- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PLACES IN NEWS 14th FEBRUARY 2025
PLACES IN NEWS 14th FEBRUARY 2025

Hindon River
Why in news?
A massive accumulation of sludge, silt, and puja remnants has recently polluted the Hindon River in Ghaziabad, further contaminating the already degraded water body.
About Hindon River:
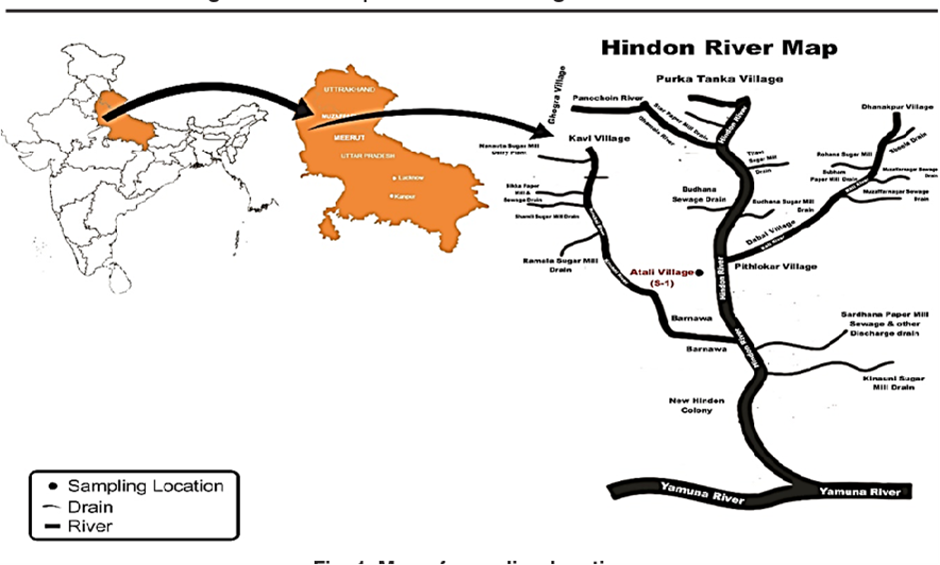
1. Location and Origin:
- The Hindon River is a major tributary of the Yamuna River, flowing through western Uttar Pradesh. It originates from the Siwalik Hills in Saharanpur district of Uttar Pradesh at an elevation of approximately 800 meters (2,625 feet) above sea level.
- The river is primarily monsoon-fed and plays a crucial role in the region’s hydrology, though seasonal variations and human activities significantly impact its flow.
- Covering a course of around 400 kilometres, the Hindon traverses industrial regions before merging with the Yamuna in Noida. Its total catchment area spans approximately 7,083 square kilometres.
- The river is fed by two major tributaries—the Kali (West) River and the Krishni River—both of which contribute to its flow and overall basin dynamics.
2. Historical and Cultural Significance:
- The banks of the Hindon River have revealed traces of ancient civilisations, with archaeological evidence suggesting Harappan settlements dating back to around 2500 BCE.
- The river played a significant role in early human settlements, providing water for agriculture and sustaining communities along its course. Excavations in the region have uncovered artefacts, pottery, and structural remains linked to ancient cultures.
- Over the centuries, the Hindon River has witnessed the rise and fall of various dynasties, serving as a lifeline for agrarian and trading activities in western Uttar Pradesh.
3. Environmental Concerns and Pollution:
- Due to unchecked urbanisation, industrialisation, and agricultural activities, the Hindon has become one of the most polluted rivers in the Ganga basin. Large volumes of untreated sewage, chemical waste, and religious offerings contribute to its deteriorating health.
- In 2015, the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) classified the Hindon as a ‘dead river,’ due to extreme pollution levels, rendering it unfit even for bathing in several stretches.
- Despite being a crucial water source for nearby communities, pollution has severely impacted aquatic life and groundwater quality, necessitating urgent conservation efforts.
Lonar Lake
Why in news?
Lonar Lake, a unique meteorite crater lake in Maharashtra, is set for a tourism boost with the government planning an annual Lonar Tourist Festival to promote its ecological and geological significance.
