- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT Batch
- Polity Module Course
- Geography Module Course
- Economy Module Course
- AMAC Module Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History Module Course
- Environment Module Course
- Governance Module Course
- Science & Tech. Module Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Module Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Module Course
- Essay Module Course
- Current Affairs Module Course
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PLACES IN NEWS 12th MARCH 2025
PLACES IN NEWS 12th MARCH 2025
12-03-2025
North Sea
Why in news?
- A cargo ship collided with a jet fuel tanker supplying the U.S. military off eastern England, igniting both vessels and causing fuel to spill into the North Sea.
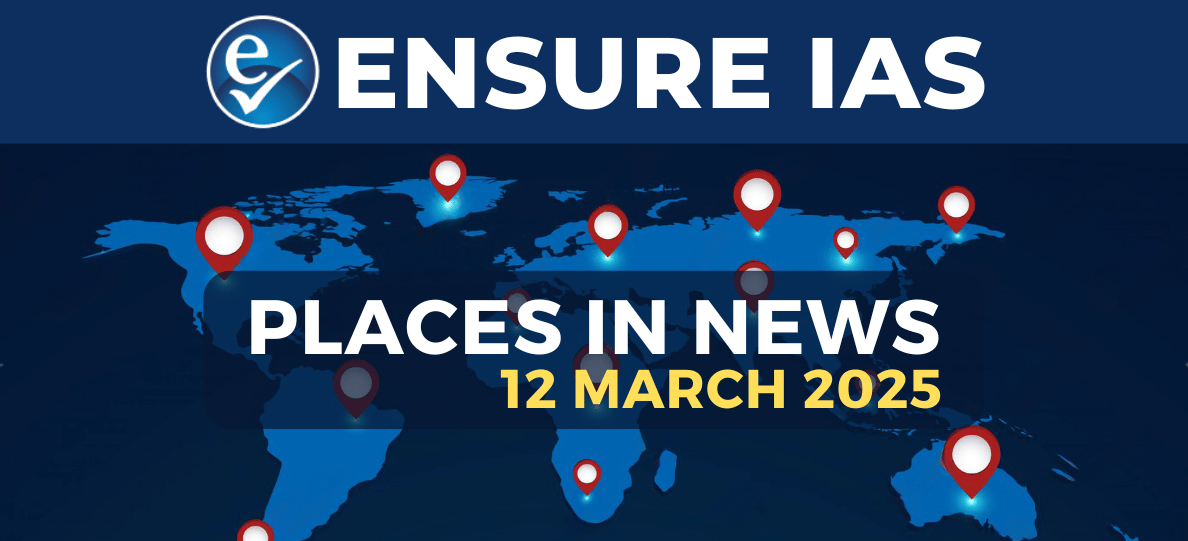
About North Sea:
- Geography and Location:
- The North Sea is a large body of water located in Northern Europe, bordered by several countries.
- It is an extension of the Atlantic Ocean, connected to the English Channel to the south and the Norwegian Sea to the north.
- The North Sea is bounded by the United Kingdom to the west, Norway to the northeast, Denmark to the east, Germany, the Netherlands, and Belgium to the south, and Scotland to the north.
- The North Sea's surface area is about 575,000 square kilometres, with an average depth of around 95 meters. The Skagerrak and Kattegat straits connect it to the Baltic Sea.
- Climate and Ocean Currents:
- The climate of the North Sea is highly influenced by the Atlantic Ocean and westerly winds, resulting in a temperate maritime climate.
- Ocean currents, such as the North Atlantic Drift, bring warm water from the Gulf Stream, helping to moderate temperatures in the North Sea, especially in Norway and the UK.
- These currents play a key role in maintaining relatively mild winters and moderate temperatures, which benefits both marine life and human activities.
- The stability of the North Sea's climate and ocean currents helps ensure year-round trade operations by maintaining navigability for commercial shipping.
- The shipping lanes in the North Sea remain operational even during the colder months, thanks to the influence of warm currents and relatively mild winter conditions, which prevents freezing.
- Furthermore, these favourable conditions allow for continuous fishing operations and energy production, contributing to the region's sustained economic importance.
