- Courses
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PLACES IN NEWS 12th APRIL 2025
PLACES IN NEWS 12th APRIL 2025
12-04-2025

Cheyyar River
Why in news?
- A new high-level bridge across the Cheyyar River in Tiruvannamalai was inaugurated on April 11, 2025.
About Cheyyar River:
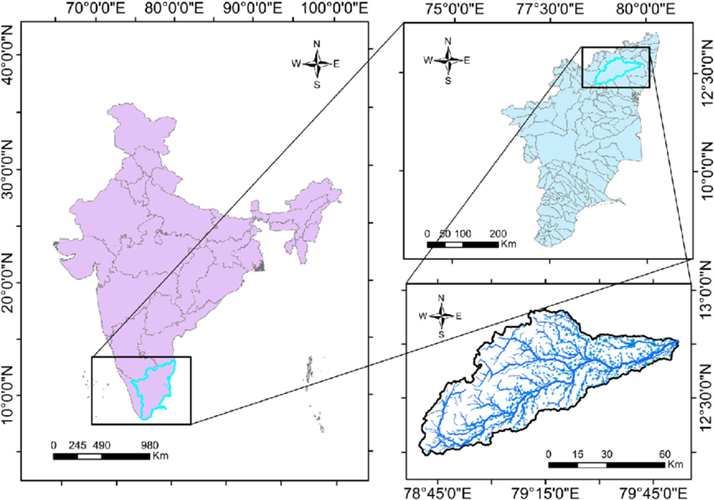
- Cheyyar River (also known as Sei Aaru, meaning Child River) is a seasonal river in Tiruvannamalai District, Tamil Nadu, South India.
- It is a tributary of the Palar River, which originates in the Jawadhu Hills and flows into the Bay of Bengal.
- The river receives water mainly from the Northeast and Southwest monsoons, making it an essential source during seasonal rains.
- It serves as a major irrigation source for several villages, including the towns of Cheyyaru and Vandavasi along its banks.
- The Vedapureeswarar Temple (also known as Vedhanadeshwarar Temple) is an ancient shrine situated on the riverbank in Cheyyar town.
- A legend recounts that Thirugnana Sambandar, a revered Saivite saint, visited the temple and transformed a male palm tree into a fruit-bearing female tree through devotional Tamil verses.
- According to myth, Goddess Parvati (as Balakusalambigai or Ilamulainayagi) drew a line on the earth with her Trisul (trident) to create the river for Lord Muruga to play.
- The river is still venerated as a Holy River by residents of Cheyyar and nearby villages due to its mythological significance.
Dalma Wildlife Sanctuary
Why in news?
- The Butterfly Festival at Dalma Wildlife Sanctuary, Jamshedpur, originally scheduled for April 4–6, has been rescheduled to April 18–20, 2025, due to logistical reasons.
About Dalma Wildlife Sanctuary:
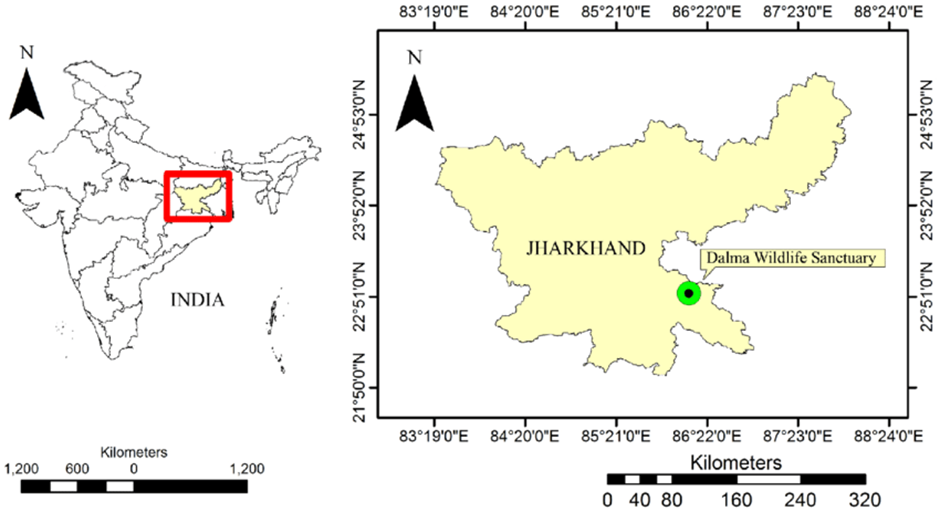
- Location and Geography:
- The Dalma Wildlife Sanctuary is located in Jharkhand, India.