About Lonar Lake:
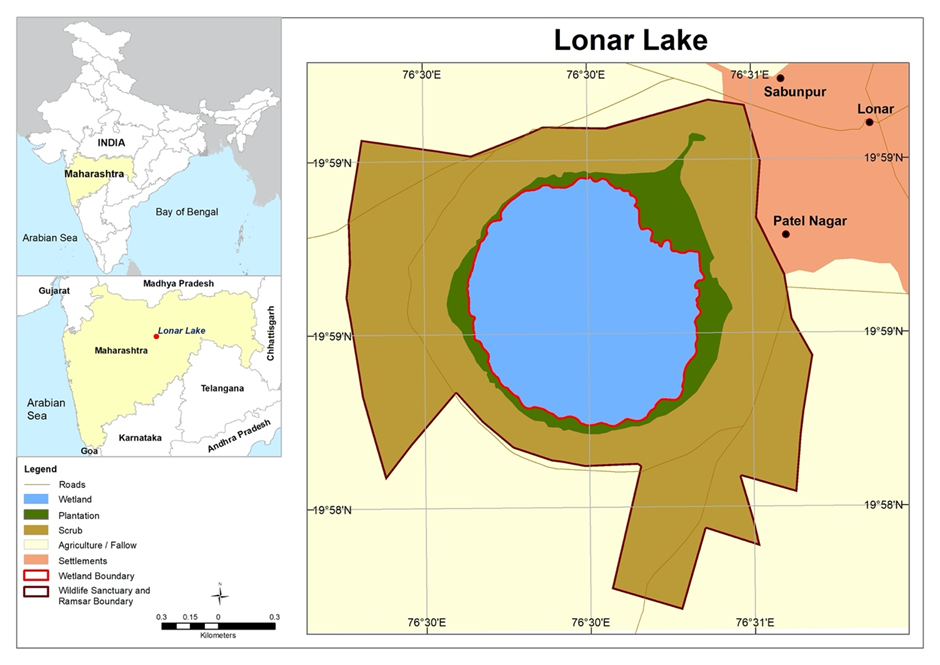
- Location: Lonar Lake is located in Buldhana district, Maharashtra, within the Deccan Plateau. It is surrounded by a forested ecosystem and holds ecological, geological, and cultural significance.
- Formation: The lake was formed approximately 50,000 years ago due to the impact of a meteorite, making it one of the world's few hyper-velocity impact craters on basaltic rock. This distinguishes it as the only known saline crater lake in the world.
- Key Features:
- The lake spans 1.2 kilometres in diameter and reaches a depth of 150 meters. It is encircled by steep hills, some with an incline of up to 75 degrees.
- It has a highly saline and alkaline composition, with water that is seven times saltier than seawater due to mineral deposits.
- A unique feature of Lonar Lake is its changing water colour, which varies from green to pink depending on microbial activity and seasonal variations. This transformation is driven by halophilic microorganisms that thrive in extreme conditions.
- The lake supports diverse flora and fauna, including several migratory bird species, making it an ecologically significant wetland.
- Recognising its ecological and scientific importance, Lonar Lake was designated a Ramsar Site in 2020. It was included under the Ramsar Convention due to its unique hydrogeological features, high biodiversity, and role in supporting rare microbial life.
Red Sea
Why in news?
Sudan and Russia have finalized an agreement for a naval base on the Red Sea, strengthening Russia’s strategic presence in this vital trade and military corridor linking the Indian Ocean and Mediterranean.