- Natural Resources:
- The North Sea is rich in a variety of natural resources, particularly hydrocarbons such as oil and natural gas.
- The North Sea oil fields are among the largest in the world, discovered in the 1960s, and have played a significant role in meeting the energy demands of Europe.
- Offshore oil rigs are extensively developed, with significant reserves in the UK sector, Norwegian sector, and the Dutch sector.
- The North Sea also contains abundant mineral deposits, including sand, gravel, and limestone, which are crucial for construction and industrial use.
- It is rich in fish and shellfish resources, supporting vital fishing industries in countries like Norway, Denmark, and the UK.
- Renewable energy resources, particularly offshore wind energy, are growing rapidly in the region, with many offshore wind farms now operational.
- Rare earth metals and other minerals are also being explored in the North Sea seabed, with growing interest in their potential for supporting emerging technologies.
- Role in Promoting International Trade and Connectivity:
- The North Sea plays a crucial role in international trade, serving as a major shipping route connecting Europe with the rest of the world.
- The sea is a vital corridor for the movement of goods, including raw materials, energy resources, consumer products, and manufactured goods.
- Ports along the North Sea coast, such as Rotterdam (Netherlands), Hamburg (Germany), and Aberdeen (Scotland), serve as key international trade hubs, handling millions of tonnes of cargo annually.
- North Sea shipping lanes connect with the wider European maritime network, facilitating trade to and from Asia, North America, and other parts of the world.
- The English Channel, a narrow passage at the southern edge of the North Sea, allows direct access to the North Atlantic Ocean, further enhancing trade routes.
- Additionally, the North Sea is integral to energy trade, as oil and gas extracted from the region are exported via pipelines and tanker ships to countries across Europe.
- Impact of Oil Spill in the Region:
- Environmental Damage: Oil spills severely impact marine ecosystems by coating marine life, reducing oxygen levels, and damaging coral reefs.
- Economic Losses: Fishing, tourism, and coastal economies suffer due to contamination of water and marine life.
- Threat to Coastal Communities: Coastal populations dependent on fisheries and tourism face job losses, displacement, and health issues due to toxic exposure.
- Long-Term Ecological Impact: Oil persists in sediments, affecting ecosystems for decades, hindering species recovery, and altering food chains.
- Geopolitical and Strategic Concerns: Oil spills in sensitive maritime zones may disrupt trade, trigger diplomatic disputes, and affect energy security.
Vizhinjam Port
Why in news?
-
- Vizhinjam Port in Kerala has received environmental clearance for its second and third phases, facilitating its expansion as a major transhipment (Transfer of cargo between vessels) hub.
- Vizhinjam Port in Kerala has received environmental clearance for its second and third phases, facilitating its expansion as a major transhipment (Transfer of cargo between vessels) hub.
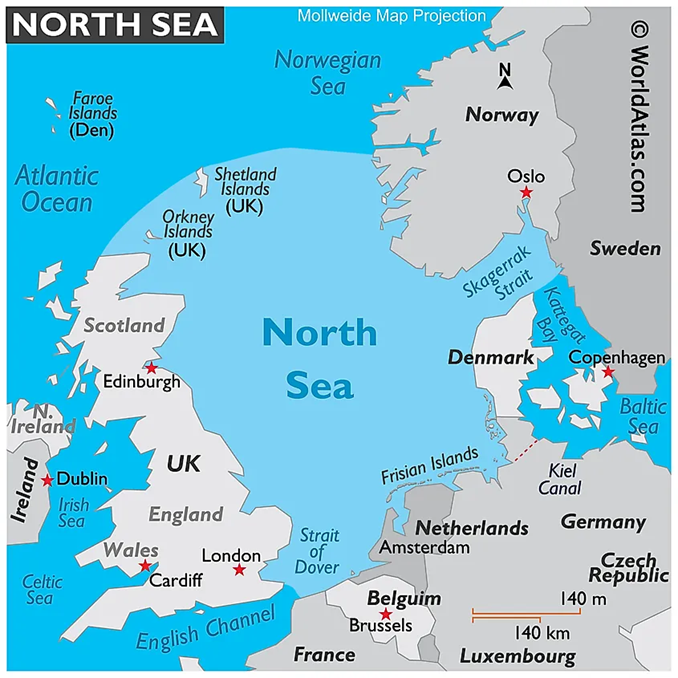
About Vizhinjam Port:
-
- Location and Geography:
- Location and Geography:
- Vizhinjam International Seaport is located in Thiruvananthapuram, the capital of Kerala.
