- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PLACES IN NEWS 13th JANUARY 2025
PLACES IN NEWS 13th JANUARY 2025
13-01-2025

Keoladeo National Park
Why in news?
- A rare carnivorous plant, Utricularia, has been discovered in significant numbers this season at Rajasthan's Keoladeo National Park, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
About Keoladeo National Park:
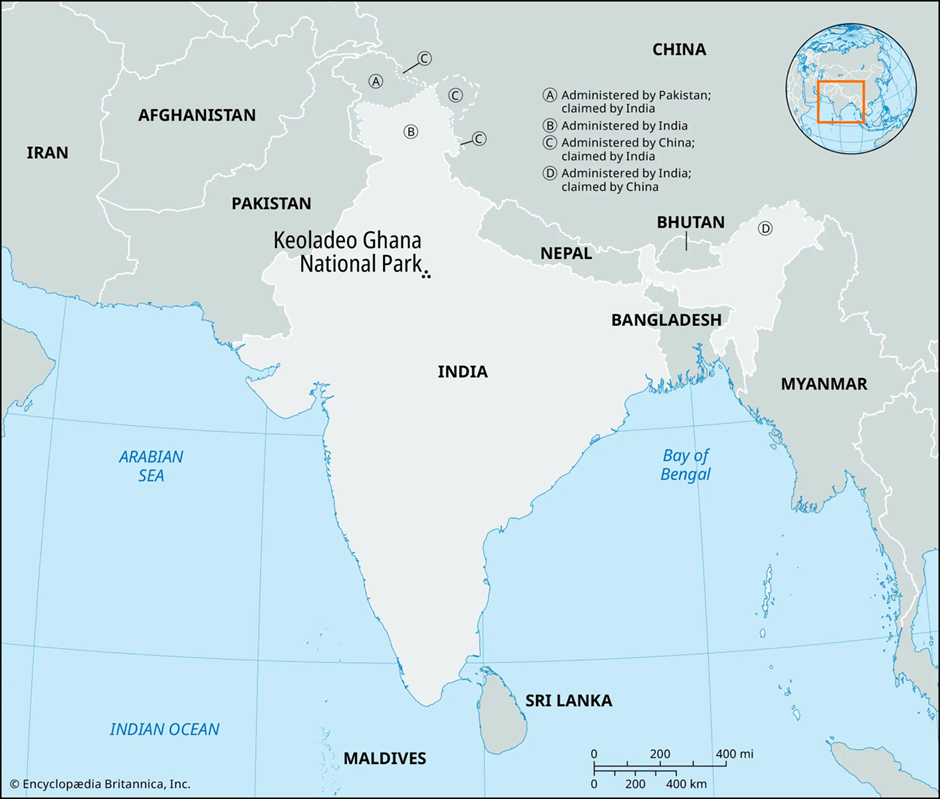
- Keoladeo National Park, located in Bharatpur, Rajasthan, spans approximately 29 square kilometres.
- Situated in the floodplains of the Gambhir and Banganga rivers, it comprises diverse habitats, including wetlands, woodlands, and grasslands. This mosaic supports a rich variety of plant and animal life.
- The park's flora includes over 370 species of flowering plants. Notably, Salvadora oleoides and Salvadora persica thrive in saline soils. Aquatic vegetation is abundant, providing essential food sources for numerous amphibious organisms.
- Efforts have been made to control invasive species like Prosopis juliflora to preserve the native plant diversity.
- Keoladeo is renowned for its avian diversity, with more than 370 bird species recorded. It serves as a crucial wintering ground for migratory waterfowl, including species such as gadwall, shoveller, common teal, and bar-headed goose. The park also provides habitat for resident birds like the painted stork, white spoonbill, and sarus crane. Raptors such as the imperial eagle and crested serpent eagle are also present.
- Among the mammals, visitors can observe nilgai, chital deer, sambar, blackbuck, and wild boar. Predators like the jungle cat, leopard cat, and striped hyena inhabit the park, alongside smaller species such as the Indian grey mongoose and smooth-coated otter.
- The park's herpetofauna is diverse, featuring seven species of turtles, including the Indian flapshell turtle; five lizard species, like the monitor lizard; and thirteen snake species, among them the Indian python and Russell's viper. Amphibians such as the Indian bullfrog and skipper frog are commonly found in the wetlands.