About Red Sea:
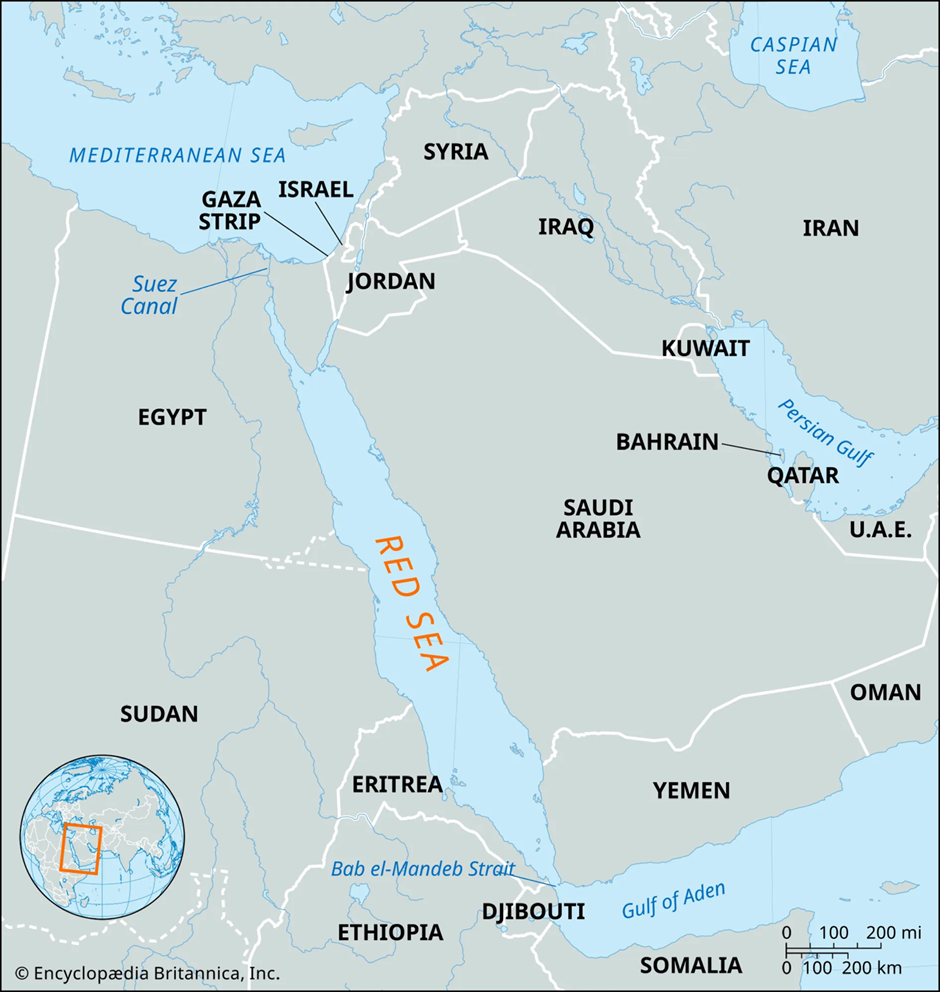
- Location:
- The Red Sea is a semi-enclosed extension of the Indian Ocean, lying between Northeast Africa and the Arabian Peninsula.
- It serves as a critical waterway, linking the Mediterranean Sea to the Indian Ocean through the Suez Canal, the Gulf of Suez, Bab el Mandeb Strait, and the Gulf of Aden.
- Bordering countries include Saudi Arabia, Yemen, Egypt, Sudan, Eritrea, and Djibouti.
- The Great Rift Valley underlies the Red Sea, making it part of the Afro-Arabian Rift System.
- It features key islands such as Tiran Island (near the Gulf of Aqaba) and Shadwan Island (at the entrance of the Gulf of Suez). The Al Wajh Bank in the northern Red Sea is ecologically significant.
- Climate and Hydrology:
- The Red Sea receives very little precipitation and experiences high evaporation rates, leading to high salinity levels.
- No rivers flow into the Red Sea, making it one of the world’s most saline bodies of water.
- The warm waters and coral reefs support diverse marine ecosystems, and the region is part of the Global 200 Ecoregions for biodiversity conservation.
- Strategic Geopolitical Importance: The Red Sea is one of the world's most critical maritime chokepoints, serving as a gateway for global trade. Key aspects of its significance include:
- Trade and Energy Transport: About 10% of global trade and 30% of global container traffic pass through the Suez Canal, connecting Europe, Asia, and Africa.
- Military and Naval Presence: Major global powers, including the U.S., China, Russia, and Iran, maintain military bases along its shores. Sudan and Russia recently finalised an agreement for a Russian naval base, increasing geopolitical tensions.