- It is India’s first deep-water container transshipment port and is situated just 10 nautical miles from the east-west international shipping route.
- The port is strategically positioned 20 km from Thiruvananthapuram International Airport and is the only Indian port adjacent to an international shipping lane.
- Its natural depth of 24 meters reduces the need for dredging, making it capable of handling Ultra Large Container Ships (ULCS).
- Key Features:
- Key Features:
- The port is a multi-purpose, all-weather, and green port developed under the landlord port model.
- The port is a special-purpose government company, fully owned by the Government of Kerala, that would act as an implementing agency for its development.
- It will be India’s first fully automated port, featuring Super Post-Panamax STS cranes with a record lifting height of 74 meters.
- A railway tunnel, the third longest in India, is planned to enhance connectivity with the national railway network.
- Economic Significance:
- Economic Significance:
-
- The port is expected to handle 50% of India’s container transhipment needs, reducing dependence on Colombo, Singapore, and Dubai.
- It will boost India's maritime trade, generate employment, and strengthen coastal economies.
- The project’s total cost is ₹28,867 crore ($3.3 billion), and it will be operated by Adani Group for 40 years.
- The port will enhance India’s strategic position in global trade and improve regional connectivity.
Romania
Why in news?
- Romania barred a pro-Russian candidate from its presidential race, citing national security concerns, sparking protests
amid rising geopolitical tensions and fears of Russian influence in Eastern Europe.
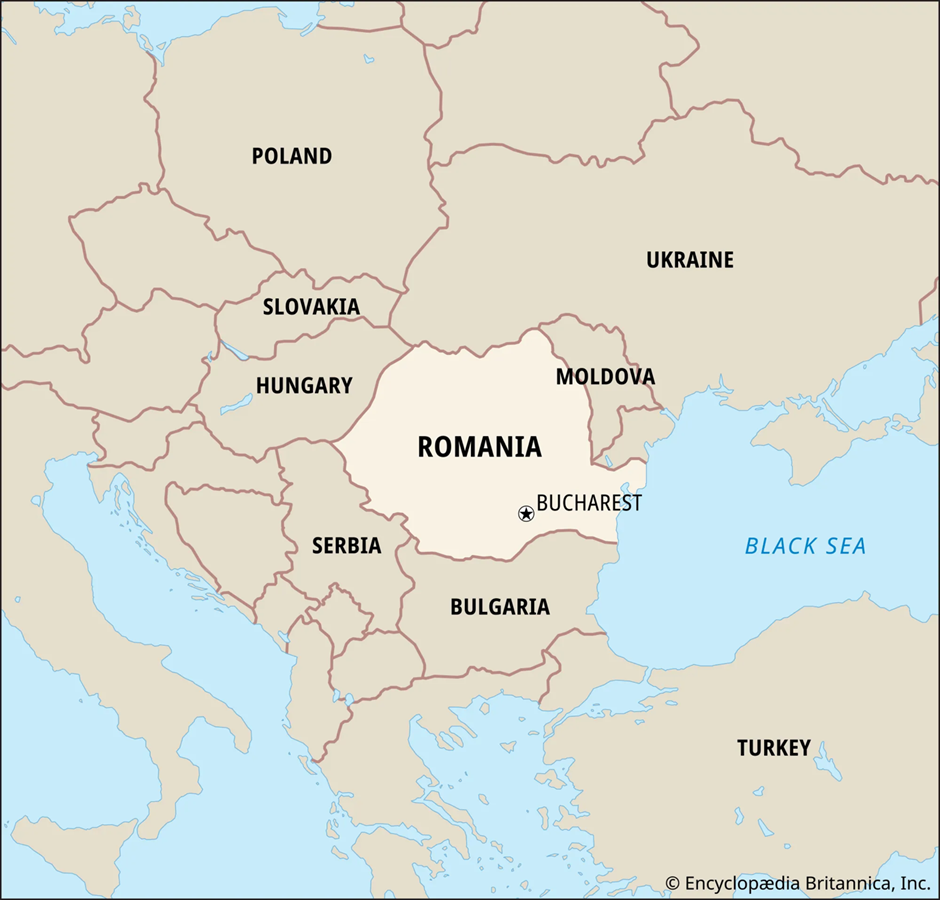
About Romania:
-
- Location and Geography:
- Location and Geography:
- Romania is located in South-eastern Europe, bordered by Ukraine to the north, Moldova to the northeast, Bulgaria to the south, Serbia to the southwest, and Hungary to the west.
