- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PLACES IN NEWS 07 NOVEMBER 2024
PLACES IN NEWS 07 NOVEMBER 2024
07-11-2024
Exercise VINBAX-2024: Ambala and Chandimandir.

VINBAX-2024 is a joint military exercise between India and Vietnam. This exercise is scheduled to take place from 4th to 23rd November 2024 at Ambala and Chandimandir.
Key Details About VINBAX-2024:
-
Bilateral Exercise:
- It is a bilateral military exercise, meaning it involves both India and Vietnam working together.
- This year’s exercise has expanded in scope, with personnel from both the Indian Army and Indian Air Force, and the Vietnam People’s Army taking part. This is the first time that both Army and Air Force personnel from both countries are involved.
-
Indian Army Participation:
- The Indian Army’s team in VINBAX-2024 includes 47 personnel from the Corps of Engineers, as well as members from other army branches and services.
-
Objectives of VINBAX-2024:
- The main aim is to improve the joint military capabilities of both India and Vietnam, especially in how they use Engineer Companies and Medical Teams in United Nations Peacekeeping Operations.
- The focus is on working together under Chapter VII of the UN Charter, which deals with peacekeeping efforts.
-
Field Training Exercise:
- VINBAX-2024 will be a field training exercise, meaning that it will simulate real-world scenarios.
- The exercise will also include a 48-hour validation phase, where both sides will demonstrate their Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) capabilities and showcase military equipment.
-
Building Confidence and Interoperability:
- By conducting this joint exercise, both countries will strengthen mutual trust, improve their ability to work together, and share best practices in military operations.
-
Cultural Exchange:
- Besides military training, the exercise will also allow the troops from both countries to learn about each other’s social and cultural heritages, enhancing bilateral relations beyond just defence cooperation.
Common Cat Snake: Valmiki Tiger Reserve in Bihar.

On 6th November 2024, The Common Cat Snake, a rare species, was discovered in the Valmiki Tiger Reserve in Bihar.
About the Common Cat Snake:
- Other Name: Also known as the Indian Gamma Snake.
- Scientific Name: Boiga trigonata.
- Region: Found across most parts of India, except the Northeast states (after Sikkim) and Indian islands.
Habitat and Distribution:
- The Common Cat Snake can be found in various types of forests and across a wide range of elevations.
- It is not highly dangerous to humans despite being venomous. The snake mainly uses its venom to capture and subdue its prey.
Features:
- Size: A medium-sized snake, typically 70-100 cm in length.
- Body: Slender, thin body with a narrow tail.
- Coloring: The upper body is grey-brown, with cream-coloured irregular patterns edged with black. The underside is yellow-white or yellow-brown.
- Head: Large, triangular-shaped, and broader than its neck.
- Identification: A distinct “gamma” or “Y”-shaped marking on its body, which helps in identifying the species in the wild.
- Lifespan: Between 12 to 20 years.
- Diet: Mainly feeds on small vertebrates.
Conservation Status: IUCN Red List: Classified as Least Concern, indicating that it is not currently at significant risk of extinction.
About Valmiki Tiger Reserve
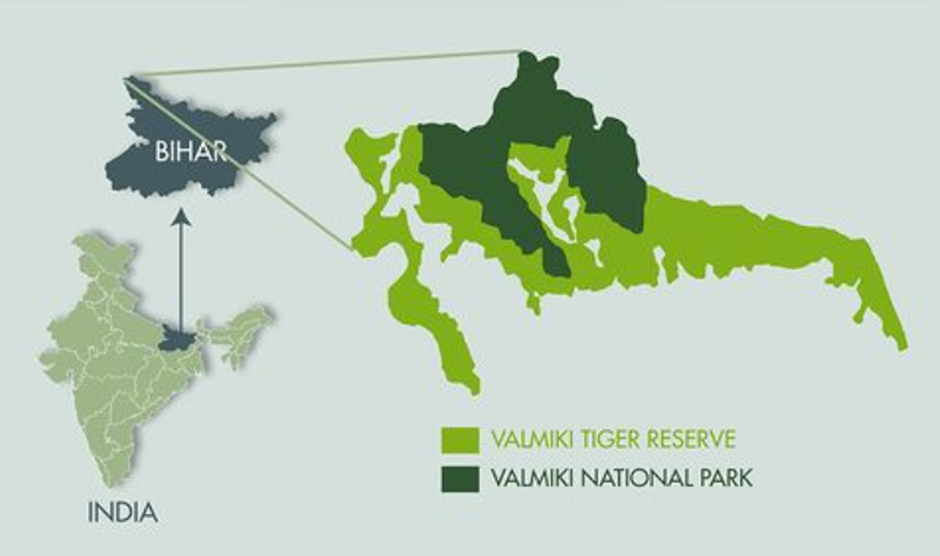
Location:
- India-Nepal Border
- Located in the northern part of West Champaran district in Bihar.
- It is the only tiger reserve in Bihar.
Key Features:
- Area: Spans over 880 sq. km.
- Composed of two parts: Valmiki National Park and Valmiki Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Marks the easternmost limit of the Himalayan Terai forests in India.
- Situated in the Gangetic Plains bio-geographic zone, with a mix of Bhabar and Terai tracts.
Geography:
- Surroundings:
- To the north, it is bordered by the Royal Chitwan National Park in Nepal.
- To the west, the Gandak River forms the boundary.
- The Himalayan mountains provide a scenic backdrop.
- Rivers:
Several rivers flow through the reserve, including Gandak, Pandai, Manor, Harha, Masan, and Bhapsa.
Vegetation:
- The reserve features a mix of various ecosystems, including:
- Moist mixed deciduous forests
- Open-land vegetation
- Sub-mountainous semi-evergreen formations
- Freshwater swamps
- Riparian fringes
- Alluvial grasslands
- High-hill savannahs
- Wetlands
Flora:
- The forest is home to a wide variety of plant species, such as:
- Sal, Rohini, Sihor, Teak, Bamboo
- Semal, Mandar, Shisham, Jamun, Gular
Fauna:
- The reserve is rich in wildlife and is known for its diverse species, including:
- Tigers, Leopards, Fishing cats, Leopard cats
- Sambar, Hog deer, Spotted deer, Black buck, Gaur
- Sloth bears, Langur, Rhesus monkeys