- Regional Influence: Nations such as Saudi Arabia and the UAE invest heavily in Red Sea ports and military infrastructure to secure their interests.
- Challenges in the Region:
- The Red Sea faces growing security threats, primarily due to Houthi attacks and piracy. The Houthis, an Iran-backed militia in Yemen, have increasingly targeted commercial and military vessels, heightening risks for global trade and energy transportation. These attacks not only threaten maritime security but also disrupt crucial shipping routes.
- Additionally, piracy remains a persistent issue, particularly in the Gulf of Aden and Bab el Mandeb Strait. In response, Djibouti has intensified anti-piracy operations to curb illegal activities that jeopardise regional stability.
- Beyond security concerns, the Red Sea also grapples with environmental and economic challenges. The heavy maritime traffic in this strategic waterway raises the risk of oil spills and pollution, endangering the rich marine biodiversity and coral reef ecosystems.
- Furthermore, geopolitical rivalries among Sudan, Ethiopia, and Eritrea continue to fuel instability, affecting maritime trade and security.
- These conflicts, coupled with external influences from major powers like Russia, China, and the U.S., add to the region’s complexity, making cooperation essential for maintaining stability and safeguarding this vital global trade route.
Estonia
Why in news?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi met Estonia's president to strengthen bilateral ties, focusing on digital cooperation, trade, cybersecurity, and India-EU relations, reinforcing Estonia's role in India's Baltic region engagement.
About Estonia:
-
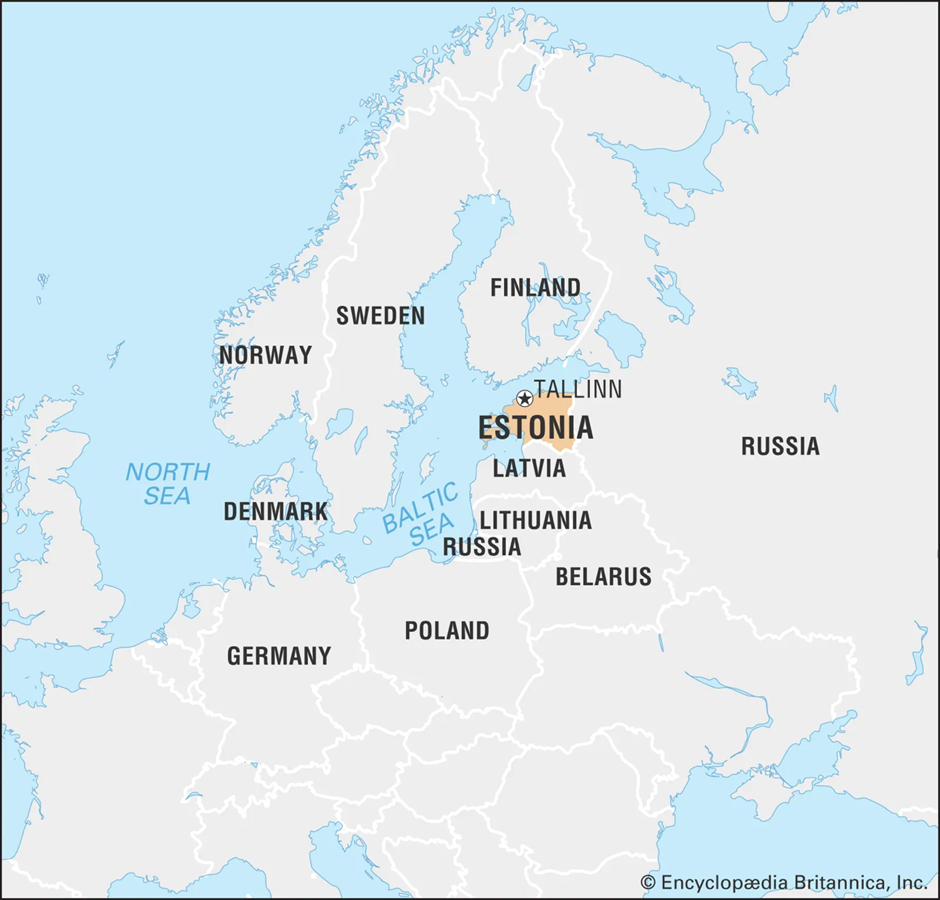
- Location and Political History:
- Location and Political History:
- Estonia is a Baltic nation in Northern Europe, bordered by Latvia to the south, Russia to the east, and the Baltic Sea to the west.