- It has a coastline along the Black Sea in the east, providing strategic access to maritime trade routes.
- The Carpathian Mountains dominate the central and northern regions, while the Danube River, one of Europe’s longest rivers, forms part of its southern border.
- The country experiences a temperate-continental climate, with hot summers and cold winters, influencing agriculture and trade.
- Political Features:
- Political Features:
- Romania is a unitary semi-presidential republic, where executive power is shared between the President and the Prime Minister.
- The president, elected for a five-year term, oversees foreign policy and national security, while the prime minister leads the government and handles domestic affairs.
- The Parliament consists of a bicameral legislature, with the Chamber of Deputies and the Senate responsible for law-making.
- Romania is a member of the European Union (EU), NATO, and the United Nations, playing a crucial role in regional security and economic policies.
- Recent Protests Amid Elections:
- Recent Protests Amid Elections:
- Mass protests erupted after authorities barred a pro-Russian presidential candidate, citing national security concerns.
- Demonstrators, including opposition supporters, accused the government of undermining democracy and restricting political competition.
- The move comes amid growing tensions between NATO countries and Russia, with concerns over Russian influence in Eastern Europe.
- Pro-European parties have gained momentum, pushing for stronger ties with the EU and NATO, while nationalist factions seek a more independent foreign policy.
- The protests highlight Romania’s deep political divisions ahead of the upcoming presidential elections, shaping the country’s geopolitical direction.
Syria
Why in news?
- The Kurdish-led Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) agreed to integrate with Syrian government forces, aiming to strengthen national defence amid escalating regional tensions and security threats, particularly from Turkey and extremist groups.
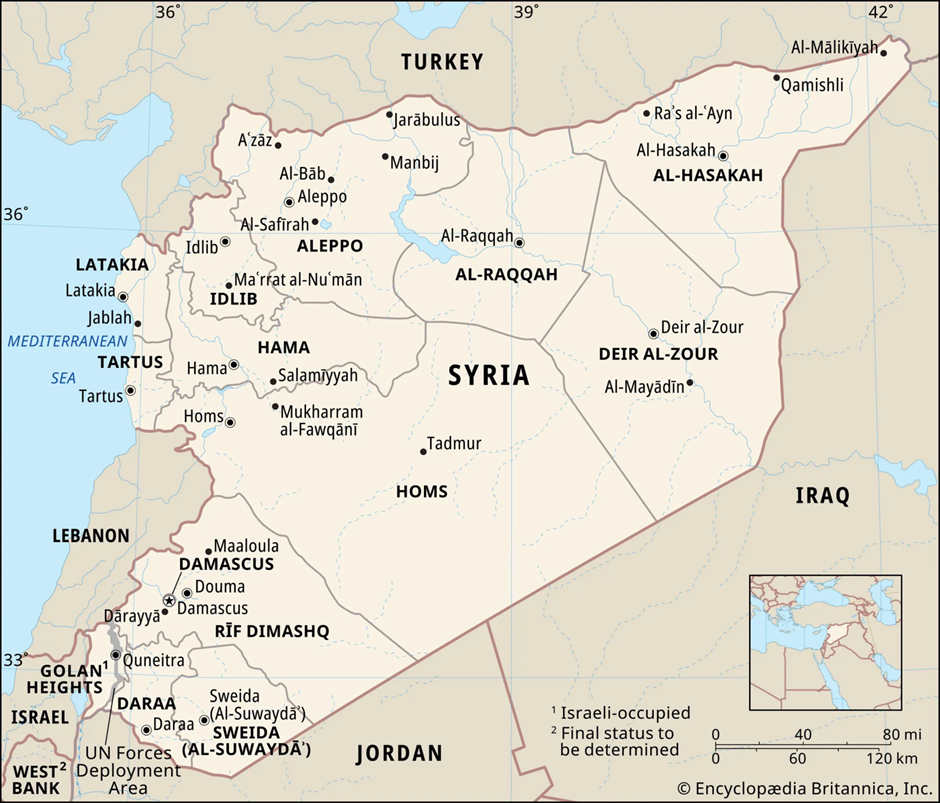
About Syria:
-
- Location and Geography:
- Location and Geography:
- Syria is located in Western Asia, bordered by Turkey to the north, Iraq to the east, Jordan to the south, Israel and Lebanon to the southwest, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west.