- Keoladeo National Park's rich biodiversity and strategic location make it a vital sanctuary for wildlife, emphasising the importance of ongoing conservation efforts to preserve its unique ecological heritage.
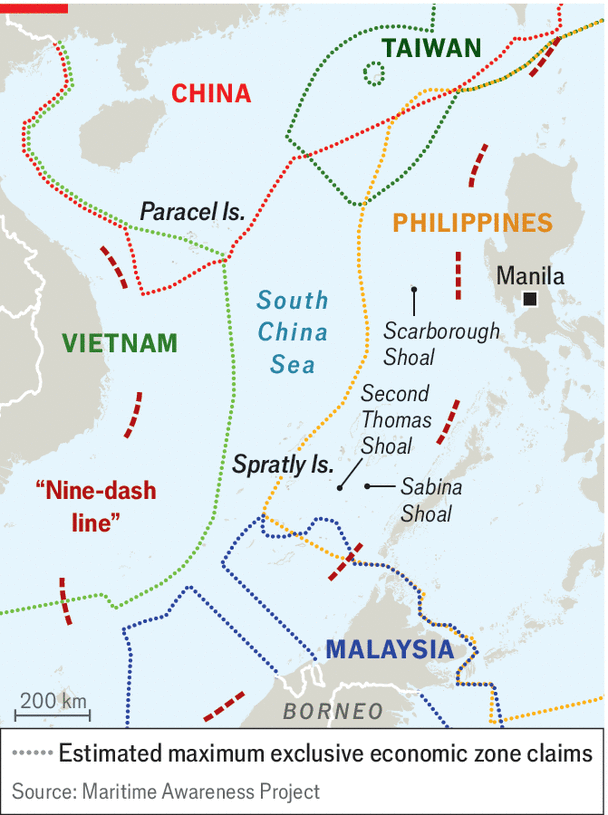
South China Sea
Why in news?
- Leaders of the United States, Japan, and the Philippines recently held discussions addressing China's assertive actions in the South China Sea, emphasizing the need for a rules-based maritime order.
About South China Sea:
-
Geography and Location:
- The South China Sea is a vital and geopolitically significant region located in the western Pacific Ocean, bounded by China to the north, Vietnam to the west, the Philippines to the east, and Malaysia and Brunei to the south.
- This semi-enclosed sea covers an area of approximately 3.5 million square kilometres and connects the Indian Ocean to the Pacific through key maritime chokepoints, including the Strait of Malacca and the Luzon Strait.
- The sea’s diverse geography includes over 200 islands, reefs, and shoals, many of which form part of contested territories such as the Spratly Islands, Paracel Islands, and Scarborough Shoal.
-
Territorial Disputes in South China Sea:
- China’s assertive actions in the South China Sea have fuelled regional tensions. Central to these disputes is the controversial "nine-dash line," an expansive demarcation drawn by China that claims nearly 90% of the South China Sea.
- This claim overlaps with the exclusive economic zones (EEZs) of several Southeast Asian nations, violating international maritime laws, particularly the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS).
- China has engaged in the militarisation of disputed territories, including the construction of artificial islands in the Spratly Islands. These islands, equipped with airstrips, radar systems, and missile installations, are strategically designed to assert dominance and control over vital waterways.
- Key flashpoints include the Scarborough Shoal, a rich fishing ground claimed by both China and the Philippines. In 2012, China effectively took control of the area after a naval standoff, forcing Filipino fishermen out.
- Similarly, the Paracel Islands, claimed by China, Vietnam, and Taiwan, have witnessed increased Chinese naval activities and military drills. These actions not only exacerbate tensions but also pose a direct challenge to freedom of navigation in international waters.
-
Significance of South China Sea in International trade:
- The South China Sea’s importance extends far beyond territorial disputes. It is one of the world’s busiest maritime trade routes, carrying over 30% of global shipping traffic, amounting to nearly $3.4 trillion in annual trade.
- Key commodities such as oil, natural gas, and raw materials transit through these waters, making their security essential for the global economy.