- Spread across an area of approximately 195 square kilometres, the sanctuary lies in the scenic Dalma Hills, which rise to the north of the industrial town of Jamshedpur.
- Established in 1975, Dalma is known for its hilly terrain and dry deciduous forest landscape.
- It plays a crucial ecological role in the region, particularly in offering a protected habitat for the Indian elephant and acting as a vital corridor for seasonal wildlife migration.
- Flora and Fauna:
- The sanctuary is home to diverse flora, including native and fruit-bearing trees such as mango, guava, lemon, jamun, mahuwa, sal, bamboo, neem, sheesham, baabul, arjuna, kadam, and karanj. This rich vegetation supports a wide range of herbivores and frugivores.
- Dalma’s wildlife includes key species like the Indian elephant (with a population of about 85 as of 2024), sloth bear, golden jackal, barking deer, wild boar, porcupine, pangolin, and Indian giant squirrel. Birds such as the jungle fowl, Indian peafowl, hornbills, and kingfishers also thrive here.
- In a significant conservation highlight, a male tiger was recorded in January 2025, having migrated from Palamu Tiger Reserve through forest corridors, underlining Dalma’s role in tiger movement and landscape connectivity.
Black Sea
Why in news?
- Former Romanian presidential candidate Calin Georgescu has warned that NATO is preparing to launch World War III from Romania as Black Sea drills intensifies.
About Black Sea:
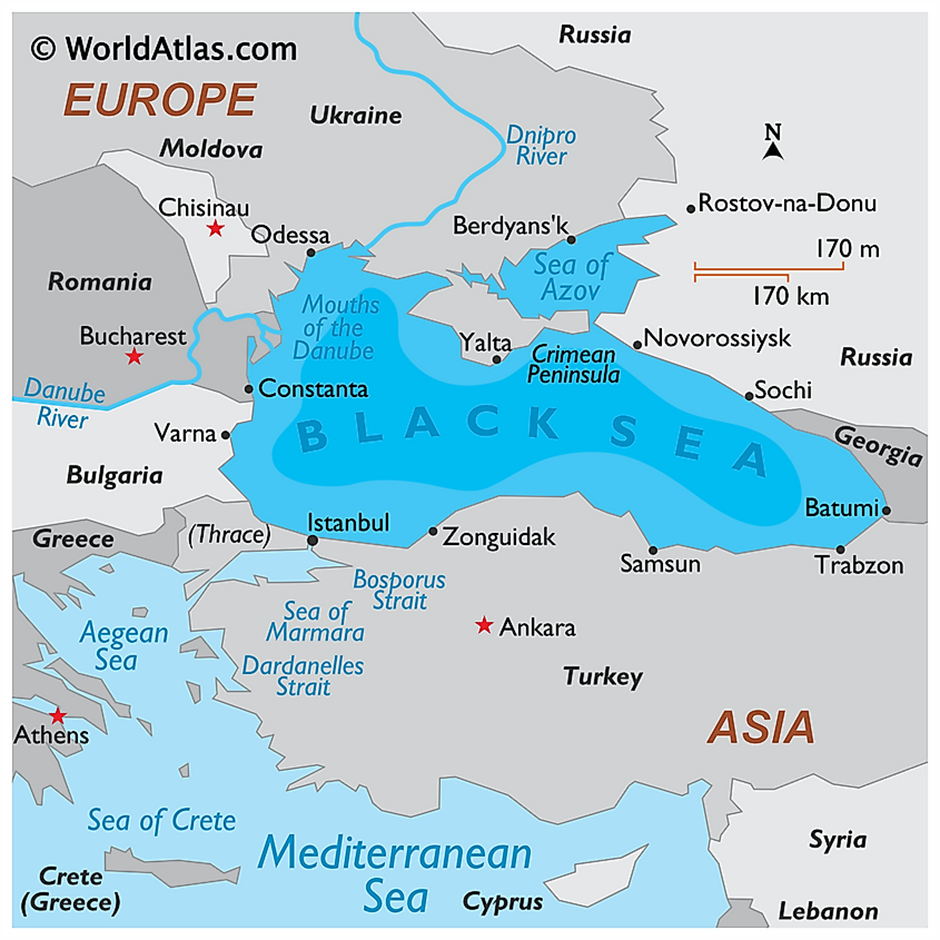
- Location and Geography:
- The Black Sea is a large inland sea situated at the crossroads of Eastern Europe, the Caucasus, and Western Asia. It is bordered by six countries: Bulgaria, Romania, Ukraine, Russia, Georgia, and Turkey.