- The country covers an area of 185,180 square kilometres, with diverse landscapes, including coastal plains, mountains, and deserts.
- The Euphrates River, Syria’s longest river, flows from Turkey through Syria into Iraq, providing vital water resources for agriculture and settlements.
- The Syrian Desert dominates the eastern part, while the Anti-Lebanon Mountains form a natural border with Lebanon.
- Syria has a Mediterranean climate in the west, with arid and semi-arid conditions in the interior, impacting agricultural productivity.
- Kurds and Their Relations with the Syrian Government:
- Kurds and Their Relations with the Syrian Government:
- The Kurds are the largest ethnic minority in Syria, primarily residing in northern and north-eastern regions, including Hasakah, Raqqa, and parts of Aleppo.
- The Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF), a Kurdish-led militia, played a significant role in defeating ISIS, with support from the United States and Western allies.
- The Syrian government historically suppressed Kurdish identity, denying them citizenship and political rights until recent years.
- Following the Syrian Civil War (2011-present), Kurdish groups gained semi-autonomous control over Rojava (North-eastern Syria), establishing their own governance structures.
- The recent SDF agreement to integrate with Syrian government forces marks a strategic shift, as the Kurds seek protection against Turkish military offensives.
- Security Issues from Turkey and Extremist Groups:
- Security Issues from Turkey and Extremist Groups:
- Turkey views the SDF and its armed wing, the YPG, as an extension of the Kurdistan Workers’ Party (PKK), a designated terrorist organisation in Turkey, the U.S., and the EU.
- Turkish forces have conducted multiple military operations, including Operation Euphrates Shield (2016), Operation Olive Branch (2018), and Operation Peace Spring (2019), targeting Kurdish-held areas.
- Idlib province, controlled by Hay'at Tahrir al-Sham (HTS) and other extremist groups, remains a major stronghold for radical Islamist factions.
- ISIS sleeper cells continue to operate in Deir ez-Zor and Homs, posing a threat to regional stability and counterterrorism efforts.
- The integration of SDF with Syrian government forces could reshape Syria’s security landscape, affecting regional power dynamics with Turkey, Iran, and Russia.
Mauritius
Why in news?
- Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi is on a two-day state visit to Mauritius to strengthen bilateral relations and participate as the Chief Guest in the country's National Day celebrations.