- Additionally, the sea is rich in natural resources, including an estimated 11 billion barrels of oil and 190 trillion cubic feet of natural gas, further intensifying competition for control.
-
Geopolitical significance:
- The geopolitical significance of the South China Sea lies in its role as a strategic crossroads for major powers. For the United States and its allies, ensuring freedom of navigation operations (FONOPs) in the region is critical to countering unilateral actions that threaten the global rules-based order. For China, dominating the South China Sea aligns with its broader ambitions of regional hegemony and securing critical supply chains.
- Despite international arbitration rulings, such as the 2016 Permanent Court of Arbitration decision that invalidated China’s nine-dash line, Beijing continues to defy international norms.
- The court’s decision, initiated by the Philippines, reaffirmed the maritime entitlements of smaller nations under UNCLOS. However, China’s noncompliance highlights the challenges of enforcing international law in the face of great power politics.
- The South China Sea’s complexity underscores the need for multilateral diplomacy and cooperation to manage disputes. Regional organisations like the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) play a crucial role in fostering dialogue, although consensus remains elusive due to China’s economic and political influence over some member states.
- As tensions persist, the South China Sea remains a focal point for understanding the interplay of sovereignty, maritime law, and global security.
Punatsangchhu-II Hydroelectric Project (PHEP-II)
Why in news?
- State-owned Bharat Heavy Electricals Ltd. (BHEL) has successfully commissioned the first two units of the 6x170 MW Punatsangchhu-II Hydroelectric Project (PHEP-II) in Bhutan.
About Punatsangchhu-II Hydroelectric Project (PHEP-II):

- The Punatsangchhu-II Hydroelectric Project (PHEP-II) is a significant run-of-the-river hydroelectric facility located in the Wangdue Phodrang district of Bhutan.
- With a planned capacity of 1,020 MW, the project aims to harness the hydropower potential of the Punatsangchhu River, contributing to Bhutan’s renewable energy generation and export capabilities.
- It is being developed under an Inter-Governmental Agreement (IGA) between the Royal Government of Bhutan and the Government of India through the Punatsangchhu-II Hydroelectric Project Authority.
Key Specifications of the Project:
- The project involves the construction of a 91-meter-high and 223.8-meter-long concrete gravity dam, designed to create sufficient water pressure for power generation.
- An 877.46-meter-long and 12-meter-diameter diversion tunnel with a discharge capacity of 1,118 cubic meters per second is a crucial component of the design, ensuring efficient water flow management.
- Additionally, the project includes a 168.75-meter-long and 22-meter-high upper cofferdam and a 102.02-meter-long and 13.5-meter-high downstream cofferdam for controlling river flow during construction and operation.
- The underground powerhouse will host six Francis turbines, each with a capacity of 170 MW, ensuring reliable and efficient power generation.
- When fully operational, the facility is expected to produce approximately 4,357 million units of electricity annually, meeting both domestic energy demands and contributing to Bhutan’s export revenues.
Funding and Collaboration:
- The project’s funding arrangement highlights the strong cooperation between India and Bhutan. It is financed by the Government of India, with 30% provided as a grant and the remaining 70% as a loan at an annual interest rate of 10%.
- The repayment period spans 30 equated semi-annual instalments, commencing one year after the mean date of operation. This structured financial model reflects the commitment of both nations to advancing renewable energy and fostering regional cooperation.
Strategic Importance:
- The Punatsangchhu-II project underscores Bhutan’s status as a leader in clean energy production. With all surplus power from the project slated for export to India, it strengthens the economic and energy partnership between the two countries.
- The facility not only enhances Bhutan’s energy infrastructure but also contributes to regional energy security and sustainable development goals.