- It gained independence from the Russian Empire in 1918 but was occupied by the Soviet Union (1940–1941, 1944–1991) and Nazi Germany (1941–1944) during World War II.
- Following the collapse of the Soviet Union, Estonia regained independence in 1991 and transitioned into a democratic republic, becoming a European Union (EU) and NATO member in 2004.
- The country is known for its digital governance and advanced technology infrastructure.
- Recent Updates on PM Modi’s Meeting with Estonian President:
- Recent Updates on PM Modi’s Meeting with Estonian President:
On the side lines of the Artificial Intelligence Summit in Paris, Prime Minister Narendra Modi met Estonian President Alar Karis to strengthen bilateral cooperation. Their discussions focused on:
- Cybersecurity, digital governance, and e-governance are areas where Estonia has expertise.
- Global conflicts, including the Russia-Ukraine war, where Estonia emphasised India's role in international stability.
- Trade, investment, and people-to-people ties, with PM Modi inviting Estonian companies to explore Digital India opportunities.
- India-EU relations, reinforcing Estonia’s role in India’s engagement with Europe.
The Estonian e-Government Academy has already contributed to India’s national ICT strategy, showcasing Estonia’s growing role in India’s digital transformation.
-
- Importance of Estonia for India: Estonia plays a crucial role in India’s strategic engagement with the EU and Baltic region, offering:
- Importance of Estonia for India: Estonia plays a crucial role in India’s strategic engagement with the EU and Baltic region, offering:
- Digital and cybersecurity expertise: Estonia is a global leader in e-governance, making it a valuable partner in India’s digital initiatives.
- Stronger EU trade relations: As an EU member, Estonia can help facilitate India’s Free Trade Agreement (FTA) negotiations with the EU.
- Geopolitical cooperation: Estonia’s stance on Russia-Ukraine and Indo-Pacific security aligns with India’s efforts to ensure a rules-based global order.
- Cultural and people-to-people ties: The popularity of yoga in Estonia signifies deepening soft power diplomacy between the two nations.
Amrabad Tiger Reserve
Why in news?
The Telangana Green Fund Development Corporation (TGFDC) conducted a nature guide training program at Amrabad Tiger Reserve, enhancing eco-tourism, wildlife conservation awareness, and local community engagement in sustainable forest management.
About Amrabad Tiger Reserve:
-
- Location:
- Location:
- Amrabad Tiger Reserve is located in the Nagarkurnool and Nalgonda districts of Telangana, forming part of the Nallamala forest range in the Eastern Ghats.
- It was previously part of the Nagarjunasagar-Srisailam Tiger Reserve (NST) before Telangana's bifurcation from Andhra Pradesh in 2014, making it one of the largest tiger reserves in India.
- The reserve is drained by the Krishna River, which flows through its eastern boundary, contributing to its diverse ecosystem.
- The terrain consists of rugged hills, deep valleys, and plateaus, providing an ideal habitat for large carnivores like tigers.
- Flora and Fauna:
- Flora and Fauna:
- The reserve features dry deciduous forests with patches of moist deciduous vegetation, dominated by teak, bamboo, and other native tree species.
- It is home to a significant population of Bengal tigers, along with other large carnivores like leopards, wild dogs (dholes), and sloth bears.
- Herbivores such as sambar deer, chital, nilgai, and four-horned antelope are commonly found, supporting the predator population.
- The reserve is also rich in avian diversity, with Indian peafowls, grey hornbills, crested serpent eagles, and other raptors frequently sighted.
- Reptiles like the Indian rock python, monitor lizards, and various species of venomous snakes are part of the reserve’s ecosystem.
|
UPSC CSE PYQs Q. Consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (2024)
Answer: Option C |
|
Also Read |
|
UPSC Foundation Course |
|
| UPSC Monthly Magazine | CSAT Foundation Course |