- The sea connects to the Mediterranean Sea through the Bosporus Strait, Sea of Marmara, and Dardanelles Strait, and to the Sea of Azov via the Kerch Strait.
- Several major rivers drain into the Black Sea, enriching its ecosystem and supporting agriculture in the surrounding regions.
- The most significant among them are the Danube (Europe's second-longest river), Dniester, Dnieper, Southern Bug, Don, and Rioni rivers. These rivers contribute freshwater and sediment, influencing the sea’s salinity and marine biodiversity.
- The Black Sea basin also includes important port cities such as Odessa (Ukraine), Constanța (Romania), Novorossiysk (Russia), and Batumi (Georgia).
- Geopolitical Tensions:
- In recent years, the Black Sea region has become a strategic flashpoint, especially following Russia's annexation of Crimea in 2014, which significantly altered the regional security dynamics.
- The sea holds immense strategic value for NATO, Russia, and regional powers, serving as a key maritime route for energy trade, naval deployments, and military surveillance.
- NATO has increased its naval presence and military drills in the region, such as “Sea Shield” exercises, aiming to deter aggression and ensure freedom of navigation.
- Tensions have further escalated with the Russia-Ukraine war, growing military build-ups, and competition over energy routes, making the Black Sea a critical zone for geopolitical rivalry and potential conflict in Eastern Europe.
Majuli Island
Why in news?
- A recent study by the Central Water and Power Research Station (CWPRS) has revealed that Majuli Island in Assam has lost 75 square kilometres of land due to erosion, while 58 square kilometres have been gained through deposition along the Brahmaputra River.
About Majuli Island:
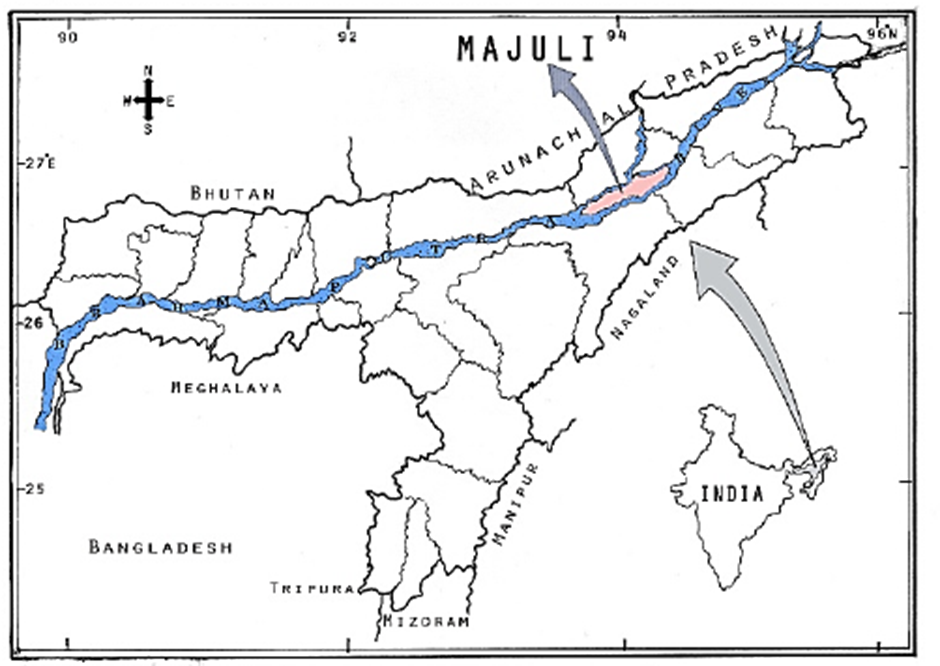
- Location and Geography:
- Majuli Island, often hailed as the soul of Assam, holds the distinction of being the world’s largest river island.