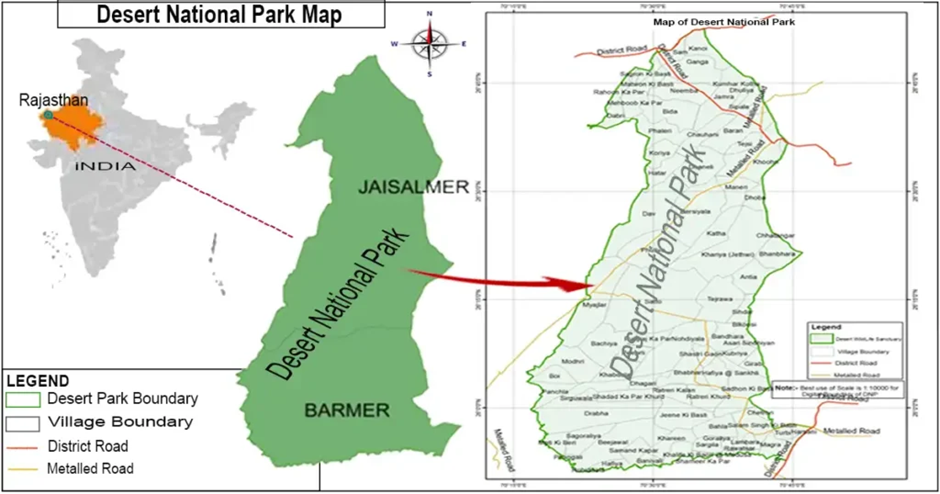
Desert National Park
Why in news?
- In a significant boost to conservation efforts, a group of at least 12 Great Indian Bustards (GIBs), one of India’s most critically endangered species, was recently spotted at the Desert National Park (DNP) in Rajasthan.
About Desert National Park:
-
Geography:
- The Desert National Park (DNP) is located in the Thar Desert of Rajasthan, primarily in the districts of Jaisalmer and Barmer.
- Spanning over 3,162 square kilometres, it is one of the largest national parks in India. The terrain is characterised by sand dunes, rocky outcrops, salt lakes, and interspersed patches of grassland.
- The park’s arid climate and unique topography support a fragile yet diverse ecosystem, making it an important region for desert conservation.
-
Flora and Fauna:
- Despite its harsh climate, the park hosts a variety of flora and fauna adapted to arid conditions. The vegetation is primarily sparse, with shrubs like Acacia and Ber and grasses like sewan and dhaman dominating the landscape.
- The park is renowned for its rich avian diversity, serving as a critical habitat for the critically endangered Great Indian Bustard (Ardeotis nigriceps).
- This majestic bird, known for its striking appearance and large size, is a flagship species of the park. Other bird species include eagles, vultures, falcons, and migratory birds like Demoiselle cranes.
- Mammals such as desert foxes, Indian wolves, and chinkaras (Indian gazelles) are also found here. Reptiles like monitor lizards, spiny-tailed lizards, and a variety of snakes thrive in the arid environment, highlighting the ecological importance of the Desert National Park.
Gulf of Mexico
Why in news?
- Recently, the US President-elect said that he will change the name of the Gulf of Mexico to “Gulf of America”.
About Gulf of Mexico:
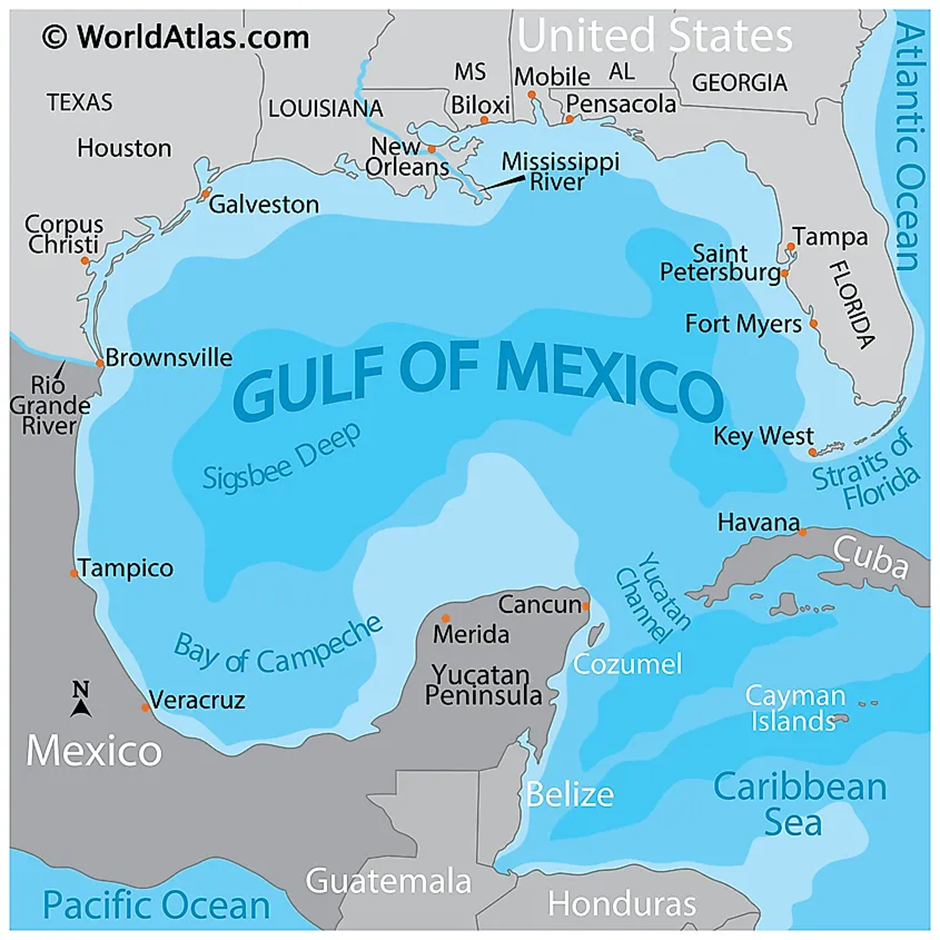
-
Geography and Location:
- The Gulf of Mexico is a vast ocean basin situated in the south-eastern region of North America. It is bordered by the United States to the north and east, Mexico to the west and south, and Cuba to the southeast.
- This semi-enclosed body of water connects to the Atlantic Ocean via the Straits of Florida and to the Caribbean Sea through the Yucatán Channel.
- Covering an area of approximately 1.5 million square kilometres, the Gulf's coastline stretches over 5,000 kilometres, encompassing diverse ecosystems such as wetlands, mangroves, and coral reefs.
- Major rivers, including the Mississippi River, drain into the Gulf, significantly influencing its hydrology and nutrient dynamics.
-
