
- High water temperatures and low oxygen levels in water contribute to the production of the botulinum toxin.
Key Facts about Sambhar Lake:
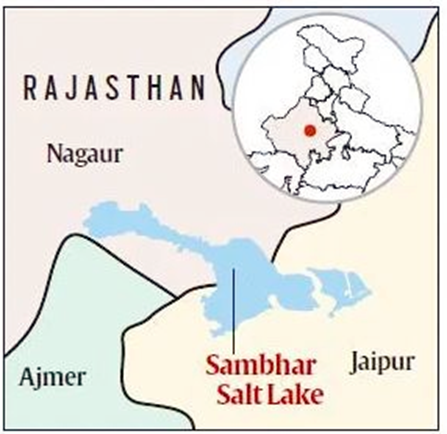
- Sambhar Lake is India’s largest saltwater lake.
- Situated in the districts of Nagaur and Jaipur in Rajasthan, India.
- The lake spans over 200 sq. km.
- It is surrounded by the Aravalli Hills on all sides.
- The lake is fed by two ephemeral streams—Mendha and Runpangarh—along with numerous rivulets and surface runoff.
- Sambhar Lake was designated a Ramsar site in 1990 due to its ecological importance.
- The lake is a vital stopover for several migratory birds during the winter season.
Dicliptera srisailamica: Eastern Ghats of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana

- In November 2024, Dicliptera srisailamica is a newly discovered flowering plant found in the Eastern Ghats of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana.
- It was identified by a team of botanists from the Botanical Survey of India (BSI), Taxonomy:
- The plant belongs to the Acanthaceae family.
- It is named after the temple town of Srisailam.
- Dicliptera srisailamica grows in rare patches along stream banks and rocky edges near waterfalls.
Plant Features:
- Height: An erect herb, reaching up to 90 cm in height.
- Stems: The stems are four-angled, covered in fine, deflexed hairs when young.
- Leaves: The leaves are ovate, with prominent veins and smooth margins.
- Flowers:
- The plant blooms with small, pink, bi-lipped flowers arranged in clusters.
- These flowers are typically seen from October to January.
- Bracts: Distinctive bracts surround the flowers.
- Seeds: The capsules containing seeds are also covered in simple hairs.
Ecological and Botanical Importance:
- Dicliptera srisailamica contributes to the diversity of the Acanthaceae family, which has 223 known species globally.
- In India, the Dicliptera genus includes 27 species, 8 of which are endemic to the country.
- Andhra Pradesh alone hosts seven recorded species of Dicliptera, making it a significant contributor to the flora of the Eastern Ghats.
Global Distribution:
- The genus Dicliptera is typically found in tropical and subtropical regions worldwide, adding to India’s rich botanical diversity.
Exercise Poorvi Prahar

Exercise Poorvi Prahar is a high-intensity tri-service exercise conducted by the Indian Army in the forward areas of Arunachal Pradesh from 10th to 18th November 2024
Objectives:
- The exercise aims to hone combat effectiveness of the Army, Navy, and Air Force in executing Integrated Joint Operations.
- It focuses on enhancing inter-service coordination and operational readiness in the challenging mountainous terrain of Arunachal Pradesh.
Features:
-
Advanced Military Technology:
- The exercise showcases cutting-edge military platforms and systems, highlighting India’s progress in modern warfare technology.
- Innovative Technologies: Swarm Drones, First Person View (FPV) Drones, and Loitering Munitions are being integrated to enhance situational awareness, precision strikes, and operational flexibility.
- Technological Integration:
- The exercise underscores the integration of next-generation tools that reshape the future of military operations, especially in multi-domain combat.
- Operational Integration:
- One key feature is the development of a Common Operating Picture (COP) through joint control structures, which optimizes coordination between ground, air, and naval forces.
- Real-time Data Sharing:
- The exercise makes use of satellite communications and AI-driven analytics for real-time information sharing, enabling faster and more accurate decision-making and response.
Strategic Importance:
- Multi-Domain Operations: It enhances the ability of the Indian Armed Forces to execute seamless operations across land, air, and sea, reinforcing India’s strategic deterrence capabilities.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi
UPSC Prelims Result 2024 Out: Expected Cut Off & Other Details, UPSC Prelims 2024 Answer with Explanation, Daily Prelims Quiz, Daily Current Affairs, MONTHLY CURRENT AFFAIRS TOTAL (CAT) MAGAZINE, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Karol Bagh, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Delhi, Daily Mains Question Answer Practice, ENSURE IAS UPSC Toppers, UPSC Toppers Marksheet, Previous Year Interview Questions, UPSC Syllabus