About Mauritius:
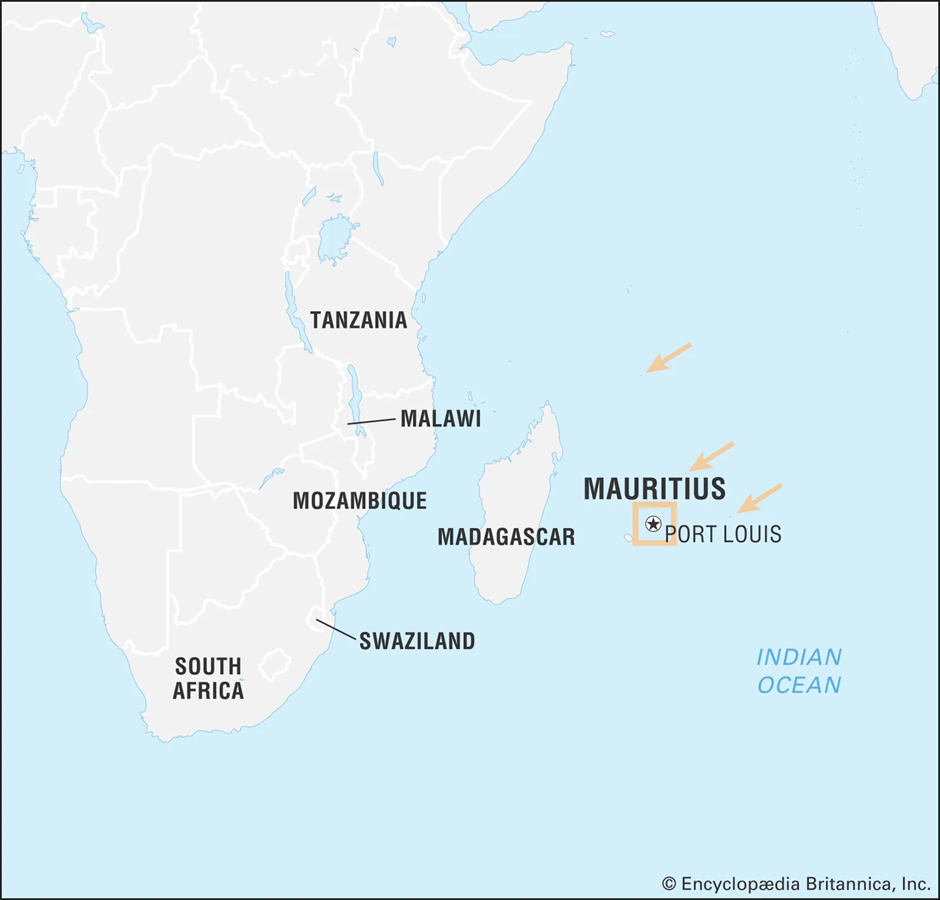
- Location and Geography:
- Mauritius is an island nation in the Indian Ocean, located about 2,000 km off the south-eastern coast of Africa.
- It consists of the main island of Mauritius, along with Rodrigues, Agalega, and Cargados Carajos Shoals (Saint Brandon).
- The country has a tropical maritime climate, with a diverse ecosystem including coral reefs, lagoons, and volcanic mountains.
- Its strategic position along major shipping routes makes it a key player in Indian Ocean trade and security.
- Significance for India:
- Historical and Cultural Ties: Mauritius has a large Indian diaspora (about 70% of the population), primarily of Bihari and Tamil origin, who migrated during British rule. Hindi, Bhojpuri, Tamil, and Marathi are widely spoken, and India supports cultural exchanges and linguistic preservation.
- Economic and Trade Relations: India is among Mauritius’ top trading partners, supplying petroleum products, pharmaceuticals, and machinery. The Comprehensive Economic Cooperation and Partnership Agreement (CECPA), signed in 2021, facilitates bilateral trade and investment.
- Strategic and Security Cooperation: India assists Mauritius in maritime security, countering piracy, and illegal fishing in the Indian Ocean. India has provided patrol vessels, surveillance aircraft, and naval training to enhance Mauritius’ defence capabilities.
- The Agaléga Islands development project, involving India, strengthens maritime surveillance and regional security.
- Connectivity and Development Assistance: India has contributed to infrastructure projects, including metro rail, hospitals, and cybercity initiatives. Mauritius receives grants and concessional loans under India’s Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation (ITEC) program.
- Challenges in Relations:
- Tax Treaty Amendments: India revised the Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) in 2016 to curb round-tripping of investments, impacting FDI flows.
- Geopolitical Balancing: Mauritius also engages with China and Western nations, leading to diplomatic recalibrations for India.
- Agaléga Island Concerns: Opposition in Mauritius over perceived military expansion by India could impact bilateral trust.
|
UPSC CSE PYQs Q. Consider the following countries:
How many of the above countries have a border with the North Sea? (2024)
Answer: Option B Q. Mediterranean Sea is a border of which of the following countries?
|
|
Also Read |
|
| FREE NIOS Books | |