- Located in the Brahmaputra River in Assam, Majuli spans an area of approximately 421 square kilometres.
- It is bordered by the Brahmaputra River to the south and the Kherkutia Xuti, an anabranch of the Brahmaputra joined by the Subansiri River, to the north.
- The island's rich, alluvial landscape is characterised by lush greenery, numerous water bodies, and extensive paddy fields. In 2016, Majuli became the first island district in India.
- Ecological and Cultural Significance:
- Majuli is not just a geographical marvel but also a cultural and ecological hotspot. The island is a biodiversity-rich floodplain, supporting a range of flora and fauna.
- It is renowned for being the cradle of Assamese neo-Vaishnavite culture, initiated by Srimanta Sankerdeva and his disciple Madhavdeva in the 16th century.
- Their spiritual movement led to the establishment of Satras (Vaishnavite monasteries), which preserve traditions such as Sattriya dance, bhaona (religious theatre), mask-making, and traditional boat and pottery-making.
- The island is also home to ethnic communities such as the Mishing, Deori, and Sonowal Kachari tribes, alongside non-tribal Assamese.
- Rice cultivation forms the backbone of Majuli’s economy, with unique varieties like Komal Saul (soft rice) and Bao Dhan (deep-water rice) grown here.
- Erosion and Environmental Concerns:
- Despite its cultural and ecological richness, Majuli faces a grave threat from riverbank erosion, primarily caused by the dynamic flow of the Brahmaputra River.
- A recent study revealed that the island lost 75 sq. km of land due to erosion, while 58 sq. km was gained through deposition.
- Factors such as bank-line migration, climate change, and human interventions have intensified the problem.
- The island, which once covered over 1,100 sq. km in the 19th century, has been steadily shrinking.
- Majuli is currently on India’s tentative list for UNESCO World Heritage status, highlighting its global cultural and environmental importance.
Pakke Tiger Reserve
Why in news?
- Pakke Tiger Reserve in Arunachal Pradesh to install ANIDER systems for early alerts, aiming to reduce human-wildlife conflict incidents.
About Pakke Tiger Reserve:
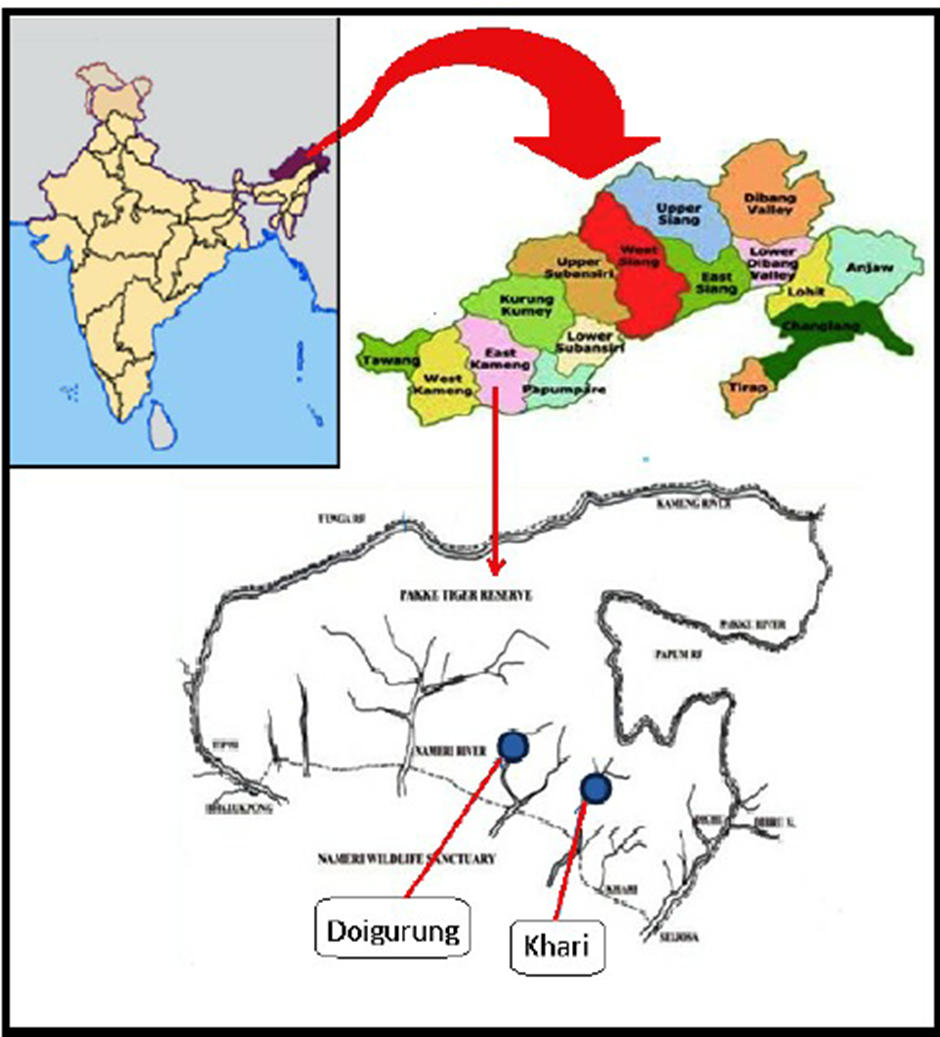
- Location and Geography:
- Pakke Tiger Reserve (PTR) is located in the East Kameng district of Arunachal Pradesh, covering an area of 862 sq. km.