Development of Twisters and Cyclones:
- The Gulf of Mexico is highly prone to the development of cyclones and twisters due to its warm waters and geographical positioning. The region plays a critical role in the formation and intensification of tropical storms and hurricanes.
- Warm sea surface temperatures exceeding 26°C provide the necessary energy for cyclonic systems to develop and strengthen.
- Hurricanes, which form during the Atlantic hurricane season (June to November), often originate in or pass through the Gulf.
- These storms can rapidly intensify due to the Gulf's warm, shallow waters and low wind shear conditions. Notable hurricanes like Katrina (2005) and Harvey (2017) caused extensive damage, highlighting the Gulf's vulnerability to extreme weather events.
- Twisters, or tornadoes, can form in the Gulf region as a result of severe thunderstorms, especially those associated with tropical cyclones. The interaction between moist air masses from the Gulf and cooler continental air often triggers these events, particularly in coastal areas.
-
Geopolitical Significance:
- The Gulf of Mexico holds substantial geopolitical significance due to its abundant natural resources and strategic location.
- It is a critical hub for the oil and gas industry, supplying about 15% of the United States' crude oil production. In fiscal year 2019, activities in the Gulf supported over 345,000 jobs and contributed more than $28 billion to the GDP.
- Additionally, the Gulf serves as a vital maritime route for international trade, with major ports like Houston, New Orleans, and Tampa facilitating significant cargo throughput. The region's fisheries are among the most productive globally, supporting both commercial and recreational fishing industries.
- Environmental concerns, such as habitat degradation and pollution, pose challenges to the Gulf's ecological health. Efforts to balance economic interests with environmental protection continue to shape policies and initiatives in the region.
- In summary, the Gulf of Mexico's unique geographical position and rich natural resources make it a region of considerable geopolitical importance, influencing economic activities, environmental policies, and international relations in the surrounding nations.
UPSC CSE PYQsQ1. With reference to India’s Desert National Park, which of the following statements are correct?
Select the correct answer using the code given below: (2020)
Answer: Option C Q. Consider the following pairs: (2014)
Which of the above pairs is/are correctly matched? (a) 1 only Answer: Option A |

|
Also Read |
|
| FREE NIOS Books | |