- It lies north of the Brahmaputra River, situated in a transition zone between the Assam plains and the hilly forests of Arunachal Pradesh, making it rich in biodiversity and endemic species.
- The reserve is bounded by the Kameng (Bhareli) River on the west and north and the Pakke River on the east.
- It is surrounded by Tenga and Doimara Reserve Forests, Nameri National Park in Assam to the south, and Papum Reserve Forest to the east.
- The elevation ranges from 100 to 2,000 metres, supporting diverse forest types, including lowland semi-evergreen, evergreen, and Eastern Himalayan broadleaf forests.
- Flora and Fauna:
- The forest is home to a variety of trees like mango, jamun, sal, bamboo, arjuna, neem, and kadam.
- About eight bamboo species are found here. The reserve hosts a wide range of animals, including tigers, leopards, clouded leopards, jungle cats, wild dogs, Himalayan black bears, elephants, gaurs, sambars, barking deer, flying squirrels, and Malayan giant squirrels.
- It is also inhabited by the Nyishi tribe, who play a crucial role in the reserve’s conservation efforts.
- ANIDER System Initiative:
- To address growing human-wildlife conflict, especially with elephants, Pakke Tiger Reserve has launched the ANIDER (Animal Intrusion Detection and Repellent) system.
- This system combines motion sensors, sirens, and deterrent lights to detect and safely repel animals while also sending real-time alerts to nearby farmers.
- The project, led by DFO Satyaprakash Singh, will install 25 ANIDER units in conflict-prone villages, each costing between ₹18,000 and ₹20,000.
- Over 50–60 conflict cases are reported annually in the area. The initiative reflects PTR’s goal of community-led conservation, blending technology and traditional knowledge to promote peaceful human-wildlife coexistence.
|
Also Read |
|
| Public Administration Optional | |
| UPSC Monthly Magazine | Question Answer Practice For UPSC |
Union Commerce Minister Highlights the Lack of Deep-Tech Innovation in Indian Startups
Union Commerce Minister Highlights the Lack of Deep-Tech Innovation in Indian Startups
India Tests Directed Energy Weapon (DEW) System Capable of Disabling Drones, Missiles, and Aircraft
India Tests Directed Energy Weapon (DEW) System Capable of Disabling Drones, Missiles, and Aircraft
Concerns Over the Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act, 2023: Impact on the RTI Framework
Concerns Over the Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act, 2023: Impact on the RTI Framework

